Asymmetric Mach–Zehnder Interferometer Based Biosensors for Aflatoxin M1 Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Functionalization Process
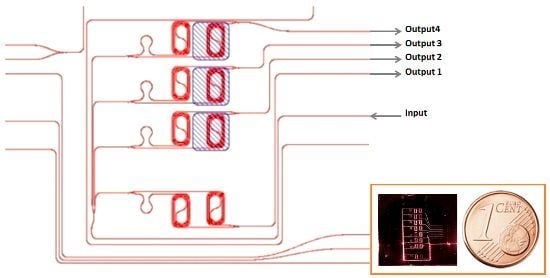
2.3. Mach–Zehnder Fabrication Process and Design

2.4. Experimental Setup
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of the Functionalization Process

3.2. Sensing Measurements

3.3. Aflatoxin M1 Measurements

3.4. Regeneration Measurements


4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, X.; Dai, D.; Thylén, L.; Wosinski, L. High-sensitivity liquid refractive-index sensor based on a Mach-Zehnder interferometer with a double-slot hybrid plasmonic waveguide. Opt. Express 2015, 23, 25688–25699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homola, J. Surface plasmon resonance sensors for detection of chemical and biological species. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 462–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, M.; Gleeson, M.A.; Spaugh, B.; Tybor, F.; Gunn, W.G.; Hochberg, M.; Baehr-Jones, T.; Bailey, R.C.; Gunn, L.C. Label-free biosensor arrays based on silicon ring resonators and high-speed optical scanning instrumentation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2010, 16, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guider, R.; Gandolfi, D.; Chalyan, T.; Pasquardini, L.; Samusenko, A.; Pucker, G.; Pederzolli, C.; Pavesi, L. Design and Optimization of SiON Ring Resonator-Based Biosensors for Aflatoxin M1 Detection. Sensors 2015, 15, 17300–17312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, F.; Sepulveda, B.; Calle, A.; Llobera, A.; Domínguez, C.; Abad, A.; Montoya, A.; Lechuga, L.M. An integrated optical interferometric nanodevice based on silicon technology for biosensor applications. Nanotechnology 2003, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, M.C.; Alvarez, M.; Lechuga, L.M. Integrated optical devices for lab-on-a-chip biosensing applications. Laser Photon. Rev. 2012, 6, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crivianu-Gaita, V.; Thompson, M. Immobilization of Fab′ fragments onto substrate surfaces: A survey of methods and applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ertürk, G.; Uzun, L.; Tümer, M.A.; Say, R.; Denizli, A. Fab fragments imprinted SPR biosensor for real-time human immunoglobulin G detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafaoglu, N.; Alves, N.J.; Bilgicer, B. Oriented Immobilization of Fab Fragments by Site-Specific Biotinylation at the Conserved Nucleotide Binding Site for Enhanced Antigen Detection. Langmuir 2015, 31, 9728–9736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, A.H.; Lee, J.; Choi, H.I.; Kwak, H.S.; Sim, S.J. Fabrication of Plasmon length-based surface enhanced Raman scattering for multiplex detection on microfluidic device. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, K.; Nishio, M.; Sugasawa, H.; Nagasaki, Y. Direct Observation of Adsorption-Induced Inactivation of Antibody Fragments Surrounded by Mixed-PEG Layer on a Gold Surface. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 7982–7989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquardini, L.; Pancheri, L.; Potrich, C.; Ferri, A.; Piemonte, C.; Lunelli, L.; Napione, L.; Comunanza, V.; Alvaro, M.; Vanzetti, L.; et al. SPAD aptasensor for the detection of circulating protein biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wörhoff, K.; Heideman, R.G.; Leinse, A.; Hoekman, M. TriPleX: A versatile dielectric photonic platform. Adv. Opt. Technol. 2015, 4, 189–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heideman, R.; Hoekman, M.; Schreuder, E. TriPleX-based integrated optical ring resonators for lab-on-a-chip and environmental detection. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2012, 18, 1583–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandolfi, D.; Guider, R.; Chalyan, T.; Pavesi, L.; Pasquardini, L.; Pederzolli, C.; Samusenko, A.; Pucker, G. Sensitivity and Limit of detection of biosensors based on ring resonators. In Proceedings of the AISEM Annual Conference 2015 XVIII, Trento, Italy, 3–5 February 2015.
- Brosinger, F.; Freimuth, H.; Lacher, M.; Ehrfeld, W.; Gedig, E.; Katerkamp, A.; Spener, F.; Cammann, K. A label-free affinity sensor with compensation of unspecific protein interaction by a highly sensitive integrated optical Mach–Zehnder interferometer on silicon. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1997, 44, 350–355. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Tu, X.; Kim, K.W.; Kee, J.S.; Shin, Y.; Han, K.; Yoon, Y.J.; Lo, G.Q.; Park, M.K. Highly sensitive Mach–Zehnder interferometer biosensor based on silicon nitride slot waveguide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 188, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jantra, J.; Kanatharana, P.; Asawatreratanakul, P.; Wongkittisuksa, B.; Limsakul, C.; Thavarungkul, P. Detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) at picogram level by a capacitive immunosensor. J. Environ. Sci. Health, Part A 2011, 46, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Duan, R.; Yuan, J.; Quan, Y.; Yang, H.; Xi, M. A reusable localized surface plasmon resonance biosensor for quantitative detection of serum squamous cell carcinoma antigen in cervical cancer patients based on silver nanoparticles array. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1097–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Edupuganti, S.R.; Edupuganti, O.P.; Hearty, S.; O’Kennedy, R. A highly stable, sensitive, regenerable and rapid immunoassay for detecting aflatoxin B1 in corn incorporating covalent AFB1 immobilization and a recombinant Fab antibody. Talanta 2013, 115, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Huang, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, K.; Chen, M.; Xiong, Y.; Yang, W.; Lai, W. A modified lateral flow immunoassay for the detection of trace aflatoxin M1 based on immunomagnetic nanobeads with different antibody concentrations. Food Control. 2015, 51, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Istamboulié, G.; Paniel, N.; Zara, L.; Reguillo, G.L.; Barthelmebs, L.; Noguer, T. Development of an impedimetric aptasensor for the determination of aflatoxin M1 in milk. Talanta 2016, 146, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chalyan, T.; Guider, R.; Pasquardini, L.; Zanetti, M.; Falke, F.; Schreuder, E.; Heideman, R.G.; Pederzolli, C.; Pavesi, L. Asymmetric Mach–Zehnder Interferometer Based Biosensors for Aflatoxin M1 Detection. Biosensors 2016, 6, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6010001
Chalyan T, Guider R, Pasquardini L, Zanetti M, Falke F, Schreuder E, Heideman RG, Pederzolli C, Pavesi L. Asymmetric Mach–Zehnder Interferometer Based Biosensors for Aflatoxin M1 Detection. Biosensors. 2016; 6(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleChalyan, Tatevik, Romain Guider, Laura Pasquardini, Manuela Zanetti, Floris Falke, Erik Schreuder, Rene G. Heideman, Cecilia Pederzolli, and Lorenzo Pavesi. 2016. "Asymmetric Mach–Zehnder Interferometer Based Biosensors for Aflatoxin M1 Detection" Biosensors 6, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6010001
APA StyleChalyan, T., Guider, R., Pasquardini, L., Zanetti, M., Falke, F., Schreuder, E., Heideman, R. G., Pederzolli, C., & Pavesi, L. (2016). Asymmetric Mach–Zehnder Interferometer Based Biosensors for Aflatoxin M1 Detection. Biosensors, 6(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios6010001