Abstract
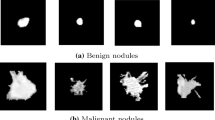
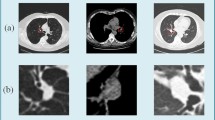
The early stage detection of benign and malignant pulmonary nodules plays an important role in clinical diagnosis. The malignancy risk assessment is usually used to guide the doctor in identifying the cancer stage and making follow-up prognosis plan. However, due to the variance of nodules on size, shape, and location, it has been a big challenge to classify the nodules in computer aided diagnosis system. In this paper, we design a novel model based on convolution neural network to achieve automatic pulmonary nodule malignancy classification. By using our model, the multi-scale features are extracted through the multi-convolution process, and the structure of residual blocks allows the network to capture more high-level and semantic information. Moreover, a strategy is proposed to fuse the features from the last avg-pooling layer and the ones from the last residual block to further enhance the performance of our model. Experimental results on the public Lung Image Database Consortium dataset demonstrate that our model can achieve a lung nodule classification accuracy of \(87.5\%\) which outperforms state-of-the-art methods.










Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.References
Armato SG III, McLennan G, Bidaut L et al (2011) The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): a completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Med Phys 38(2):915–931. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3528204
Bengio Y, Courville A et al (2013) Representation learning: a review and new perspectives. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 35(8):1798–1828. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2013.50
Boureau YL, Ponce J, LeCun Y (2010) A theoretical analysis of feature pooling in visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the 27th international conference on machine learning, pp 111–118
Chen S, Qin J, Ji X et al (2017) Automatic scoring of multiple semantic attributes with multi-task feature leverage: a study on pulmonary nodules in CT images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 36(3):802–814. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2629462
Ciompi F, de Hoop B, van Riel et al (2015) Automatic classification of pulmonary peri-fissural nodules in computed tomography using an ensemble of 2D views and a convolutional neural network out-of-the-box. Med Image Anal 26(1):195–202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2015.08.001
Dhara AK, Mukhopadhyay S, Dutta A, Garg M, Khandelwal N (2016) A combination of shape and texture features for classification of pulmonary nodules in lung CT images. J Digit Imaging 29(4):466–475. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-015-9857-6
Dou Q, Chen H, Yu L, Qin J, Heng PA (2017) Multilevel contextual 3-D CNNS for false positive reduction in pulmonary nodule detection. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 64(7):1558–1567. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2016.2613502
Gould MK, Ananth L, Barnett PG (2007) A clinical model to estimate the pretest probability of lung cancer in patients with solitary pulmonary nodules. Chest 131(2):383–388. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.06-1261
Han F, Wang H, Zhang G et al (2015) Texture feature analysis for computer-aided diagnosis on pulmonary nodules. J Digit Imaging 28(1):99–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-014-9718-8
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 770–778
Huang GB, Lee H, Learned-Miller E (2012) Learning hierarchical representations for face verification with convolutional deep belief networks. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), 2012 IEEE conference on IEEE, pp 2518–2525. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2012.6247968
Huang Y, Tian K, Wu A, Zhang G (2017) Feature fusion methods research based on deep belief networks for speech emotion recognition under noise condition. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-017-0644-8
Hussein S, Cao K, Song Q, Bagci U (2017) Risk stratification of lung nodules using 3D CNN-based multi-task learning. In: International conference on information processing in medical imaging. Springer, Berlin, pp 249–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59050-9_20
Kamnitsas K, Ledig C, Newcombe VF et al (2017) Efficient multi-scale 3D CNN with fully connected CRF for accurate brain lesion segmentation. Med Image Anal 36:61–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2016.10.004
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I et al (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 2015:1097–1105
Kumar D, Wong A, Clausi D et al. (2015) Lung nodule classification using deep features in CT images. In: Computer and robot vision (CRV), 2015 12th conference on, IEEE, pp 133–138. https://doi.org/10.1109/CRV.2015.25
Lin M, Chen Q et al (2013) Network in network. arXiv:1312.4400 (arXiv preprint)
Maninis KK, Pont-Tuset J et al. (2016) Deep retinal image understanding. In: International conference on medical imagecomputing and computer-assisted intervention. Springer, pp 140–148.https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_17
Messay T, Hardie RC, Rogers SK (2010) A new computationally efficient CAD system for pulmonary nodule detection in CT imagery. Med Image Anal 14(3):390–406. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2010.02.004
Nibali A, He Z, Wollersheim D (2017) Pulmonary nodule classification with deep residual networks. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 12(10):1799–1808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1605-6p
Setio A, Ciompi F, Litjens G et al (2016) Pulmonary nodule detection in CT images: false positive reduction using multi-view convolutional networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(5):1160–1169. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2536809
Shen W, Zhou M, Yang F et al (2017) Multi-crop convolutional neural networks for lung nodule malignancy suspiciousness classification. Pattern Recognit 61:663–673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.05.029
Shi J, Zheng X, Li Y, Zhang Q, Ying S (2018) Multimodal neuroimaging feature learning with multimodal stacked deep polynomial networks for diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 22(1):173–183. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2017.2655720
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O et al (2011) Cancer statistics, 2011: the impact of eliminating socioeconomic and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J Clin 61(4):212–236. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.20121
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv:1409.1556 (arXiv preprint)
Song Y, Zhang L, Chen S, Ni D, Lei B, Wang T (2015) Accurate segmentation of cervical cytoplasm and nuclei based on multiscale convolutional network and graph partitioning. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 62(10):2421–2433. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2015.2430895
Song W, Li S, Fang L, Lu T (2018) Hyperspectral image classification with deep feature fusion network. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 56(6):3173–3184. https://doi.org/10.1109/TGRS.2018.2794326
Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, Alemi AA (2017) Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning. AAAI 4:12
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y et al (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–9
Tang L, Yang ZX, Jia K (2018) Canonical correlation analysis regularization: an effective deep multi-view learning baseline for RGB-D object recognition. IEEE Trans Auton Ment Dev. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCDS.2018.2866587
Uchiyama Y, Katsuragawa S, Abe H, Shiraishi J et al (2003) Quantitative computerized analysis of diffuse lung disease in high resolution computed tomography. Med Pyhs 30(9):2440–2454. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.1597431
Way TW, Hadjiiski LM et al (2006) Computer-aided diagnosis of pulmonary nodules on CT scans: segmentation and classification using 3D active contours. Med Pyhs 33(7Part1):2323–2337. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.2207129
Wen Z, Liu D, Liu X, Zhong L, Lv Y, Jia Y (2018) Deep learning based smart radar vision system for object recognition. J Ambient Intell Humaniz Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-0853-9
Xu Y, Zhang G, Li Y, Luo Y, Lu J (2017) A Hybrid Model: DGnet-SVM for the Classification of Pulmonary Nodules. In: International conference on neural information processing. Springer, pp 732–741. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-70093-9_78
Yang H, Yu H, Wang G (2016) Deep learning for the classification of lung nodules. arXiv:1611.06651 (arXiv preprint)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by the General Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) under Grant nos. 61572362, 81571347, and 61806147, the Central Universities under Grant no. 22120180012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Zhu, D., Liu, X. et al. Multi-scale pulmonary nodule classification with deep feature fusion via residual network. J Ambient Intell Human Comput 14, 14829–14840 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-1132-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12652-018-1132-5