Abstract
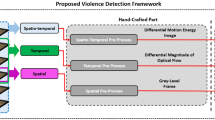
Violent behavior detection (VioBD), as a special action recognition task, aims to detect violent behaviors in videos, such as mutual fighting and assault. Some progress has been made in the research of violence detection, but the existing methods have poor real-time performance and the algorithm performance is limited by the interference of complex backgrounds and the occlusion of dense crowds. To solve the above problems, we propose an end-to-end real-time violence detection framework based on 2D CNNs. First, we propose a lightweight skeletal image (SI) as the input modality, which can obtain the human body posture information and richer contextual information, and at the same time remove the background interference. As tested, at the same accuracy, the resolution of SI modality is only one-third of that of RGB modality, which greatly improves the real-time performance of model training and inference, and at the same resolution, SI modality has higher inaccuracy. Second, we also design a parallel prediction module (PPM), which can simultaneously obtain the single image detection results and the inter-frame motion information of the video, which can improve the real-time performance of the algorithm compared with the traditional “detect the image first, understand the video later" mode. In addition, we propose an auxiliary parameter generation module (APGM) with both efficiency and accuracy, APGM is a 2D CNNs-based video understanding module for weighting the spatial information of the video features, processing speed can reach 30–40 frames per second, and compared with models such as CNN-LSTM (Iqrar et al., Aamir: Cnn-lstm based smart real-time video surveillance system. In: 2022 14th International Conference on Mathematics, Actuarial, Science, Computer Science and Statistics (MACS), pages 1–5. IEEE, 2022) and Ludl et al. (Cristóbal: Simple yet efficient real-time pose-based action recognition. In: 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), pages 581–588. IEEE, 1999), the propagation effect speed can be increased by an average of \(3 \sim 20\) frames per second per group of clips, which further improves the video motion detection efficiency and accuracy, greatly improving real-time performance. We conducted experiments on some challenging benchmarks, and RVBDN can maintain excellent speed and accuracy in long-term interactions, and are able to meet real-time requirements in methods for violence detection and spatio-temporal action detection. Finally, we update our proposed new dataset on violence detection images (violence image dataset). Dataset is available at https://github.com/ChinaZhangPeng/Violence-Image-Dataset











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Iqrar, W., Abidien, M.Z., Hameed, W., Shahzad, A.: Cnn-lstm based smart real-time video surveillance system. In: 2022 14th International Conference on Mathematics, Actuarial Science, Computer Science and Statistics (MACS), pages 1–5. IEEE (2022)
Ludl, D., Gulde, T., Curio, C.: Simple yet efficient real-time pose-based action recognition. In: 2019 IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Conference (ITSC), pages 581–588. IEEE (2019)
Guedes, A.R.M., Guillermo, C.: Real-time violence detection in videos using dynamic images. In: 2020 XLVI Latin American Computing Conference (CLEI), pages 503–511. IEEE (2020)
Irfanullah, H., Tariq, I., Arshad, Y., Bailin, H.A.: Real time violence detection in surveillance videos using convolutional neural networks. Multimed. Tools Appl. 81(26), 38151–38173 (2022)
Zhou, P., Ding, Q., Luo, H., Hou, X.: Violent interaction detection in video based on deep learning. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 844(1), 012044 (2017)
Gao, Y., Liu, H., Sun, X., Wang, C., Liu, Y.: Violence detection using oriented violent flows. Image Vis. Comput. 48, 37–41 (2016)
Kaelon, L., Paul, L.R., David, M., Simon, C.M.: Detecting violent and abnormal crowd activity using temporal analysis of grey level co-occurrence matrix (glcm)-based texture measures. Mach. Vis. Appl. 28, 361–371 (2017)
Pratama, R.A., Yudistira, N., Bachtiar, F. A.: Violence recognition on videos using two-stream 3d cnn with custom spatiotemporal crop. Multimedia Tools and Applications, pages 1–23 (2023)
Maji, D., Nagori, S., Mathew, M., Poddar, D.: Yolo-pose: enhancing yolo for multi person pose estimation using object keypoint similarity loss. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 2637–2646 (2022)
Enrique, B.N., Enrique, D.S., Oscar, B.G., Gloria, S.R.: Violence detection in video using computer vision techniques. In: Computer Analysis of Images and Patterns: 14th International Conference, CAIP 2011, Seville, Spain, August 29-31, 2011, Proceedings, Part II 14, pages 332–339. Springer (2011)
Deniz, O., Serrano, I., Bueno, G., Kim, T.-K.: Fast violence detection in video. In: 2014 international conference on computer vision theory and applications (VISAPP), volume 2, pages 478–485. IEEE (2014)
Zhang, T., Yang, Z., Jia, W., Yang, B., Yang, J., He, Xiangjian: A new method for violence detection in surveillance scenes. Multimed Tools Appl 75, 7327–7349 (2016)
Rendón-Segador, F.J., Álvarez-García, J.A., Enríquez, F., Deniz, O.: Violencenet: dense multi-head self-attention with bidirectional convolutional lstm for detecting violence. Electronics 10(13), 1601 (2021)
Magdy, M., Fakhr, M., Waleed, M., Fahima, A.: Violence 4d: Violence detection in surveillance using 4d convolutional neural networks. IET Computer Vis. (2023)
Singh, S., Dewangan, S., Krishna, G.S., Tyagi, V., Reddy, S., Medi, P.R.: Video vision transformers for violence detection (2022). arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.03561
Duan, H., Zhao, Y., Chen, K., Lin, D., Bo, D.: Revisiting skeleton-based action recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 2969–2978 (2022)
Huang, X., Zhou, H., Feng, B., Wang, X., Liu, W., Wang, J., Feng, H., Han, J., Ding, E., Wang, J.: Graph contrastive learning for skeleton-based action recognition (2023). arXiv preprint arXiv:2301.10900
Jocher, G., Stoken, A., Borovec, J., Chaurasia, A., Changyu, L., Hogan, A., Hajek, J., Diaconu, L., Kwon, Y., Defretin, Y., et al: Ultralytics/yolov5: v5.0-yolov5-p6 1280 models, aws, supervise. ly and youtube integrations. Zenodo (2021)
Wang, Z., She, Q., Smolic, A.: Action-net: Multipath excitation for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 13214–13223 (2021)
Lin, T.-Y., Dollár, P., Girshick, R., He, K., Hariharan, B., Belongie, S.: Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 2117–2125 (2017)
MacQueen, J., et al.: Some methods for classification and analysis of multivariate observations. In Proceedings of the fifth Berkeley symposium on mathematical statistics and probability, volume 1, pages 281–297. Oakland, CA, USA (1967)
Degardin, B., Proença, H.: Iterative weak/self-supervised classification framework for abnormal events detection. Pattern Recogn Lett 145, 50–57 (2021)
Cheng, M., Cai, K., Li, M.: Rwf-2000: an open large scale video database for violence detection. In: 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pages 4183–4190. IEEE (2021)
Ş aktı, E.T., Gözde Ayşe , E., Hazım, K.: Vision-based fight detection from surveillance cameras. In: 2019 Ninth International Conference on Image Processing Theory, Tools and Applications (IPTA), pages 1–6. IEEE (2019)
Bianculli, M., Falcionelli, N., Sernani, P., Tomassini, S., Contardo, P., Lombardi, M., Dragoni, A.F.: A dataset for automatic violence detection in videos. Data Brief 33, 106587 (2020)
Kim, M., Spinola, F., Benz, P., Kim, T.-H.: A*: Atrous spatial temporal action recognition for real time applications. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, pages 7014–7024 (2024)
Üstek, İ, Desai, J, Torrecillas, I., Abadou, S., Wang, J., Fever, Q., Kasthuri, S.R., Xing, Y., Guo, W., Tsourdos, A.: two-stage violence detection using vitpose and classification models at smart airports (2023). arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.16325
Lee, J., Ahn, B.: Real-time human action recognition with a low-cost rgb camera and mobile robot platform. Sensors 20(10), 2886 (2020)
Zhou, L., Nagahashi, H.: Real-time action recognition based on key frame detection. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing, pages 272–277 (2017)
Shi, F., Petriu, E., Laganiere, R.: Sampling strategies for real-time action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 2595–2602 (2013)
Huillcen B., Herwin A., Palomino V., Flor de Luz, S., Ivan Soria, C., Mario A., Carlos Gutierrez Caceres J.: Human violence recognition in video surveillance in real-time. In: Future of Information and Communication Conference, pages 783–795. Springer (2023)
Sudhakaran, S., Lanz, O.: Learning to detect violent videos using convolutional long short-term memory. In: 2017 14th IEEE international conference on advanced video and signal based surveillance (AVSS), pages 1–6. IEEE (2017)
Carreira, J., Zisserman, A.: Quo vadis, action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset. In: proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 6299–6308 (2017)
Zolfaghari, M., Singh, K., Brox, T.: Eco: Efficient convolutional network for online video understanding. In: Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), pages 695–712 (2018)
Su, Y., Lin, G., Zhu, J., Wu, Q.: Human interaction learning on 3d skeleton point clouds for video violence recognition. In: Computer Vision–ECCV 2020: 16th European Conference, Glasgow, UK, August 23–28, 2020, Proceedings, Part IV 16, pages 74–90. Springer (2020)
Li, Y., Ji, B., Shi, X., Zhang, J., Kang, B., Wang, L.: Tea: Temporal excitation and aggregation for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pages 909–918 (2020)
Gupta, H., Ali, S.T.: Violence detection using deep learning techniques. In: 2022 International Conference on Emerging Techniques in Computational Intelligence (ICETCI), pages 121–124 (2022)
Su, Y., Lin, G., Wu, Q.: Improving video violence recognition with human interaction learning on 3d skeleton point clouds (2023). arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.13866
Parui, S.K., Biswas, S.K. , Das, S., Chakraborty, M., Purkayastha, B.: An efficient violence detection system from video clips using convlstm and keyframe extraction. In: 2023 11th International Conference on Internet of Everything, Microwave Engineering, Communication and Networks (IEMECON), pages 1–5. IEEE (2023)
Hachiuma, R., Sato, F., Sekii, T.: Unified keypoint-based action recognition framework via structured keypoint pooling. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 22962–22971 (2023)
Lee, J.-W., Kang, H.-S.: Three-stage deep learning framework for video surveillance. Appl Sci 14(1), 408 (2024)
Tran, D., Bourdev, L., Fergus, R., Torresani, L., Paluri, M.: Learning spatiotemporal features with 3d convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pages 4489–4497 (2015)
Wang, Y., Sun, Y., Liu, Z., Sarma, S.E., Bronstein, M.M., Solomon, J.M.: Dynamic graph cnn for learning on point clouds. ACM Trans. Graph. (tog) 38(5), 1–12 (2019)
Islam, Z., Rukonuzzaman, M., Ahmed, R., Kabir, M.H., Farazi, M.: Efficient two-stream network for violence detection using separable convolutional lstm. In: 2021 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), pages 1–8. IEEE (2021)
Ullah, F.U.M., Muhammad, K., Haq, I.U., Khan, N., Heidari, A.A., Baik, S.W., de Albuquerque, V.H.C.: Ai-assisted edge vision for violence detection in iot-based industrial surveillance networks. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 18(8), 5359–5370 (2021)
Zhang, Y., Li, Y., Guo, S., Liang, Q.: Not all temporal shift modules are profitable. J. Electron Imaging 31(4), 043030–043030 (2022)
Zhou, L., Li, W., Chen, Y., Liu, H., Yang, M., Liu, Z.: Human keypoint change detection for video violence detection based on cascade transformer. In: 2023 IEEE 6th International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence (PRAI), pages 88–94. IEEE (2023)
Sato, F., Hachiuma, R., Sekii, T.: Prompt-guided zero-shot anomaly action recognition using pretrained deep skeleton features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 6471–6480 (2023)
Chaturvedi, K., Dhiman, C., Vishwakarma, D.K.: Fight detection with spatial and channel wise attention-based ConvLSTM model. Expert Syst. 41(1), e13474 (2024)
Sernani, P., Falcionelli, N., Tomassini, S., Contardo, P., Dragoni, A.F.: Deep learning for automatic violence detection: tests on the AIRTLab dataset. IEEE Access 9, 160580–160595 (2021)
Haque, M., Afsha, S., Nyeem, H.: Developing brutnet: a new deep cnn model with gru for realtime violence detection. In: 2022 International Conference on Innovations in Science, Engineering and Technology (ICISET), pages 390–395. IEEE (2022)
Freire-Obregón, D., Barra, P., Castrillón-Santana, M., De Marsico, M.: Inflated 3d convnet context analysis for violence detection. Mach. Vis. Appl. 33, 1–13 (2022)
Quentin, P., Swan, S., Hugo, W., Léo, R., Siba, H., Antoun, Y.: Balancing accuracy and training time in federated learning for violence detection in surveillance videos: a study of neural network architectures (2023). arXiv preprint arXiv:2308.05106
Kang, M.-S., Park, R.-H., Park, H.-M.: Efficient spatio-temporal modeling methods for real-time violence recognition. IEEE Access 9, 76270–76285 (2021)
Ullah, F.U., Min, O., Mohammad, S., Muhammad, K., Ullah, A., Baik, S.W., Cuzzolin, F., Rodrigues, Joel, J.P.C., Hugo C de Albuquerque, V.: An intelligent system for complex violence pattern analysis and detection. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 37(12):10400–10422 (2022)
Şeymanur A., Ofli, F., Imran, M., Ekenel, H. K.: Fight detection from still images in the wild. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision, pages 550–559 (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization, P.Z.; methodology, P.Z.; software, P.Z.; validation, P.Z. and L.D.; formal analysis, P.Z. and L.D.; investigation, X.Z.; data curation, L.D. and X.Z.; wrote the main manuscript text, P.Z.; supervision, W.L. and W.Z.; project administration, P.Z.; funding acquisition, W.L. and P.Z. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Dong, L., Zhao, X. et al. An end-to-end framework for real-time violent behavior detection based on 2D CNNs. J Real-Time Image Proc 21, 57 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-024-01443-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-024-01443-7