Abstract
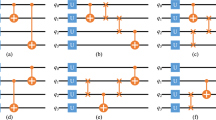
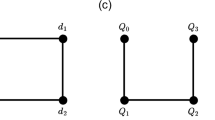
Implementing large-scale quantum circuits is one of the challenges of quantum computing. One of the central challenges of accurately modeling the architecture of these circuits is to schedule a quantum application and generate the layout while taking into account the cost of communications and classical resources as well as the maximum exploitable parallelism. In this paper, we present and evaluate a design flow for arbitrary quantum circuits in ion trap technology. Our design flow consists of two parts. First, a scheduler takes a description of a circuit and finds the best order for the execution of its quantum gates using integer linear programming regarding the classical resources (qubits) and instruction dependencies. Then a layout generator receives the schedule produced by the scheduler and generates a layout for this circuit using a graph-drawing algorithm. Our experimental results show that the proposed flow decreases the average latency of quantum circuits by about 11 % for a set of attempted benchmarks and by about 9 % for another set of benchmarks compared with the best in literature.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles, news and stories from top researchers in related subjects.Notes
\(C_{A}\) is an empty set in case of an uncontrolled gate.
As Soon As Possible.
As Late As Possible.
References
GDToolkit, Online available at http://www.dia.uniroma3.it/gdt/gdt4/index.php (2011). Accessed on Feb 2011
Gelfand, N., Tamassia, R.: Algorithmic patterns for graph drawing. In: Lecture Notes in Computer Science Issue 1547, pp. 138–152 (1998)
Grover, L.: A fast quantum mechanical algorithm for database search. In: Proceeding of ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, pp. 212–219 (1996)
Shor, P.: Polynomial time algorithms for prime factorization and discrete logarithms on a quantum computer. SIAM J. Comput. 26(5), 1484–1509 (1997)
Zalka, C.: Simulating quantum systems on a quantum computer. In: Proceeding of Mathematical, Physical and, Engineering Sciences, pp. 313–322 (1998)
Metodi, T.S., Chong, F.T.: Synthesis lectures on computer architecture. In: Hill, M.D. (ed.) Quantum Computing for Computer Architects. Morgan and Claypool Publishers, San Rafael, CA (2006)
Copsy, D., Oskin, M., Impens, F., Metodi, T., Cross, A., Chong, F., Chuang, I., Kubiatowicz, J.: Toward a scalable, silicon-based quantum computing architecture. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 9(6), 1552–1569 (2003)
Cirac, J., Zoller, P.: Quantum computation with cold trapped ions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 4091–4094 (1995)
Tan, T.R., Gaebler, J.P., Bowler, R., Lin, Y., Jost, J.D.: Leibfried, D., Wineland, D. J., Demonstration of a Dressed-State Phase Gate for Trapped Ions, ArXiv, preprint, arXiv:1301.3786 (2013)
Bowler, R., Warring, U., Britton, J.W., Sawyer, B.C., Amini, J.: Arbitrary Waveform Generator for Quantum Information Processing with Trapped Ions, ArXiv, preprint, arXiv:1301.2543 (2013)
Cirac, J., Zoller, P.: A scalable quantum computer with ions in an array of microtraps. Nature 404, 578–581 (2000)
Whitney, M.G., Isailovic, N., Patel, Y., Kubiatowicz, J.: A fault tolerant, area efficient architecture for Shor’s factoring algorithm. ACM SIGARCH Comput. Archit. News 37(3), 383–394 (2009)
Kielpinski, D., Monroe, C., Wineland, D.: Architecture for a large-scale ion-trap quantum computer. Nature 417, 709–711 (2002)
Whitney, M., Isailovic, N., Patal, Y., Kubiatowics, J.: AutomatedGeneration of layout and control for quantum circuits. In: Proceeding of Computing Frontiers, pp. 83–94 (2007)
Svore, k, Aho, A., Cross, A., Chuang, I., Markov, I.: A layered software architecture for quantum computing design tools. Computer 39(1), 74–83 (2006)
Chiaverini, J., Blakestad, R., Britton, J., Jost, J., Langer, C., Leibfried, D., Ozeri, R., Wineland, D.: Surface-electrode architecture for ion- trap quantum information processing. J. Quantum Inf. Comput. 5(5), 419–439 (2005)
Hucul, F., Yeo, M., Henginger, W., Rabchuk, J., Olmschenk, S., Monroe, C.: On the transport of atomic ions in linear and multidimensional ion trap arrays. J. Quantum Inf. Comput. 8(6), 501–578 (2008)
Cross, A.: Synthesis and Evaluation of Fault-Tolerant Quantum Computer Architectures, PhD Thesis. Massachusetts Institute of Technology (2005)
Mohammadzadeh, N., Saheb Zamani, M., Sedighi, M.: Improving latency of quantum circuits by gate exchanging. In: Conference on Digital System Design/Architectures, Methods and Tools (2009). doi:10.1109/DSD.2009.191
Metodi, T., Thaker, D., Cross, A., Chong, F., Chuang, I.: A quantum logic array microarchitecture: scalable quantum data movement and computation. In: Proceedings of the International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO), pp. 305–318 (2005)
Metodi, T., Thaker, F., Cross, A., Chong, F., Chuang, I.: Scheduling physical operations in a quantum information processor. In: Proceedings of SPIE Defense and Security Symposium vol. 6244, p. 62440T (2006)
Maslov, D., Dueck, G.W., Miller, D.M., Negrevergne, C.: Quantum circuit simplification and level compaction. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 27(3), 436–444 (2008)
Grassl, M.: Circuits for Quantum Error-Correcting Codes. Online available at http://iaks-www.ira.uka.de/home/grassl/QECC/index.html (2011), Accessed on June 2011
Isailovic, N., Whitney, M., Patal, Y., Kubiatowicz, J.: Running a quantum circuit at the speed of data. In: Proceedings of International Symposium in Computer Architecture (ISCA), pp. 177–188 (2008)
Maslov, D., Dueck, G., Scott, N.: Reversible Logic Synthesis Benchmarks Page. Online available at http://www.cs.uvic.ca/dmaslov/ (2011), Accessed on June 2011
Mohammadzadeh, N., Sedighi, M., Saheb Zamani, M.: Quantum physical synthesis: improving physical design by netlist modification. Microelectron. J. Elsevier 41(4), 219–230 (2010)
Mohammadzadeh, N., Saheb Zamani, M., Sedighi, M.: Auxiliary Qubit Selection: A Physical Synthesis Technique for Quantum Circuits. Springer Quantum Information Processing Journal (QIP), pp. 1–16 (2010)
Nielsen, M.A., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computation and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2000)
Barenco, A., Bennett, C.H., Cleve, R., DiVincenzo, D.P., Margolus, N., Shor, P., Sleator, T., Smolin, J.A., Weinfurter, H.: Elementary gates for quantum computation. Phys. Rev. A 52(5), 3457 (1995)
Lingo 13, Online available at http://www.lindo.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=2&Itemid=10. Accessed on Feb 2011
Maslov, D.: Linear depth stabilizer and quantum Fourier transformation circuits with no auxiliary qubits in finite-neighbor quantum architectures. Phys. Rev. A 76(5), 052310 (2007)
Andre, V.R., Muhammad, A., Mehta, A.C., Hussmann, J., Kim, J.: A Quantum Performance Simulator based on fidelity and fault-path counting, ArXiv, preprint, arXiv:1212.0845 (2012)
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Mehdi Saeedi for his helpful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yazdani, M., Saheb Zamani, M. & Sedighi, M. A quantum physical design flow using ILP and graph drawing. Quantum Inf Process 12, 3239–3264 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-013-0597-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-013-0597-6