Abstract
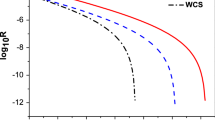
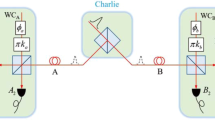
Twin-field quantum key distribution (TF-QKD) is known for its capacity of overcoming the fundamental rate-distance limit of QKD, and a variety of its variants have been derived. One of them, the phase-matching quantum key distribution (PM-QKD) not only inherits the high rate-distance capacity, but also outperforms the original TF-QKD. Moreover, the relatively less single-photon component of the most frequently used weak coherent source (WCS) makes it unable to meet the high-performance requirements of communication. In this paper, we propose a four-intensity decoy-state PM-QKD protocol based on heralded pair-coherent source to improve the secure key rate and the practicality. The simulations show that the secure key rate of our scheme is about an order of magnitude higher than that of four-intensity decoy-state PM-QKD protocol based on WCS. Meanwhile, the transmission distance is increased by more than 100 km. And the performance of our protocol has been greatly improved, in comparison with the better performance protocol known as ‘new PM-QKD’. In addition, the proposed protocol also shows excellent performance when finite data size and statistical fluctuation are considered.





Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Mayers, D.: Unconditional security in quantum cryptography. J. ACM 48(3), 351–406 (2001)
Lo, H.K., Chau, H.F.: Unconditional security of quantum key distribution over arbitrarily long distances. Science 283(5410), 2050–2056 (1999)
Shor, P.W., Preskill, J.: Simple proof of security of the BB84 quantum key distribution protocol. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(2), 441 (2000)
Bennett, C. H., Brassard, G.: Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computers Systems and Signal Processing, pp. 175-C179 (1984)
Wang, X.B.: Decoy-state protocol for quantum cryptography with four different intensities of coherent light. Phys. Rev. A 72(1), 012322 (2005)
Wang, X.B.: Beating the photon-number-splitting attack in practical quantum cryptography. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(23), 230503 (2005)
Lo, H.K., Ma, X., Chen, K.: Decoy state quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 94(23), 230504 (2005)
Wang, X.B., Yang, L., Peng, C.Z., Pan, J.W.: Decoy-state quantum key distribution with both source errors and statistical fluctuations. New J. Phys. 11(7), 075006 (2009)
Lo, H.K., Curty, M., Qi, B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. Lett. 108(13), 130503 (2012)
Ma, X., Razavi, M.: Alternative schemes for measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 86(6), 062319 (2012)
Wang, L., Zhao, S.M., Gong, L.Y., Cheng, W.W.: Free-space measurement-device-independent quantum-key-distribution protocol using decoy states with orbital angular momentum. Chin. Phys. B 24(12), 120307 (2015)
Zhou, Y.H., Yu, Z.W., Wang, X.B.: Making the decoy-state measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution practically useful. Phys. Rev. A 93(4), 042324 (2016)
Wu, X.D., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.B.: High-capacity measurement-device-independent quantum secure direct communication. Quantum Inf. Process. 19(10), 1–14 (2020)
Cui, Z.X., Zhong, W., Zhou, L., Sheng, Y.B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with hyper-encoding. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 62(11), 1–10 (2019)
Yan, Y.F., Zhou, L., Zhong, W., Sheng, Y.B.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution of multiple degrees of freedom of a single photon. Front. Phys. 16(1), 1–11 (2021)
Mizutani, A., Imoto, N., Tamaki, K.: Robustness of the round-robin differential-phase-shift quantum-key-distribution protocol against source flaws. Phys. Rev. A 92(6), 060303 (2015)
Zhang, Y.Y., Bao, W.S., Zhou, C., Li, H.W., Wang, Y., Jiang, M.S.: Practical round-robin differential phase-shift quantum key distribution. Opt. Express 24(18), 20763–20773 (2016)
Mao, Q.P., Wang, L., Zhao, S.M.: Decoy-state round-robin differential-phase-shift quantum key distribution with source errors. Quantum Inf. Process. 19(2), 1–12 (2020)
Pirandola, S., Laurenza, R., Ottaviani, C., Banchi, L.: Fundamental limits of repeaterless quantum communications. Nat. Commun. 8(1), 1–15 (2017)
Lucamarini, M., Yuan, Z.L., Dynes, J.F., Shields, A.J.: Overcoming the rate-distance limit of quantum key distribution without quantum repeaters. Nature 557(7705), 400–403 (2018)
Wang, X.B., Yu, Z.W., Hu, X.L.: Twin-field quantum key distribution with large misalignment error. Phys. Rev. A 98(6), 062323 (2018)
Ma, X., Zeng, P., Zhou, H.: Phase-matching quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. X 8(3), 031043 (2018)
Cui, C., Yin, Z.Q., Wang, R., Chen, W., Wang, S., Guo, G.C., Han, Z.F.: Twin-field quantum key distribution without phase postselection. Phys. Rev. Appl. 11(3), 034053 (2019)
Xue, K., Zhao, S., Mao, Q., Xu, R.: Plug-and-play sending-or-not-sending twin-field quantum key distribution. Quantum Inf. Process. 20(10), 1–16 (2021)
Li, W.T., Wang, L., Li, W., Zhao, S.M.: Phase-matching quantum key distribution with light source monitoring. Chin. Phys. B 31(5), 050310 (2022)
Li, W., Wang, L., Zhao, S.: Phase matching quantum key distribution based on single-photon entanglement. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 1–12 (2019)
Zeng, P., Wu, W., Ma, X.: Symmetry-protected privacy: beating the rate-distance linear bound over a noisy channel. Phys. Rev. Appl. 13(6), 064013 (2020)
Chen, G., Wang, L., Li, W., Zhao, Y., Zhao, S.M., Gruska, J.: Multiple-pulse phase-matching quantum key distribution. Quantum Inf. Process. 19(11), 1–16 (2020)
Yu, Y., Wang, L., Zhao, S., Mao, Q.: Decoy-state phase-matching quantum key distribution with source errors. Opt. Express 29(2), 2227–2243 (2021)
Zhang, X.X., Wang, Y., Jiang, M.S., Zhou, C., Lu, Y.F., Bao, W.S.: Finite-key analysis of asymmetric phase-matching quantum key distribution with unstable sources. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 38(3), 724–731 (2021)
Yu, Y., Wang, L., Zhao, S., Mao, Q.: Prefixed-threshold real-time selection for free-space phase-matching quantum key distribution. Europhys. Lett. 138(2), 28001 (2022)
Agarwal, G.S.: Generation of pair coherent states and squeezing via the competition of four-wave mixing and amplified spontaneous emission. Phys. Rev. Lett. 57(7), 827 (1986)
Zhang, S., Zou, X., Li, C., Jin, C., Guo, G.: A universal coherent source for quantum key distribution. Chin. Sci. Bull. 54(11), 1863–1871 (2009)
Wang, L., Zhao, S.: Round-robin differential-phase-shift quantum key distribution with heralded pair-coherent sources. Quantum Inf. Process. 16(4), 100 (2017)
Chen, D., Shang-Hong, Z., Lei, S.: Measurement device-independent quantum key distribution with heralded pair coherent state. Quantum Inf. Process. 15(10), 4253–4263 (2016)
Wang, X., Wang, Y., Chen, R.K., Zhou, C., Li, H.W., Bao, W.S.: Measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution with heralded pair coherent state. Laser Phys. 26(6), 065203 (2016)
Xu, R., Zhao, S.: Sending or not sending quantum key distribution based on heralded pair-coherent source. Laser Optoelectron. Progress 58(23), 2327001 (2021)
Bennett, C.H., DiVincenzo, D.P., Smolin, J.A., Wootters, W.K.: Mixed-state entanglement and quantum error correction. Phys. Rev. A 54(5), 3824 (1996)
Horikiri, T., Kobayashi, T.: Decoy state quantum key distribution with a photon number resolved heralded single photon source. Phys. Rev. A 73(3), 032331 (2006)
Wang, Y., Bao, W.S., Zhou, C., Jiang, M.S., Li, H.W.: Tight finite-key analysis of a practical decoy-state quantum key distribution with unstable sources. Phys. Rev. A 94(3), 032335 (2016)
Ma, X., Qi, B., Zhao, Y., Lo, H.K.: Practical decoy state for quantum key distribution. Phys. Rev. A 72(1), 012326 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (61871234). Yang Yu acknowledges the Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (Grant KYCX22_0958).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Han, L., Yu, Y., Lu, W. et al. Phase-matching quantum key distribution based on heralded pair-coherent source. Quantum Inf Process 22, 37 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03787-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-022-03787-0