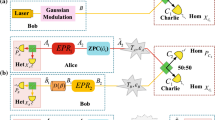
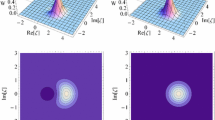
Abstract
We propose a new non-Gaussian version of the continuous variables measurement device independent quantum key distribution (CV-MDI-QKD) protocol by utilizing a photon added-then-subtracted (PAS) state. We report that our single- and two-mode PAS-CV-MDI-QKD protocols outperform pure state CV-MDI-QKD protocol when considering weak squeezing and high noise, which is the practical regime. With such resources, CV-MDI-QKD is inaccessible when using a pure TMSV state, while PAS-CV-MDI-QKD can generate a useful key rate in this regime. We also compare PAS-CV-MDI-QKD with a two-mode photon replaced (2PR) state, which was not studied in low squeezing for MDI-QKD before.







Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Shor, P.W.: Algorithms for quantum computation: discrete logarithms and factoring. In: Proceedings 35th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science, pp. 124–134. IEEE (1994)
Scarani, V., Bechmann-Pasquinucci, H., Cerf, N.J., šek, M., Lütkenhaus, N., Peev, M.: The security of practical quantum key distribution. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 1301–1350 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.81.1301
Gisin, N., Ribordy, G., Tittel, W., Zbinden, H.: Quantum cryptography. Rev. Mod. Phys. 74, 145–195 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/RevModPhys.74.145
Bennett, C.H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers, Systems, and Signal Processing, India, p. 175 (1984)
Nauerth, S., Moll, F., Rau, M., Fuchs, C., Horwath, J., Frick, S., Weinfurter, H.: Air-to-ground quantum communication. Nature Photon 7(5), 382–386 (2013)
Grünenfelder, F., Boaron, A., Resta, G.V., Perrenoud, M., Rusca, D., Barreiro, C., Houlmann, R., Sax, R., Stasi, L., El-Khoury, S., Hänggi, E., Bosshard, N., Bussières, F., Zbinden, H.: Fast single-photon detectors and real-time key distillation enable high secret-key-rate quantum key distribution systems. Nature Photon. 17(5), 422–426 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-023-01168-2
Ma, D., Liu, X., Huang, C., Chen, H., Lin, H., Wei, K.: Simple quantum key distribution using a stable transmitter-receiver scheme. Opt. Lett. 46(9), 2152 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1364/ol.418851
Tian, X.-H., Yang, R., Zhang, J.-N., Yu, H., Zhang, Y., Fan, P., Chen, M., Gu, C., Ni, X., Hu, M., Cao, X., Hu, X., Zhao, G., Lu, Y.-Q., Yin, Z.-J., Liu, H.-Y., Gong, Y.-X., Xie, Z., Zhu, S.-N.: Drone-based quantum key distribution (2023). https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.14012
Bouchard, F., Sit, A., Hufnagel, F., Abbas, A., Zhang, Y., Heshami, K., Fickler, R., Marquardt, C., Leuchs, G., Boyd, R., Karimi, E.: Quantum cryptography with twisted photons through an outdoor underwater channel. Opt. Express 26(17), 22563–22573 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1364/OE.26.022563
Sax, R., Boaron, A., Boso, G., Atzeni, S., Crespi, A., Grünenfelder, F., Rusca, D., Al-Saadi, A., Bronzi, D., Kupijai, S., Rhee, H., Osellame, R., Zbinden, H.: High-speed integrated qkd system. Photon. Res. 11(6), 1007–1014 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1364/PRJ.481475
Wei, K., Hu, X., Du, Y., Hua, X., Zhao, Z., Chen, Y., Huang, C., Xiao, X.: Resource-efficient quantum key distribution with integrated silicon photonics (2023). https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.12980
Du, Y., Zhu, X., Hua, X., Zhao, Z., Hu, X., Qian, Y., Xiao, X., Wei, K.: Silicon-based decoder for polarization-encoding quantum key distribution (2022). https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.04019
Wei, K., Li, W., Tan, H., Li, Y., Min, H., Zhang, W.-J., Li, H., You, L., Wang, Z., Jiang, X., Chen, T.-Y., Liao, S.-K., Peng, C.-Z., Xu, F., Pan, J.-W.: High-speed measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with integrated silicon photonics. Phys. Rev. X (2020). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevx.10.031030
Ralph, T.C.: Security of continuous-variable quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. A 62, 062306 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.62.062306
Grosshans, F., Grangier, P.: Continuous variable quantum cryptography using coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 057902 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.057902
Weedbrook, C., Pirandola, S., García-Patrón, R., Cerf, N.J., Ralph, T.C., Shapiro, J.H., Lloyd, S.: Gaussian quantum information. Rev. Modern Phys. 84(2), 621 (2012)
Laudenbach, F., Pacher, C., Fung, C.F., Poppe, A., Peev, M., Schrenk, B., Hentschel, M., Walther, P., Hübel, H.: Continuous-variable quantum key distribution with gaussian modulation-the theory of practical implementations. Adv. Quant. Technol. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1002/qute.201800011
Grosshans, F.: Collective attacks and unconditional security in continuous variable quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(2), 020504 (2005)
Renner, R., Cirac, J.I.: de finetti representation theorem for infinite-dimensional quantum systems and applications to quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 102, 110504 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.110504
Leverrier, A.: Composable security proof for continuous-variable quantum key distribution with coherent states. Phys. Rev. Lett. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.114.070501
Zhang, Y., Chen, Z., Pirandola, S., Wang, X., Zhou, C., Chu, B., Zhao, Y., Xu, B., Yu, S., Guo, H.: Long-distance continuous-variable quantum key distribution over 202.81 km of fiber. Phys. Rev. Lett. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrevlett.125.010502
Zhang, G., Haw, J.Y., Cai, H., Xu, F., Assad, S.M., Fitzsimons, J.F., Zhou, X., Zhang, Y., Yu, S., Wu, J., Ser, W., Kwek, L.C., Liu, A.Q.: An integrated silicon photonic chip platform for continuous-variable quantum key distribution. Nat. Photon. 13(12), 839–842 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-019-0504-5
Xu, F., Wei, K., Sajeed, S., Kaiser, S., Sun, S., Tang, Z., Qian, L., Makarov, V., Lo, H.-K.: Experimental quantum key distribution with source flaws. Phys. Rev. A 92(3), 032305 (2015)
Li, H.-W., Wang, S., Huang, J.-Z., Chen, W., Yin, Z.-Q., Li, F.-Y., Zhou, Z., Liu, D., Zhang, Y., Guo, G.-C., et al.: Attacking a practical quantum-key-distribution system with wavelength-dependent beam-splitter and multiwavelength sources. Phys. Rev. A 84(6), 062308 (2011)
Zhao, Y., Fung, C.-H.F., Qi, B., Chen, C., Lo, H.-K.: Quantum hacking: Experimental demonstration of time-shift attack against practical quantum-key-distribution systems. Phys. Rev. A 78(4), 042333 (2008)
Makarov, V., Anisimov, A., Skaar, J.: Effects of detector efficiency mismatch on security of quantum cryptosystems. Phys. Rev. A 74(2), 022313 (2006)
Lamas-Linares, A., Kurtsiefer, C.: Breaking a quantum key distribution system through a timing side channel. Opt. Express 15(15), 9388–9393 (2007)
Lo, H.-K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108(13), 130503 (2012)
Acín, A., Brunner, N., Gisin, N., Massar, S., Pironio, S., Scarani, V.: Device-independent security of quantum cryptography against collective attacks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98(23), 230501 (2007)
Yang, Y., Li, F.-L.: Entanglement properties of non-gaussian resources generated via photon subtraction and addition and continuous-variable quantum-teleportation improvement. Phys. Rev. A 80, 022315 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.80.022315
Lee, S.-Y., Ji, S.-W., Kim, H.-J., Nha, H.: Enhancing quantum entanglement for continuous variables by a coherent superposition of photon subtraction and addition. Phys. Rev. A 84, 012302 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.84.012302
Ourjoumtsev, A., Dantan, A., Tualle-Brouri, R., Grangier, P.: Increasing entanglement between gaussian states by coherent photon subtraction. Phys. Rev. Lett. 98, 030502 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.030502
Takahashi, H., Neergaard-Nielsen, J.S., Takeuchi, M., Takeoka, M., Hayasaka, K., Furusawa, A., Sasaki, M.: Entanglement distillation from gaussian input states. Nat. Photon. 4(3), 178–181 (2010)
Kurochkin, Y., Prasad, A.S., Lvovsky, A.I.: Distillation of the two-mode squeezed state. Phys. Rev. Lett. 112, 070402 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.070402
Boyd, R.W., Chan, K.W.C., O’Sullivan, M.N.: Quantum weirdness in the lab. Science 317(5846), 1874–1875 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1148947
Bartley, T.J., Walmsley, I.A.: Directly comparing entanglement-enhancing non-gaussian operations. New J. Phys. 17(2), 023038 (2015)
Borelli, L.F.M., Aguiar, L.S., Roversi, J.A., Vidiella-Barranco, A.: Quantum key distribution using continuous-variable non-gaussian states. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(2), 893–904 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-015-1193-8
Aguiar, L.S., Borelli, L.F.M., Roversi, J.A., Vidiella-Barranco, A.: Performance analysis of continuous-variable quantum key distribution using non-gaussian states. Quantum Inf. Process. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03645-z
Hu, L., Al-amri, M., Liao, Z., Zubairy, M.S.: Continuous-variable quantum key distribution with non-gaussian operations. Phys. Rev. A 102, 012608 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.102.012608
Ma, H.-X., Huang, P., Bai, D.-Y., Wang, S.-Y., Bao, W.-S., Zeng, G.-H.: Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with photon subtraction. Phys. Rev. A 97(4), 042329 (2018)
Ye, W., Zhong, H., Wu, X., Hu, L., Guo, Y.: Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution via quantum catalysis. Quantum Inf. Process. 19(10), 1–22 (2020)
Khan, M.B., Waseem, M., Irfan, M., Mehmood, A., Qamar, S.: Zero-photon catalysis based eight-state discrete modulated measurement-device-independent continuous-variable quantum key distribution. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 40(4), 763–772 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1364/JOSAB.482577
Li, Z., Zhang, Y.-C., Xu, F., Peng, X., Guo, H.: Continuous-variable measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 89(5), 052301 (2014)
Vahlbruch, H., Mehmet, M., Danzmann, K., Schnabel, R.: Detection of 15 db squeezed states of light and their application for the absolute calibration of photoelectric quantum efficiency. Phys. Rev. Lett. 117, 110801 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.110801
Ma, S.-L., Li, X.-K., Xie, J.-K., Li, F.-L.: Two-mode squeezed states of two separated nitrogen-vacancy-center ensembles coupled via dissipative photons of superconducting resonators. Phys. Rev. A 99, 012325 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.99.012325
Mølmer, K.: Non-gaussian states from continuous-wave gaussian light sources. Phys. Rev. A 73, 063804 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.73.063804
Singh, J., Bose, S.: Non-gaussian operations in measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 104, 052605 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.104.052605
Mardani, Y., Shafiei, A., Ghadimi, M., Abdi, M.: Continuous-variable entanglement distillation by cascaded photon replacement. Phys. Rev. A (2020). https://doi.org/10.1103/physreva.102.012407
Malpani, P., Thapliyal, K., Banerji, J., Pathak, A.: Enhancement of non-Gaussianity and nonclassicality of photon added displaced Fock state: A quantitative approach (2021). https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.12145
Thapliyal, K., Samantray, N.L., Banerji, J., Pathak, A.: Comparison of lower- and higher-order nonclassicality in photon added and subtracted squeezed coherent states. Phys. Lett. A 381(37), 3178–3187 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2017.08.019
Zavatta, A., Viciani, S., Bellini, M.: Quantum-to-classical transition with single-photon-added coherent states of light. Science 306(5696), 660–662 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1103190
Hosseinidehaj, N., Malaney, R.: Cv-mdi quantum key distribution via satellite. Quantum Inf. Comput. (2017). https://doi.org/10.26421/qic17.5-6
Hosseinidehaj, N.: Continuous-variable quantum communication over free-space lossy channels. PhD thesis, The University of New South Wales (2017)
Villasenor, E., Malaney, R.: Improving qkd for entangled states with low squeezing via non-gaussian operations. In: 2019 IEEE Globecom Workshops (GC Wkshps), pp. 1–6 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/GCWkshps45667.2019.9024548
Pirandola, S., Ottaviani, C., Spedalieri, G., Weedbrook, C., Braunstein, S., Lloyd, S., Gehring, T., Jacobsen, C., Andersen, U.: High-rate measurement-device-independent quantum cryptography. Nat. Photon. 9, 397–402 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2015.83
Vidal, G., Werner, R.F.: Computable measure of entanglement. Phys. Rev. A 65, 032314 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevA.65.032314
Plenio, M.B.: Logarithmic negativity: a full entanglement monotone that is not convex. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95, 090503 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.090503
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
FA did the main work and analysis. JL contributed in conceptualisation. AK supervised the work and contributed in analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, F., Li, J. & Khalique, A. Enabling CV-MDI-QKD for weakly squeezed states using non-Gaussian operations. Quantum Inf Process 23, 353 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-024-04565-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-024-04565-w