Abstract
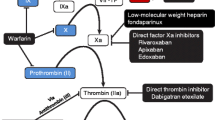
For the past five decades, there has been little progress in the development of oral anticoagulants, with the choices being limited to the vitamin K antagonists (VKAs). The situation is changing with the development of orally active small molecules that directly target thrombin or activated factor X (FXa). The two agents in the most advanced stages of development are dabigatran etexilate and rivaroxaban, which inhibit thrombin and FXa, respectively. Both are approved in the EU and Canada for venous thromboprophylaxis in patients undergoing elective hip- or knee-replacement surgery. Other agents in the early stages of development include several FXa inhibitors (apixaban, DU 176b, LY 517717, YM 150, betrixaban, eribaxaban [PD 0348292] and TAK 442) and one thrombin inhibitor (AZD 0837). With a predictable anticoagulant response and low potential for drug-drug interactions, these new agents can be given in fixed doses without coagulation monitoring. This renders them more convenient than VKAs. While the anticoagulant effect of the new thrombin and FXa inhibitors is similar, differences in the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic parameters may influence their use in clinical practice. Here, we compare the pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic features of these new oral agents.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Ansell J, Hirsh J, Hylek E, et al. Pharmacology and management of the vitamin K antagonists: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines (8th edition). Chest 2008 Jun; 133 (6 Suppl.): 160S–98S
Krynetskiy E, McDonnell P. Building individualized medicine: prevention of adverse reactions to warfarin therapy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2007 Aug; 322(2): 427–34
Dal Pozzo A, Acquasaliente M, Geron MR, et al. New heparin complexes active by intestinal absorption: I. Multiple ion pairs with basic organic compounds. Thromb Res 1989 Oct 1; 56(1): 119–24
Abbenante G, Fairlie DP. Protease inhibitors in the clinic. Med Chem 2005 Jan; 1(1): 71–104
Di Nisio M, Middeldorp S, Büller HR. Direct thrombin inhibitors. N Engl J Med 2005 Sep 8; 353(10): 1028–40
Hauptmann J, Sturzebecher J. Synthetic inhibitors of thrombin and factor Xa: from bench to bedside. Thromb Res 1999 Mar 1; 93(5): 203–41
Gustafsson D, Elg M. The pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor ximelagatran and its active metabolite melagatran: a mini-review. Thromb Res 2003 Jul 15; 109 Suppl. 1: S9–S15
Direct Thrombin Inhibitor Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Direct thrombin inhibitors in acute coronary syndromes: principal results of a meta-analysis based on individual patients’ data. Lancet 2002 Jan 26; 359(9303): 294–302
Gustafsson D, Bylund R, Antonsson T, et al. A new oral anticoagulant: the 50-year challenge. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2004 Aug; 3(8): 649–59
Kindmark A, Jawaid A, Harbron CG, et al. Genome-wide pharmacogenetic investigation of a hepatic adverse event without clinical signs of immunopathology suggests an underlying immune pathogenesis. Pharmacogenomics J 2008 Jun; 8(3): 186–95
AstraZeneca. AstraZeneca decides to withdraw Exanta [media release]. 2006 Feb 14 [online]. Available from URL: http://www.astrazeneca.com/pressrelease/5217.aspx [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Mungall D. BIBR-1048 Boehringer Ingelheim. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2002 Jun; 3(6): 905–7
Hauel NH, Nar H, Priepke H, et al. Structure-based design of novel potent nonpeptide thrombin inhibitors. J Med Chem 2002 Apr 25; 45(9): 1757–66
Wienen W, Stassen JM, Priepke H, et al. In-vitro profile and ex-vivo anticoagulant activity of the direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran and its orally active prodrug, dabigatran etexilate. Thromb Haemost 2007 Jul; 98(1): 155–62
van Ryn J, Hauel N, Waldmann L, et al. Dabigatran inhibits both clot-bound and fluid phase thrombin in vitro: effects compared to heparin and hirudin [abstract no. 3998]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2007 Nov 16; 110 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol110/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
European Medicines Agency (EMEA). European public assessment report: Pradaxa [online]. Available from URL: http://www.emea.europa.eu/humandocs/PDFs/EPAR/pradaxa/H-829-PI-en.pdf [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Samama MM, Le Flem L, Guinet C, et al. Three different patterns of calibrated automated thrombogram obtained with six different anticoagulants. J Thromb Haemost 2007 Dec; 5(12): 2554–6
van Ryn J, Kink-Eiband M, Hauel N, et al. Effects of dabigatran, a direct thrombin inhibitor, as compared to the direct factor Xa inhibitors, rivaroxaban and apixaban, on tissue factor-induced human platelet aggregation in platelet rich plasma [abstract no. 1884]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2007 Nov 16; 110 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol110/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Eriksson BI, Dahl OE, Rosencher N, et al. Dabigatran etexilate versus enoxaparin for prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip replacement: a randomised, double-blind, non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2007 Sep 15; 370(9591): 949–56
Eriksson BI, Dahl OE, Rosencher N, et al. Oral dabigatran etexilate vs subcutaneous enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after total knee replacement: the RE-MODEL randomized trial. J Thromb Haemost 2007 Aug 24; 5(11): 2178–85
The RE-MOBILIZE Writing Committee. The oral thrombin inhibitor dabigatran etexilate vs the North American enoxaparin regimen for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after knee arthroplasty surgery. J Arthroplasty. Epub 2008 Apr 11
van Ryn J, Priepke H, Ries UJ, et al. Dabigatran inhibits arterial thrombosis in a porcine model of cyclic flow reduction [abstract no. 906]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2006 Nov 16; 108 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol108/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Wienen W, Stassen JM, Priepke H, et al. Antithrombotic and anticoagulant effects of the direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran, and its oral prodrug, dabigatran etexilate, in a rabbit model of venous thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost 2007 Jun; 5(6): 1237–42
Wienen W, Stassen JM, Priepke H, et al. Effects of the direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran and its orally active prodrug, dabigatran etexilate, on thrombus formation and bleeding time in rats. Thromb Haemost 2007 Aug; 98(2): 333–8
van Ryn J, Hauel N, Priepke H, et al. Comparison of the antithrombotic effectiveness of the direct thrombin inhibitor, dabigatran etexilate, and two factor Xa inhibitors in an A-V shunt model of thrombosis in rabbits [abstract no. 3154]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2007 Nov 16; 110 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol110/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Stangier J, Rathgen K, Stähle H, et al. The pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and tolerability of dabigatran etexilate, a new oral direct thrombin inhibitor, in healthy male subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2007 Sep; 64(3): 292–303
Stangier J, Stähle H, Rathgen K, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the direct oral thrombin inhibitor dabigatran in healthy elderly subjects. Clin Pharmacokinet 2008; 47(1): 47–59
Liesenfeld KH, Schafer HG, Troconiz IF, et al. Effects of the direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran on ex vivo coagulation time in orthopaedic surgery patients: a population model analysis. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2006 Nov; 62(5): 527–37
Carlsson SC, Mattsson C, Eriksson UG, et al. A review of the effects of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor ximelagatran on coagulation assays. Thromb Res 2005; 115(1–2): 9–18
Wienen W, Ruehl D, Stassen JM, et al. Effect of recombinant factor VIIa or activated prothrombin complex concentrate on the bleeding time in anaesthetized rats during anticoagulant treatment with the direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran [abstract no. P1703]. XXth Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2005 Aug 6–12; Sydney [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2005/abstract.asp?id=47211 [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Schipper NG, Osterberg T, Wrange U, et al. In vitro intestinal permeability of factor Xa inhibitors: influence of chemical structure on passive transport and susceptibility to efflux. Pharm Res 2001; 18: 1735–41
Stangier J. Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran etexilate. Clin Pharmacokinet 2008; 47(5): 285–95
Blech S, Ebner T, Ludwig-Schwellinger E, et al. The metabolism and disposition of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor, dabigatran, in humans. Drug Metab Dispos 2008 Feb; 36(2): 386–99
Stangier J, Eriksson BI, Dahl OE, et al. Pharmacokinetic profile of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran etexilate in healthy volunteers and patients undergoing total hip replacement. J Clin Pharmacol 2005 May; 45(5): 555–63
Clement B, Lopian K. Characterization of in vitro biotransformation of new, orally active, direct thrombin inhibitor ximelagatran, an amidoxime and ester prodrug. Drug Metab Dispos 2003 May; 31(5): 645–51
Stangier J, Nehmiz G, Reilly P, et al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran in a dose finding trial in atrial fibrillation [abstract no. OR271]. XXth Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2005 Aug 6–12; Sydney [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2005/abstract.asp?id=47339 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Frydman A. Low-molecular-weight heparins: an overview of their pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics and metabolism in humans. Haemostasis 1996; 26 Suppl. 2: 24–38
Eriksson BI, Dahl OE, Ahnfelt L, et al. Dose escalating safety study of a new oral direct thrombin inhibitor, dabigatran etexilate, in patients undergoing total hip replacement: BISTRO I. J Thromb Haemost 2004 Sep; 2(9): 1573–80
Eriksson BI, Dahl OE, Büller HR, et al. A new oral direct thrombin inhibitor, dabigatran etexilate, compared with enoxaparin for prevention of thromboembolic events following total hip or knee replacement: the BISTRO II randomized trial. J Thromb Haemost 2005 Jan; 3(1): 103–11
Troconiz IF, Tillmann C, Liesenfeld KH, et al. Population pharmacokinetic analysis of the new oral thrombin inhibitor dabigatran etexilate (BIBR 1048) in patients undergoing primary elective total hip replacement surgery. J Clin Pharmacol 2007 Mar; 47(3): 371–82
Stangier J, Stähle H, Rathgen K, et al. Coadministration of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran etexilate and diclofenac has little impact on the pharmacokinetics of either drug [abstract no. P-T-677]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6-12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67231 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Stangier J, Rathgen K, Stähle H, et al. Lack of interaction between dabigatran etexilate, an oral direct thrombin inhibitor, and atorvastatin. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. In press
Stangier J, Stähle H, Rathgen K, et al. The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dabigatran etexilate, an oral direct thrombin inhibitor, are not affected by moderate hepatic impairment. J Clin Pharmacol. Epub 2008 Sep 30
Stangier J, Stähle H, Rathgen K, et al. No interaction of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor dabigatran etexilate and digoxin [abstract no. P-W-672]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67922 [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Gyzander E, Deinum J. Enzyme kinetic characterisation of the active form of the novel oral direct thrombin inhibitor AZD0837 [abstract no. P-S-066]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=65233 [Accessed 2008 Sep 29]
Mattsson C, Lundin A, Ulvinge J. Characterisation of the active form of the novel oral direct thrombin inhibitor AZD0837 in coagulation assays [abstract no. P-T-636]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67190 [Accessed 2008 Sep 29]
AstraZeneca PLC. General presentation: 2Q & HY 2008 results [online]. Available from URL: http://www.astrazeneca.com/sites/7/imagebank/typearticleparam511773/astrazeneca-general-presentation-august-2008.pdf [Accessed 2008 Sep 29]
Pehrsson S, Elg M. The antithrombotic effect of AR-H067637, the active form of the novel oral direct thrombin inhibitor AZD0837, in rat models of arterial and venous thrombosis [abstract no. P-W-637]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67887 [Accessed 2008 Sep 29]
Hockings PD, Adler G, Palmer M, et al. The oral direct thrombin inhibitor AZD0837 reduces thrombus formation in a rat model [abstract no. P-S-697]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=65858 [Accessed 2008 Sep 29]
Badimon L, Turitto V, Rosemark JA, et al. Characterization of a tubular flow chamber for studying platelet interaction with biologic and prosthetic materials: deposition of indium 111-labeled platelets on collagen, subendothelium, and expanded polytetrafluoroethylene. J Lab Clin Med 1987 Dec; 110(6): 706–18
Elg M, Zachrisson H. Investigation of the antithrombotic effect of AR-H067637, the active metabolite of the oral anticoagulant AZD0837, using human blood in a flow chamber model in vitro [abstract 1186]. 13th Congress, European Haematology Association; 2008 Jun 12–15: Copenhagen [online]. Available from URL: http://congress.ehaweb.org/13th/ [Accessed 2008 Sep 29]
Cullberg M, Wahlander K, Jansson SO, et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor AZD0837 in young healthy volunteers [abstract no. 206]. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2007; 101: 130
Cullberg M, Eriksson U, Wernevik L, et al. Effect of ketoconazole and grapefruit juice on the pharmacokinetics of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor AZD0837 [abstract no. 205]. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2007; 101: 130
Johansson S, Eriksson U, Schützer KM, et al. Effect on cytochrome P450 2C9 and 3A activity by the oral direct thrombin inhibitor AZD0837 given in immediate-release and extended release formulations [abstract no. P4564]. Annual Congress, European Society of Cardiology; 2007 Sep 1–5; Vienna [online]. Available from URL: http://spo.escardio.org/AbstractDetails.aspx?id=53431 [Accessed 2008 Sep 29]
Cullberg M, Schutzer KM, Eriksson U, et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor AZD0837 in combination with digoxin [abstract no. 204]. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 2007; 101 Suppl. 1: 130
Schützer KM, Svensson M, Dellstrand M, et al. Effect of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor AZD0837 on glomerular filtration rate in elderly healthy subjects [abstract no. P-W-668]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67918 [Accessed 2008 Sep 29]
Olsson B, Rasmussen LH, Tveit A, et al. Safety and tolerability of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor AZD0837 in prevention of stroke and other thromboembolic complications associated with atrial fibrillation (AF) [abstract no. O-W-053]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=65124 [Accessed 2008 Sep 29]
Walfridsson H, Johansson B, Englund A, et al. Assessment of the electrophysiological effects of the oral direct thrombin inhibitor AZD0837, in subjects undergoing an invasive electrophysiological procedure [abstract no. P-W-674]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67924 [Accessed 2008 Sep 29]
Rezaie AR. Prothrombin protects factor Xa in the prothrombinase complex from inhibition by the heparin-antithrombin complex. Blood 2001 Apr 15; 97(8): 2308–13
Turpie AG, Bauer KA, Eriksson BI, et al. Fondaparinux vs enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in major orthopedic surgery: a metaanalysis of 4 randomized double-blind studies. Arch Intern Med 2002 Sep 9; 162(16): 1833–40
Büller HR, Davidson BL, Decousus H, et al. Subcutaneous fondaparinux versus intravenous unfractionated heparin in the initial treatment of pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 2003 Oct 30; 349(18): 1695–702
The Fifth Organization to Assess Strategies in Acute Ischemic Syndromes Investigators. Comparison of fondaparinux and enoxaparin in acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med 2006 Apr 6; 354(14): 1464–76
Roehrig S, Straub A, Pohlmann J, et al. Discovery of the novel antithrombotic agent 5-chloro-N-((5S)-2-oxo-3-[4-(3-oxomorpholin-4-yl)phenyl]-1,3-oxazolidin-5-ylmethyl)thiophene-2-carboxamide (BAY 59-7939): an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor. J Med Chem 2005 Sep 22; 48(19): 5900–8
Tersteegen A, Burkhart N. Rivaroxaban - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - binds rapidly to factor Xa [abstract no. P-W-651]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67901 [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Eriksson BI, Borris LC, Friedman RJ, et al. Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after hip arthroplasty. N Engl J Med 2008 Jun 26; 358(26): 2765–75
Kakkar AK, Brenner B, Dahl OE, et al. Extended duration rivaroxaban versus short-term enoxaparin for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip arthroplasty: a double-blind, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2008 Jul 5; 372(9632): 31–9
Lassen MR, Ageno W, Borris LC, et al. Rivaroxaban versus enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after total knee arthroplasty. N Engl J Med 2008 Jun 26; 358(26): 2776–86
Turpie AG, Bauer K, Davidson B, et al. Comparison of rivaroxaban - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - and subcutaneous enoxaparin for thromboprophylaxis after total knee replacement (RECORD4: a phase III study) [abstract no. F85]. Annual Meeting, European Federation of National Associations of Orthopaedics and Traumatology; 2008 May 29–Jun 1; Nice [online]. Available from URL: http://www.efort.org/cdrom2008/F85.pdf [Accessed 2008 Nov 4]
Bayer Inc. Xarelto® (rivaroxaban 10 mg tablets): product monograph [online]. Available from URL: http://www.bayerhealth.com/BayerHC/display.cfm?Object_ID=272&Article_ID=56&expandMenu_ID=53&prev-SubItem=5_52 [Accessed 2008 Sep 29]
Bayer Schering Pharma. Xarelto® (rivaroxaban 10 mg tablets): summary of product characteristics - EU [online]. Available from URL: http://www.xarelto.com/html/downloads/Xarelto_Summary_of_Product_Characteristics_30Sept2008.pdf [Accessed 2008 Nov 24]
Perzborn E, Strassburger J, Wilmen A, et al. In vitro and in vivo studies of the novel antithrombotic agent BAY 59-7939-an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor. J Thromb Haemost 2005 Mar; 3(3): 514–21
Depasse F, Busson J, Mnich J, et al. Effect of BAY 59-7939 - a novel, oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - on clot-bound factor Xa activity in vitro [abstract no. P1104]. XXth Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2005 Aug 6–12; Sydney [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2005/abstract.asp?id=46540 [Accessed 2008 Apr 27]
Gerotziafas GT, Elalamy I, Depasse F, et al. In vitro inhibition of thrombin generation, after tissue factor pathway activation, by the oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban. J Thromb Haemost 2007 Apr; 5(4): 886–8
Graff J, von Hentig N, Misselwitz F, et al. Effects of the oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban on platelet-induced thrombin generation and prothrombinase activity. J Clin Pharmacol 2007 Nov; 47(11): 1398–407
Graff J, Picard-Willems B, Harder S. Monitoring effects of direct FXa-inhibitors with a new one-step prothrombinase-induced clotting time (PiCT) assay: comparative in vitro investigation with heparin, enoxaparin, fondaparinux and DX 9065a. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2007 Apr; 45(4): 237–43
Biemond BJ, Perzborn E, Friederich PW, et al. Prevention and treatment of experimental thrombosis in rabbits with rivaroxaban (BAY 597939): an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor. Thromb Haemost 2007 Mar; 97(3): 471–7
Perzborn E, Fischer E, Lange U. Combining rivaroxaban with acetylsalicylic acid increases antithrombotic potency without affecting bleeding times in animal models [abstract no. P-W-639]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67889 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Perzborn E, Fischer E, Lange U. Rivaroxaban - a novel, oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - enhanced the antithrombotic effects of clopidogrel in rats [abstract no. P-W-641]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67891 [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Perzborn E, Arndt B, Fischer E, et al. An in vivo risk/benefit comparison of the effects of rivaroxaban - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - with thrombin inhibitors, warfarin and clopidogrel [abstract no. P-W-638]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67888 [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Haertlein B, Parry TJ, Chen C, et al. Rivaroxaban an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor prevents arterial thrombotic occlusion in electrolytically injured rat carotid arteries [abstract no. 3]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2007 Nov 16; 110 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol110/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 28]
Kubitza D, Becka M, Voith B, et al. Safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of single doses of BAY 59-7939, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2005 Oct; 78(4): 412–21
Kubitza D, Becka M, Wensing G, et al. Safety, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of BAY 59-7939 - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - after multiple dosing in healthy male subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2005 Nov 17; 61: 873–80
Kubitza D, Becka M, Zuehlsdorf M, et al. Effect of food, an antacid, and the H2 antagonist ranitidine on the absorption of BAY 59-7939 (rivaroxaban), an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor, in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol 2006 May; 46(5): 549–58
Kubitza D, Becka M, Zuehlsdorf M, et al. Body weight has limited influence on the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, or pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban (BAY 59-7939) in healthy subjects. J Clin Pharmacol 2007 Feb; 47(2): 218–26
Mueck W, Eriksson BI, Bauer KA, et al. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - in patients undergoing major orthopaedic surgery. Clin Pharmacokinet 2008; 47(3): 203–16
Mueck W, Becka M, Kubitza D, et al. Population model of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - in healthy subjects. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2007 Jun; 45(6): 335–44
Tobu M, Iqbal O, Hoppensteadt D, et al. Anti-Xa and anti-IIa drugs alter international normalized ratio measurements: potential problems in the monitoring of oral anticoagulants. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 2004 Oct; 10(4): 301–9
Smith SA, Morrissey JH. Thromboplastin composition affects the sensitivity of prothrombin time (PT) clotting tests to direct factor Xa inhibitors [abstract no. 928]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2007 Nov 16; 110 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol110/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 28]
Perzborn E, Strassburger J, Wilmen A, et al. Biochemical and pharmacologic properties of BAY 59-7939, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor [abstract no. PO079]. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb 2004 Jun; 33 Suppl. 2: 98
Fareed J, Hoppensteadt D, Maddineni J, et al. Antithrombotic mechanism of action of BAY 59-7939 - a novel, oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor [abstract no. P0518]. XXth Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2005 Aug 6–12; Sydney [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2005/abstract.asp?id=45857 [Accessed 2008 Apr 27]
Kubitza D, Becka M, Mueck W, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of rivaroxaban - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - are not affected by aspirin. J Clin Pharmacol 2006 Sep; 46(9): 981–90
Kubitza D, Becka M, Mueck W, et al. Rivaroxaban (BAY 59-7939) - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - has no clinically relevant interaction with naproxen. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2007 Apr; 63(4): 469–76
Perzborn E, Lange U. Rivaroxaban - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - inhibits tissue factor-mediated platelet aggregation [abstract no. PW-642]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67892 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Walenga JM, Prechel M, Jeske WP, et al. Rivaroxaban - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - has potential for the management of patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol 2008 Oct; 143(1): 92–9
Tinel H, Huetter J, Perzborn E. Partial reversal of the anticoagulant effect of high-dose rivaroxaban - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - by recombinant factor VIIa in rats [abstract no. 905]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2006 Nov 16; 108 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol108/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Perzborn E, Harwardt M. Recombinant factor VIIa partially reverses the effects of the factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban on thrombin generation, but not the effects of thrombin inhibitors, in vitro [abstract no. P-W-640]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67890 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Kubitza D, Becka M, Roth A, et al. Dose-escalation study of the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of rivaroxaban in healthy elderly subjects. Curr Med Res Opin 2008 Oct; 24(10): 2757–65
Weinz C, Buetehorn U, Daehler HP, et al. Pharmacokinetics of BAY 59-7939 - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - in rats and dogs. Xenobiotica 2005 Sep; 35(9): 891–910
Mueck W, Borris LC, Dahl OE, et al. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of once- and twice-daily rivaroxaban for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in patients undergoing total hip replacement. Thromb Haemost 2008 Sep; 100(3): 453–61
Mueck W, Agnelli G, Büller H. Rivaroxaban has predictable pharmacokinetics (PK) and pharmacodynamics (PD) when given once or twice daily for the treatment of acute, proximal deep vein thrombosis (DVT) [abstract no. 1880]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2007 Nov 16; 110 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol110/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Halabi A, Maatouk H, Klause N, et al. Effects of renal impairment on the pharmacology of rivaroxaban (BAY 59-7939) - an oral, direct, factor Xa inhibitor [abstract no. 913]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2006 Nov 16; 108 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol108/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Kubitza D, Becka M, Mueck W, et al. The effect of age and gender on the pharmacology and safety of the oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban [abstract no. PW-628]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67182 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Weinz C, Radtke M, Schmeer K, et al. In vitro metabolism of BAY 59-7939 - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor [abstract no. 195]. Drug Metab Rev 2004; 36 Suppl. 1: 98
Gross PL, Weitz JI. New anticoagulants for treatment of venous thromboembolism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008 Mar; 28(3): 380–6
Weinz C, Schwarz T, Pleiss U, et al. Metabolism and distribution of [14C]BAY 59-7939 - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - in rat, dog and human [abstract no. 196]. Drug Metab Rev 2004; 36 Suppl. 1: 98
Laux V, Perzborn E, Kubitza D, et al. Preclinical and clinical characteristics of rivaroxaban: a novel, oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor. Semin Thromb Hemost 2007 Jul; 33(5): 515–23
Halabi A, Kubitza D, Zuehlsdorf M, et al. Effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and tolerability of rivaroxaban - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor [abstract no. PM-635]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=66495 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Kubitza D, Mueck W, Becka M. No interaction between rivaroxaban - a novel, oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - and atorvastatin [abstract no. PO62]. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb 2008 Jun; 36 Suppl. 1: A40
Kubitza D, Becka M, Voith B, et al. Effect of enoxaparin on the safety, tolerability, pharmacodynamics, and pharmacokinetics of BAY 59-7939 - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor [abstract no. P1704]. XXth Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2005 Aug 6–12; Sydney [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2005/abstract.asp?id=47212 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Kubitza D, Becka M, Mueck W, et al. Rivaroxaban - an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor - has no clinically relevant interaction with acetylsalicylic acid or naproxen [abstract no. PT-659]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67213 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Kubitza D, Becka M, Zuehlsdorf M, et al. No interaction between the novel, oral direct factor Xa inhibitor BAY 59-7939 and digoxin [abstract no. 11]. J Clin Pharmacol 2006 Jun; 46(6): 702
Kubitza D, Mueck W, Becka M. Randomized, double-blind, crossover study to investigate the effect of rivaroxaban on QT-interval prolongation. Drug Saf 2008; 31(1): 67–77
Agnelli G, Gallus A, Goldhaber SZ, et al. Treatment of proximal deep-vein thrombosis with the oral direct factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban (BAY 59-7939): the ODIXa-DVT (Oral DIrect factor Xa inhibitor BAY 59-7939 in patients with acute symptomatic Deep-Vein Thrombosis) study. Circulation 2007 Jul 10; 116(2): 180–7
Pinto DJ, Orwat MJ, Koch S, et al. Discovery of 1-(4-methoxyphenyl)-7-oxo-6-(4-(2-oxopiperidin-1-yl)phenyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]pyridine-3-carboxamide (apixaban, BMS-562247), a highly potent, selective, efficacious, and orally bioavailable inhibitor of blood coagulation factor Xa. J Med Chem 2007 Nov 1; 50(22): 5339–56
Lassen MR, Davidson BL, Gallus A, et al. The efficacy and safety of apixaban, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor, as thromboprophylaxis in patients following total knee replacement. J Thromb Haemost 2007 Dec; 5(12): 2368–75
Büller H, Deitchman D, Prins M, et al. Efficacy and safety of the oral direct factor Xa inhibitor apixaban for symptomatic deep vein thrombosis: the Botticelli DVT dose-ranging study. J Thromb Haemost 2008 Aug; 6(8): 1313–8
Alexander J. Safety of the factor Xa inhibitor, apixaban, in combination with antiplatelet therapy after acute coronary syndrome: results of the APPRAISE-I dose guiding trial [abstract no. 3208]. Annual Congress, European Society of Cardiology; 2008 Aug 30–Sep 3; Munich [online]. Available from URL: http://www.escardio.org/congresses/esc2008/congress-reports/Pages/3208-3209-alexander.aspx [Accessed 2008 Sep 29]
Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. Bristol-Myers Squibb and Pfizer provide update on apixaban clinical development program [media release]. 2008 Aug 26 [online]. Available from URL: http://newsroom.bms.com/article_display.cfm?article_id=5371 [Accessed 2008 Sep 29]
Wong PC, Crain EJ, Xin B, et al. Apixaban, an oral, direct and highly selective factor Xa inhibitor: in vitro, antithrombotic and antihemostatic studies. J Thromb Haemost 2008 May; 6(5): 820–9
Luettgen JM, Bozarth TA, Bozarth JM, et al. In vitro evaluation of apixaban, a novel, potent, selective and orally bioavailable factor Xa inhibitor [abstract no. 4130]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2006 Nov 16; 108 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol108/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Jiang XS, Crain EJ, Schumacher WA, et al. Apixaban, an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor, inhibits human clot-bound factor Xa activity in vitro [abstract no. P571]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008 Jun; 28(6): E137
Luettgen JM, Wang Z, Seiffert DA, et al. Inhibition of measured thrombin generation in human plasma by apixaban: a predictive mathematical model based on experimentally determined rate constants [abstract no. PT-633]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67187 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Wong PC, Watson CA, Crain EJ. Arterial antithrombotic and bleeding time effects of apixaban, a direct factor Xa inhibitor, in combination with antiplatelet therapy in rabbits. J Thromb Haemost 2008 Oct; 6(10): 1736–41
Wong PC, Watson CA, Crain EJ, et al. Potent antithrombotic activity of apixaban, a direct factor Xa inhibitor, with minimum bleeding time effect in rabbit models of arterial thrombosis and hemostasis [abstract no. PW-656]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67906 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Wong PC, Watson CA, Crain EJ. Dual combination of apixaban, a direct factor Xa inhibitor, with heparin or enoxaparin produced additive antithrombotic effects with low bleeding in rabbits [abstract no. P191]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008 Jun; 28(6): E68
Frost C, Yu Z, Nepal S, et al. Apixaban, an oral direct, factor Xa inhibitor: single-dose safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in healthy subjects [abstract no. PM-665]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=66524 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Frost C, Yu Z, Moore K, et al. Apixaban, an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor: multiple-dose safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics in healthy subjects [abstract no. PM-664]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=66523 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Frost C, Yu Z, Nepal S, et al. Apixaban, a direct factor Xa inhibitor: single-dose pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of an intravenous formulation [abstract no. 142]. J Clin Pharmacol 2008 Sep; 48(9): 1132
He K, He B, Grace JE, et al. Preclinical pharmacokinetic and metabolism of apixaban, a potent and selective factor Xa inhibitor [abstract no. 910]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2006 Nov 16; 108 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol108/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Raghavan N, Frost CE, Yu Z, et al. Apixaban metabolism and pharmacokinetics following oral administration to humans. Drug Metab Dispos. Epub 2008 Oct 2
Feng Y, Li LY, Shenker A, et al. Exposure-clinical outcome modeling and simulation to facilitate dose selection of apixaban in subjects undergoing elective total knee replacement surgery [abstract no. P-M-663]. XXth Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2005 Aug 6–12; Sydney [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=66522 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Weitz JI. Emerging anticoagulants for the treatment of venous thromboembolism. Thromb Haemost 2006 Sep; 96(3): 274–84
Frost C, Lee L, Li LY, et al. Apixaban does not affect the pharmacokinetics of digoxin [abstract no. 60]. J Clin Pharmacol 2007 Sep; 47(9): 1196
Wastall P, Nepal S, Frost C, et al. A randomized, blinded, placebo and positive-controlled, crossover study to determine the effect of repeated doses of the factor Xa inhibitor apixaban on the QTc interval [abstract no. PII-18]. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2008 Mar; 83 Suppl. 1: S48
Morishima Y, Furugohri T, Isobe K, et al. In vitro characteristics, anticoagulant effects and in vivo antithrombotic efficacy of a novel, potent and orally active direct factor Xa inhibitor, DU-176b [abstract no. 1862]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2004 Nov 16; 104 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol104/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Furugohri T, Isobe K, Honda Y, et al. DU-176b, a potent and orally active factor Xa inhibitor: in vitro and in vivo pharmacological profiles. J Thromb Haemost 2008 Sep; 6(9): 1542–9
Raskob G, Cohen A, Eriksson B, et al. Randomized double-blind multi-dose trial of the oral factor-Xa inhibitor DU-176b versus LMW heparin (dalteparin) for prevention of venous thromboembolism after total hip replacement [abstract no. P3712]. Annual Congress, European Society of Cardiology; 2008 Aug 30–Sep 3; Munich [online]. Available from URL: http://spo.escardio.org/AbstractDetails.aspx?id=57150 [Accessed 2008 Sep 29]
Hylek E. DU-176b, an oral, direct factor Xa antagonist. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 2007 Sep; 8(9): 778–83
Shibano T, Tsuji N, Kito F, et al. Effects of DU-176b, a novel direct factor Xa inhibitor, on prothrombinase activity and platelet aggregation in vitro [abstract no. PT-642]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67196 [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Furugohri T, Honda Y, Matsumoto C, et al. Antithrombotic and hemorrhagic effects of DU-176b, a novel, potent and orally active direct factor Xa inhibitor: a wider safety margin compared to heparins and warfarin [abstract no. 1851]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2004 Nov 16; 104 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol104/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Fukuda T, Matsumoto C, Honda Y, et al. Antithrombotic properties of DU-176b, a novel, potent and orally active direct factor Xa inhibitor in rat models of arterial and venous thrombosis: comparison with fondaparinux, an antithrombin dependent factor Xa inhibitor [abstract no. 1852]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2004 Nov 16; 104 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol104/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 21]
Morishima Y, Furugohri T, Honda Y, et al. Antithrombotic properties of DU-176b, a novel orally active factor Xa inhibitor: inhibition of both arterial and venous thrombosis, and combination effects with other antithrombotic agents [abstract no. PO511]. XXth Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2005 Aug 6–12; Sydney [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2005/abstract.asp?id=45850 [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Furugohri T, Isobe K, Honda Y, et al. Pharmacological characterization, antithrombotic and bleeding effects of DU-176b, a novel, potent and orally active direct inhibitor of factor Xa: a wider safety margin of antithrombotic and bleeding effects compared to heparin, LMWH and warfarin [abstract no. P1110]. XXth Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2005 Aug 6–12; Sydney [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2005/abstract.asp?id=46546 [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Morishima Y, Shirasaki Y, Kito F, et al. A wide safety margin of a factor Xa inhibitor, DU-176b, between antithrombotic effect and exacerbation of intracerebral hemorrhage in rats: comparison with a thrombin inhibitor [abstract no. 632]. Annual Scientific Sessions, American Heart Association; 2006 Nov 12–15; Chicago (IL) [online]. Available from URL: http://circ.ahajournals.org/cgi/content/meeting_abstract/114/18_MeetingAbstracts/II_104-b [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Morishima Y, Shirasaki Y, Kito F, et al. Effect of a factor Xa inhibitor DU-176b on intracerebral hemorrhage in rats: a wider safety margin compared with a thrombin inhibitor [abstract no. PT-641]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67195 [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Zafar MU, Vorchheimer DA, Gaztanaga J, et al. Antithrombotic effects of factor Xa inhibition with DU-176b: phase-I study of an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor using an ex-vivo flow chamber. Thromb Haemost 2007 Oct; 98(4): 883–8
Morishima Y, Fukuda T, Honda Y, et al. Activated prothrombin complex concentrate, recombinant factor VIII and factor IX reverse prolonged clotting time induced by DU-176b, a direct factor Xa inhibitor, in human plasma [abstract no. PT-639]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67193 [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Morishima Y, Honda Y, Matsumoto C, et al. Recombinant factor VIIa reverses the prolonged bleeding time induced by a high dose of DU-176b, a novel direct factor Xa inhibitor, in rats [abstract no. P0512]. XXth Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2005 Aug 6–12; Sydney [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2005/abstract.asp?id=45851 [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Agnelli G, Haas S, Ginsberg JS, et al. A phase II study of the oral factor Xa inhibitor LY517717 for the prevention of venous thromboembolism after hip or knee replacement. J Thromb Haemost 2007 Apr; 5(4): 746–53
Saiah E, Soares C. Small molecule coagulation cascade inhibitors in the clinic. Curr Top Med Chem 2005; 5(16): 1677–95
Turpie AG. Oral, direct factor Xa inhibitors in development for the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic diseases. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2007 Jun; 27(6): 1238–47
Norman P. 12th RSC-SCI Medicinal Chemistry Symposium (Part I): enzyme inhibitors; 2003 Sep 7–10; Cambridge, UK [meeting report]. London: Investigation Drugs Database (IDdb), Thomson Scientific, 2003
Agnelli G, Haas SK, Krueger KA, et al. A phase II study of the safety and efficacy of a novel oral FXa inhibitor (LY517717) for the prevention of venous thromboembolism following TKR or THR [abstract no. 278]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2005 Nov 16; 106 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol106/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Eriksson BI, Turpie AG, Lassen MR, et al. A dose escalation study of YM150, an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor, in the prevention of venous thromboembolism in elective primary hip replacement surgery. J Thromb Haemost 2007 Aug; 5(8): 1660–5
Eriksson BI, Turpie AGG, Lassen MR, et al. Once daily YM150, an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor, for prevention of venous thromboembolism in patients undergoing elective primary hip replacement [abstract no. 309]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2007 Nov 16; 110 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol110/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Iwatsuki Y, Shigenaga T, Moritani Y, et al. Biochemical and pharmacological profiles of YM150, an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor [abstract no. 911]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2006 Nov 16; 108 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol108/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Kaku S, Suzuki K, Funatsu T, et al. Effects of direct factor Xa inhibitor, YM150, on clot formation and clot lysis in vitro compared with other anticoagulants [abstract no. 3153]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2007 Nov 16; 110 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol110/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Saitoh M, Kaku S, Funatsu T, et al. Comparison of YM150, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor, with other antithrombotic agents in rodent venous and arterial thrombosis models [abstract no. 3155]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2007 Nov 16; 110 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol110/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Abe K, Siu G, Edwards S, et al. Animal models of thrombosis help predict the human therapeutic concentration of PRT54021, a potent oral factor Xa inhibitor [abstract no. 901]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2006 Nov 16; 108 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol108/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Sinha U, Edwards ST, Wong PW, et al. Antithrombotic activity of PRT54021, a potent oral direct factor Xa inhibitor, can be monitored using a novel prothrombinase inhibition bioassay [abstract no. 907]. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 2006 Nov 16; 108 (11) [online]. Available from URL: http://abstracts.hematologylibrary.org/content/vol108/issue11/ [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Turpie AG, Gent M, Bauer K, et al. Evaluation of the factor Xa (FXa) inhibitor, PRT054021 (PRT021), against enoxaparin in a randomized trial for the prevention of venous thromboembolic events after total knee replacement (EXPERT) [abstract no. PT-652]. XXIst Congress, International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis; 2007 Jul 6–12; Geneva [online]. Available from URL: http://www.blackwellpublishing.com/isth2007/abstract.asp?id=67206 [Accessed 2008 Apr 20]
Turpie AG. New oral anticoagulants in atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J 2008 Jan; 29(2): 155–65
Kohrt JT, Bigge CF, Bryant JW, et al. The discovery of (2R,4R)-N-(4-chlorophenyl)-N-(2-fluoro-4-(2-oxopyridin-1(2H)-yl)phenyl)-4-methoxypyrrolidine-1,2-dicarboxamide (PD 0348292), an orally efficacious factor Xa inhibitor. Chem Biol Drug Des 2007 Aug; 70(2): 100–12
McBane RD, Leadley Jr RJ, Baxi SM, et al. Iliac venous stenting: antithrombotic efficacy of PD0348292, an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor, compared with antiplatelet agents in pigs. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008 Mar; 28(3): 413–8
Karnicki K, Leadley Jr RJ, Baxi SM, et al. Comparison of PD0348292, a selective factor Xa inhibitor, to antiplatelet agents for the inhibition of arterial thrombosis. Thromb Haemost 2008 Apr; 99(4): 759–66
Imaeda Y, Kawamoto T, Tobisu M, et al. Discovery of piperazinylimidazo[1,2a]pyridines as novel S4 binding elements for orally active factor Xa inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 2008 Mar 15; 16(6): 3125–401
Imaeda Y, Kuroita T, Sakamoto H, et al. Discovery of imidazo[1,5-c]imidazol-3-ones: weakly basic, orally active factor Xa inhibitors. J Med Chem 2008 Jun; 51(12): 3422–36
Stangier J, Rathgen K, Stähle H. Bioavailability of BIBR 953 after 50mg administered in 4 experimental formulations relative to drinking solution, with and without pantoprazole, in healthy subjects [clinical study report]. Biberach (Germany): Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH and Co. KG, 2002
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Gothenburg, Sweden. Dr Eriksson has received fees as a consultant or speaker for Astellas, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Daiichi Sankyo and Takeda. Dr Quinlan has received fees as a consultant for Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr Weitz holds the Canada Research Chair in Thrombosis and the HSFO/J.F. Mustard Chair in Cardiovascular Research. Dr Weitz has received fees as a consultant or speaker for Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim and BMS. The authors have no other conflicts of interest that are directly relevant to the content of this review.
Further information concerning ongoing trials of the compounds mentioned in the article is available online from www.clinicaltrials.gov.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eriksson, B.I., Quinlan, D.J. & Weitz, J.I. Comparative Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics of Oral Direct Thrombin and Factor Xa Inhibitors in Development. Clin Pharmacokinet 48, 1–22 (2009). https://doi.org/10.2165/0003088-200948010-00001
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/0003088-200948010-00001