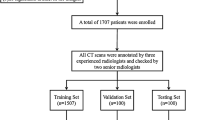
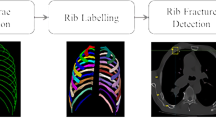
Abstract
Purpose
Clinical rib fracture diagnosis via computed tomography (CT) screening has attracted much attention in recent years. However, automated and accurate segmentation solutions remain a challenging task due to the large sets of 3D CT data to deal with. Down-sampling is often required to face computer constraints, but the performance of the segmentation may decrease in this case.
Methods
A new multi-angle projection network (MAPNet) method is proposed for accurately segmenting rib fractures by means of a deep learning approach. The proposed method incorporates multi-angle projection images to complementarily and comprehensively extract the rib characteristics using a rib extraction (RE) module and the fracture features using a fracture segmentation (FS) module. A multi-angle projection fusion (MPF) module is designed for fusing multi-angle spatial features.
Results
It is shown that MAPNet can capture more detailed rib fracture features than some commonly used segmentation networks. Our method achieves a better performance in accuracy (88.06 ± 6.97%), sensitivity (89.26 ± 5.69%), specificity (87.58% ± 7.66%) and in terms of classical criteria like dice (85.41 ± 3.35%), intersection over union (IoU, 80.37 ± 4.63%), and Hausdorff distance (HD, 4.34 ± 3.1).
Conclusion
We propose a rib fracture segmentation technique to deal with the problem of automatic fracture diagnosis. The proposed method avoids the down-sampling of 3D CT data through a projection technique. Experimental results show that it has excellent potential for clinical applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pieracci FM, Majercik S, Ali-Osman F, Ang D, Doben A, Edwards JG, French B, Gasparri M, Marasco S, Minshall C, Sarani B, Tisol W, VanBoerum DH, White TW (2016) Consensus statement: surgical stabilization of rib fractures rib fracture colloquium clinical practice guidelines. Injury 48(2):307–321
Cho SH, Sung YM, Kim MS (2012) Missed rib fractures on evaluation of initial chest CT for trauma patients: pattern analysis and diagnostic value of coronal multiplanar reconstruction images with multidetector row CT. Br J Radiol 85(1018):e845–e850
Lin FC, Li R, Tung Y, Jeng K, Tsai SC (2016) Morbidity, mortality, associated injuries, and management of traumatic rib fractures. J Chin Med Assoc 79(6):329–334
Talbot BS, Gange CP, Chaturvedi A, Klionsky N, Hobbs SK, Chaturvedi A (2017) Traumatic rib injury: patterns, imaging pitfalls, complications, and treatment. Radiographics 37(2):628–651
Ke S, Duan H, Cai Y, Kang J, Feng Z (2014) Thoracoscopy-assisted minimally invasive surgical stabilization of the anterolateral flail chest using Nuss bars. Ann Thorac Surg 97(6):2179–2182
Murphy CE, Raja AS, Baumann BM, Medak AJ, Langdorf MI, Nishijima DK, Hendey GW, Mower WR, Rodriguez RM (2017) Rib fracture diagnosis in the panscan era. Ann Emerg Med 70(6):904–909
Langdorf MI, Medak AJ, Hendey GW, Nishijima DK, Mower WR, Raja AS, Baumann BM, Anglin DR, Anderson CL, Lotfipour S, Reed KE, Zuabi N, Khan NA, Bithell CA, Rowther AA, Villar J, Rodriguez RM (2015) Prevalence and clinical import of thoracic injury identified by chest computed tomography but not chest radiography in blunt trauma: multicenter prospective cohort study. Ann Emerg Med 66(6):589–600
Kim J, Kim S, Kim YJ, Kim KG, Park J (2013) Quantitative measurement method for possible rib fractures in chest radiographs. Healthcare Inform Res 19(3):196–204
Kim EY, Yang HJ, Sung YM, Hwang K, Kim JH, Kim HS (2012) Sternal fracture in the emergency department: diagnostic value of multidetector CT with sagittal and coronal reconstruction images. Eur J Radiol 81(5):e708–e711
Sollmann N, Mei K, Hedderich DM, Maegerlein C, Kopp FK, Löffler MT, Zimmer C, Rummeny EJ, Kirschke JS, Baum T, Noël PB (2019) Multi-detector CT imaging : impact of virtual tube current reduction and sparse sampling on detection of vertebral fractures. Eur Radiol 29(7):3606–3616
Urbaneja A, Verbizier JD, Formery A, Tobon-Gomez C, Nace L, Blum A, Teixeira PAG (2019) Automatic rib cage unfolding with CT cylindrical projection reformat in polytraumatized patients for rib fracture detection and characterization: feasibility and clinical application. Eur J Radiol 110:121–127
Dankerl P, Seuss H, Ellmann S, Cavallaro A, Uber M, Hammon M (2017) Evaluation of rib fractures on a single-in-plane image reformation of the rib cage in CT examinations. Acad Radiol 24(2):153–159
Ringl H, Lazar M, Töpker M, Woitek R, Prosch H, Asenbaum U, Balassy C, Toth D, Weber M, Hajdu S, Soza G, Wimmer A, Mang T (2015) The ribs unfolded-a CT visualization algorithm for fast detection of rib fractures: effect on sensitivity and specificity in trauma patients. Eur Radiol 25(7):1865–1874
Janowczyk A, Madabhushi A (2016) Deep learning for digital pathology image analysis: a comprehensive tutorial with selected use cases. J Pathol Inform 7
Alom Z, Yakopcic C, Nasrin MS, Taha TM, Asari VK (2019) Breast cancer classification from histopathological images with inception recurrent residual convolutional neural network. J Digit Imag 32(4):605–617
Zhao Z, Zheng P, Xu S, Wu X (2019) Object detection with deep learning : a review. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 30(11):3212–3232
Gulshan V, Peng L, Coram M, Stumpe MC, Wu D, Narayanaswamy A, Venugopalan S, Widne K, Madams T, Cuadros J, Kim R, Raman R, Nelson PC, Mega JL, Webster DR (2016) Development and validation of a deep learning algorithm for detection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. JAMA 316(22):2402–2410
Kermany DS, Goldbaum M, Cai W, Lewis MA (2018) Identifying medical diagnoses and treatable diseases by image-based deep learning. Cell 172(5):1122-1131.e9
Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa RA, Ko J, Swetter SM, Blau HM, Thrun S (2017) Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature 542(7639):115–118
Cheng JZ, Ni D, Chou YH, Qin J, Tiu CM, Chang YC, Huang CS, Shen D, Chen CM (2016) Computer-aided diagnosis with deep learning architecture: applications to breast lesions in US images and pulmonary nodules in CT scans. Sci Rep 6(1):1–13
Jiang F, Jiang Y, Zhi H, Dong Y, Li H, Ma S, Wang Y, Dong Q, Shen H, Wang Y (2017) Artificial intelligence in healthcare: past, present and future. Stroke Vascular Neurol 2(4)
Weikert T, Noordtzij LA, Bremerich J, Stieltjes B, Parmar V, Cyriac J, Sommer G, Sauter AW (2020) Assessment of a deep learning algorithm for the detection of rib fractures on whole-body trauma computed tomography. Korean J Radiol 21(7):891
Zhou QQ, Tang W, Wang J, Hu ZC, Xia ZY, Zhang R, Fan X, Yong W, Yin X, Zhang B, Zhang H (2021) Automatic detection and classification of rib fractures based on patients’ CT images and clinical information via convolutional neural network. Eur Radiol 31(6):3815–3825
Jin L, Yang J, Kuang K, Ni B, Gao Y, Sun Y, Gao P, Ma W, Tan M, Kang H, Chen J, Li M (2020) Deep-learning-assisted detection and segmentation of rib fractures from CT scans: development and validation of FracNet. EBioMedicine 62:103106
Kallel F, Hamida AB (2017) A new adaptive gamma correction based algorithm using DWT-SVD for non-contrast CT image enhancement. IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 16(8):666–675
Tiwari M, Gupta B (2016) Brightness preserving contrast enhancement of medical images using adaptive gamma correction and homomorphic filtering. In: IEEE Students' conference on electrical, electronics and computer science (SCEECS), 1–4
Somasundaram K, Kalavathi P (2011) Medical image contrast enhancement based on gamma correction. Int J Knowl Manag e-Learn 3(1):15–18
Rajpurkar P, Irvin J, Ball RL, Zhu K, Yang B, Mehta H, Duan T, Ding D, Bagul A, Langlotz CP, Patel BN, Yeom KW, Shpanskaya K, Blankenberg FG, Seekins J, Amrhein TJ, Mong DA, Halabi SS, Zucker EJ, Ng AY, Lungren MP (2018) Deep learning for chest radiograph diagnosis: a retrospective comparison of the CheXNeXt algorithm to practicing radiologists. PLoS Med 15(11):e1002686
Feng S, Zhao H, Shi F, Cheng X, Wang M, Ma Y, Xiang D, Zhu W, Chen X (2020) Cpfnet: context pyramid fusion network for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imag 39(10):3008–3018
Zhang W, Yang G, Huang H, Yang W, Xu X, Liu Y, Lai X (2021) ME-Net: Multi-encoder net framework for brain tumor segmentation. Int J Imag Syst Technol 31(4):1834–1848
Li M, Wang C, Zhang H, Yang G (2020) MV-RAN: multiview recurrent aggregation network for echocardiographic sequences segmentation and full cardiac cycle analysis. Comput Biol Med 120:103728
Çiçek Ö, Abdulkadir A, Lienkamp SS, Brox T, Ronneberger O (2016) 3D U-Net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, 424–432
Oktay O, Schlemper J, Folgoc LL, Lee M, Heinrich M, Misawa K, Mori K, McDonagh S, Hammerla NY, Kainz B, Glocker B, Rueckert D (2018) Attention u-net: learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, 234–241
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the State’s Key Project of Research and Development Plan under Grants 2017YFA0104302, 2017YFC0109202, and 2017YFC0107900, in part by National Natural Science Foundation under Grants 81530060 and 61871117, in part by the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong under Grant 2018B030333001, in part by the Key R&D Joint Project of Liaoning under Grant 2020JH-10300164.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Chen, H., Ge, R. et al. Deep learning-based framework for segmentation of multiclass rib fractures in CT utilizing a multi-angle projection network. Int J CARS 17, 1115–1124 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-022-02607-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-022-02607-1