Abstract
It has been 65 years since the Calvin–Benson cycle was first formulated. In this paper, the development of the concepts that are critical to the cycle is traced and the contributions of Calvin, Benson, and Bassham are discussed. Some simplified views often found in text books such as ascending paper chromatography and the use of the “lollipop” for short labeling are discussed and further details given. Key discoveries that underpinned elucidation of the cycle such as the importance of sedoheptulose phosphate and ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate are described. The interchange of ideas between other researchers working on what is now called the pentose phosphate pathway and the development of the ideas of Calvin and Benson are explored while the gluconeogenic aspects of the cycle are emphasized. Concerns raised about anomalies of label distribution in glucose are considered. Other carbon metabolism pathways associated with the Calvin–Benson cycle are also described. Finally, there is a section describing the rift between Calvin and Benson.


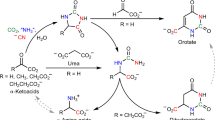
Reproduced with permission from Bassham et al. (1954)




Reproduced with permission from Bassham et al. (1954)

Reproduced with permission from Wilson and Calvin (1955)






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The name rubisco was coined by David Eisenberg in 1979 as a joke at Sam Wildman’s retirement party (Wildman 2002). The name emphasized the recent change in nomenclature from diphosphate to bisphosphate and the recent discovery that the enzyme is also an oxygenase (Bowes et al. 1971). In Sam’s next paper, he used the acronym rubisco, but soon after many variations in capitalization appeared. Style manuals provide clear guidelines for capitalization in this case. If the abbreviation is pronounced as a word (making it an acronym), and if it is so well known that people recognize the acronym more easily than the words it stands for, it is not capitalized (examples—laser and scuba). Wildman did not capitalize rubisco in his first publication using it (Wildman 1981). If an acronym is not quite so universally known but is more than four letters, the first letter (only) is capitalized (Hepes and Unesco). I have found no style manuals that would accept RuBisCO, RubisCO or any of the other capitalization schemes that are used. Because rubisco is so central to photosynthesis and better recognized than the words it stands for I believe it should be all lower case like “laser,” which is more easily understood than light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The use of Rubisco is tolerable, but other capitalization schemes should be abandoned. I will use rubisco here.
References
Anderson LE, Ng T-CL, Kyung-Eun Yoon P (1974) Inactivation of pea leaf chloroplastic and cytoplasmic glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenases by light and dithiothreitol. Plant Physiol 53(6):835–839. https://doi.org/10.2307/4263632
Andrews TJ, Kane HJ (1990) Pyruvate as a by-product of rubisco catalysis. Plant Physiol 93s:9–9
Arnon DI (1951) Extracellular photosynthetic reactions. Nature 167:1008–1010
Ball S, Guan H-P, James M, Myers A, Keeling P, Mouille G, Buléon A, Colonna P, Preiss J (1996) From glycogen to amylopectin: a model for the biogenesis of the plant starch granule. Cell 86(3):349–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80107-5
Bar-Even A, Noor E, Milo R (2012) A survey of carbon fixation pathways through a quantitative lens. J Exp Bot 63(6):2325–2342. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/err417
Barltrop JA, Hayes PM, Calvin M (1954) The chemistry of 1,2-dithiolane (trimethylene disulfide) as a model for the primary quantum conversion act in photosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc 76(17):4348–4367. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01646a029
Bassham JA (2003) Mapping the carbon reduction cycle: a personal retrospective. Photosynth Res 76:37–52. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024929725022
Bassham JA, Krause GH (1969) Free energy changes and metabolic regulation in steady-state photosynthetic carbon reduction. Biochim Biophys Acta 189(2):207–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2728(69)90048-6
Bassham JA, Benson AA, Kay LD, Harris AZ, Wilson AT, Calvin M (1954) The path of carbon in photosynthesis. XXI. The cyclic regeneration of carbon dioxide acceptor. J Am Chem Soc 76(7):1760–1770. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01636a012
Benson AA (1951) Identification of ribulose in C14O2 photosynthesis products. J Am Chem Soc 73:2971–2972
Benson A (2002) Following the path of carbon in photosynthesis: a personal story. Photosynth Res 73(1):29–49. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020427619771
Benson AA (2010) Last days in the old radiation laboratory (ORL), Berkeley, California, 1954. Photosynth Res 105:209–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-010-9592-2
Benson A, Calvin M (1947) The dark reductions of photosynthesis. Science 105(2738):648–649. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.105.2738.648
Benson AA, Calvin M (1950) The path of carbon in photosynthesis VII. Respiration and photosynthesis. J Exp Bot 1(1):63–68. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/1.1.63
Benson AA, Bassham JA, Calvin M, Goodale TC, Haas VA, Stepka W (1950) The path of carbon in photosynthesis. V. Paper chromatography and radioautography of the products. J Am Chem Soc 72(4):1710–1718. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01160a080
Benson AA, Bassham JA, Calvin M (1951) Sedoheptulose in photosynthesis by plants. J Am Chem Soc 73(6):2970–2970. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01150a543
Benson AA, Bassham JA, Calvin M, Hall AG, Hirsch HE, Kawaguchi S, Lynch V, Tolbert NE (1952a) The path of carbon in photosynthesis XV. Ribulose and sedoheptulose. J Biol Chem 196:703–716
Benson AA, Kawauchi S, Hayes P, Calvin M (1952b) The path of carbon in photosynthesis. XVI. Kinetic relationships of the intermediates in steady state photosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc 74(18):4477–4482. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01138a001
Blackman FF (1905) Optima and limiting factors. Ann Bot 19:281–295
Bowes G, Ogren WL, Hageman RH (1971) Phosphoglycolate production catalyzed by ribulose diphosphate carboxylase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 45:716–722
Buchanan BB (2016a) The carbon (formerly dark) reactions of photosynthesis. Photosynth Res 128(2):215–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-015-0212-z
Buchanan BB (2016b) The path to thioredoxin and redox regulation in chloroplasts. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67(1):1–24. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-043015-111949
Buchanan BB, Arnon DI (1990) A reverse KREBS cycle in photosynthesis: consensus at last. Photosynth Res 24:47–53
Buchanan BB, Wong JH (2013) A conversation with Andrew Benson: reflections on the discovery of the Calvin–Benson cycle. Photosynth Res 114(3):207–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-012-9790-1
Caillau M, Quick WP (2005) New insights into plant transaldolase. Plant J 43(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02427.x
Calvin M (1949) The path of carbon in photosynthesis, VI. J Chem Educ 26(12):639. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed026p639
Calvin M (1964) The path of carbon in photosynthesis. In: Nobel lectures, chemistry 1942–1962. Elsivier, Amsterdam, pp 618–644. https://doi.org/10.2172/928404
Calvin M (1989) Intermediates in the photosynthetic cycle: a commentary by Melvin Calvin on ‘Intermediates in the photosynthetic cycle’ by J.A. Bassham, S.A. Barker, M. Calvin and U.C. Quarck, Biochim. Biophys. Acta 21 (1956) 376-377. Biochim Biophys Acta 1000:403–409
Calvin M, Barltrop JA (1952) A possible primary quantum conversion act of photosynthesis. J Am Chem Soc 74(23):6153–6154. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01143a544
Calvin M, Massini P (1952) The path of carbon in photosynthesis. XX. The steady state. Experientia 8(12):445–457
Canvin DT (1979) Photorespiration: comparison between C3 and C4 plants. In: Gibbs M, Latzko E (eds) Encyclopedia of plant physiology NS vol 6 photosynthesis II. Springer, Berlin, pp 368–396
Delwiche CF, Sharkey TD (1993) Rapid appearance of 13C in biogenic isoprene when 13CO2 is fed to intact leaves. Plant Cell Environ 16:587–591
Dietz KJ, Schreiber U, Heber U (1985) The relationship between the redox state of QA and photosynthesis in leaves at various carbon-dioxide, oxygen and light regimes. Planta 166:219–226
Driever SM, Simkin AJ, Alotaibi S, Fisk SJ, Madgwick PJ, Sparks CA, Jones HD, Lawson T, Parry MAJ, Raines CA (2017) Increased SBPase activity improves photosynthesis and grain yield in wheat grown in greenhouse conditions. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2016.0384
Ebenhöh O, Spelberg S (2018) The importance of the photosynthetic Gibbs effect in the elucidation of the Calvin–Benson–Bassham cycle. Biochem Soc Trans 46(1):131. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20170245
Eichelmann H, Laisk A (1999) Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase content, assimilatory charge, and mesophyll conductance in leaves. Plant Physiol 119:179–189
Evans MCW, Buchanan BB, Arnon DI (1966) A new ferredoxin-dependent carbon reduction cycle in a photosynthetic bacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 55:928–934
Fager EW, Rosenberg JL (1950) Phosphoglyceric acid in photosynthesis. Science 112(2917):617–618
Farquhar GD, von Caemmerer S, Berry JA (1980) A biochemical model of photosynthetic CO2 assimilation in leaves of C3 species. Planta 149:78–90
Flanigan IL, MacLeod JK, Williams JF (2006) A re-investigation of the path of carbon in photosynthesis utilizing GC/MS methodology. Unequivocal verification of the participation of octulose phosphates in the pathway. Photosynth Res 90(2):149–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-006-9114-4
Gauthier PPG, Bligny R, Gout E, Mahé A, Nogués S, Hodges M, Tcherkez GGB (2010) In folio isotopic tracing demonstrates that nitrogen assimilation into glutamate is mostly independent from current CO2 assimilation in illuminated leaves of Brassica napus. New Phytol 185(4):988–999. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.03130.x doi
Gerhardt R, Stitt M, Heldt HW (1987) Subcellular metabolite levels in spinach leaves. Regulation of sucrose synthesis during diurnal alterations in photosynthetic partitioning. Plant Physiol 83:399–407
Gibbs M (1966) Intermediary metabolism and pathology. In: Sterward FC (ed) Plant pysiology, vol IVB. Academic Press, New York, pp 3–115
Gibbs M, Kandler O (1957) Asymmetric distribution of C14 in sugars formed during photosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 43(6):446
Gong XY, Tcherkez G, Wenig J, Schäufele R, Schnyder H (2018) Determination of leaf respiration in the light: comparison between an isotopic disequilibrium method and the Laisk method. New Phytol 218(4):1371–1382. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.15126
Gotoh E, Matsumoto M, Ogawa K, Kobayashi Y, Tsuyama M (2010) A qualitative analysis of the regulation of cyclic electron flow around photosystem I from the post-illumination chlorophyll fluorescence transient in Arabidopsis: a new platform for the in vivo investigation of the chloroplast redox state. Photosynth Res 103(2):111–123. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-009-9525-0
Harrison EP, Willingham NM, Lloyd JC, Raines CA (1998) Reduced sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase levels in transgenic tobacco lead to decreased photosynthetic capacity and altered carbohydrate accumulation. Planta 204(1):27–36
Harrison EP, Olcer H, Lloyd JC, Long SP, Raines CA (2001) Small decreases in SBPase cause a linear decline in the apparent RuBP regeneration rate, but do not affect Rubisco carboxylation capacity. J Exp Bot 52:1779–1784. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/52.362.1779
Heskel MA, Tang J (2018) Environmental controls on light inhibition of respiration and leaf and canopy daytime carbon exchange in a temperate deciduous forest. Tree Physiol. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpy103:tpy103-tpy103
Horecker BL, Smyrniotis PZ (1952) The enzymatic formation of sedoheptulose phosphate from pentose phosphate. J Am Chem Soc 74(8):2123–2123. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01128a524
Horecker BL, Smyrniotis PZ (1953a) The coenzyme function of thiamine pyrophosphate in pentose phosphate metabolism. J Am Chem Soc 75(4):1009–1010. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01100a525
Horecker BL, Smyrniotis PZ (1953b) Transaldolase: the formation of fructose-6-phosphate from sedoheptulose-7-phosphate. J Am Chem Soc 75(8):2021–2022. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01104a532
Horecker BL, Smyrniotis PZ, Seegmiller JE (1951) The enzymatic conversion of 6-phosphogluconate to ribulose-5-phosphate and ribose-5-phosphate. J Biol Chem 193(1):383–396
Horecker BL, Gibbs M, Klenow H, Smyrniotis PZ (1954) The mechanism of pentose phosphate conversion to hexose monophosphate: I. With a liver enzyme preparation. J Biol Chem 207(1):393–404
Horecker BL, Paoletti F, Williams JF (1982) Occurrence and significance of octulose phosphates in liver. Ann N Y Acad Sci 378(1):215–224. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb31198.x
Jakoby WB, Brummond DO, Ochoa S (1956) Formation of 3-phosphoglyceric acid by carbon dioxide fixation with spinach leaf enzymes. J Biol Chem 218(2):811–822
Johnson HS (1972) Dithiothreitol: an inhibitor of glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase activity in leaf extracts and isolated chloroplasts. Planta 106(3):273–277. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00388105
Kammerer B, Fischer K, Hilpert B, Schubert S, Gutensohn M, Weber A, Flügge UI (1998) Molecular characterization of a carbon transporter in plastids from heterotrophic tissues: the glucose 6-phosphate phosphate antiporter. Plant Cell 10(1):105–117
Kandler O, Gibbs M (1956) Asymmetric distribution of C14 in the glucose phosphates formed during photosynthesis. Plant Physiol 31(5):411–412
Karl T, Fall R, Rosenstiel TN, Prazeller P, Larsen B, Seufert G, Lindinger W (2002) On-line analysis of the 13CO2 labeling of leaf isoprene suggests multiple subcellular origins of isoprene precursors. Planta 215(6):894–905. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-002-0825-2
Kunz HH, Häusler RE, Fettke J, Herbst K, Niewiadomski P, Gierth M, Bell K, Steup M, Flügge UI, Schneider A (2010) The role of plastidial glucose-6-phosphate/phosphate translocators in vegetative tissues of Arabidopsis thaliana mutants impaired in starch biosynthesis. Plant Biol 12:115–128. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1438-8677.2010.00349.x
La Forge FB, Hudson CS (1917) Sedoheptose, a new sugar from Sedum spectabile I. J Biol Chem 30(1):61–77
Lawson T, Bryant B, Lefebvre S, Lloyd JC, Raines CA (2006) Decreased SBPase activity alters growth and development in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Cell Environ 29(1):48–58. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2005.01399.x
Leakey ADB, Xu F, Gillespie KM, McGrath JM, Ainsworth EA, Ort DR (2009) Genomic basis for stimulated respiration by plants growing under elevated carbon dioxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(9):3597–3602. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0810955106
Lefebvre S, Lawson T, Fryer M, Zakhleniuk OV, Lloyd JC, Raines CA (2005) Increased sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase activity in transgenic tobacco plants stimulates photosynthesis and growth from an early stage in development. Plant Physiol 138(1):451
Lendzian KJ (1980) Modulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase by NADPH, NADP+ and dithiothreitol at variable NADPH/NADP+ ratios in an illuminated reconstituted Spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.) chloroplast system. Planta 148(1):1–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00385434
Li J, Weraduwage SM, Preiser AL, Weise SE, Strand DD, Froehlich JE, Kramer DM, Hu J, Sharkey TD (2018) Loss of peroxisomal hydroxypyruvate reductase inhibits triose phosphate isomerase but stimulates cyclic photosynthetic electron flow and the Glc-6-phosphate shunt. bioRxiv:278580
Livingston AK, Cruz JA, Kohzuma K, Dhingra A, Kramer DM (2010) An Arabidopsis mutant with high cyclic electron flow around Photosystem I (hcef) involving the NADPH dehydrogenase complex. Plant Cell 22(1):221. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.071084
Loreto F, Ciccioli P, Brancaleoni E, Cecinato A, Frattoni M, Sharkey TD (1996) Different sources of reduced carbon contribute to form three classes of terpenoid emitted by Quercus ilex L. leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93(18):9966–9969
Mahon JD, Fock H, Canvin DT (1974) Changes in specific radioactivities of sunflower leaf metabolites during photosynthesis in 14CO2 and 12C02 at normal and low oxygen. Planta 120:125–134
Martin W, Scheibe R, Schnarrenberger C (2000) The Calvin cycle and its regulation. In: Leegood RC, Sharkey TD, von Caemmerer S (eds) Advances in photosynthesis, vol 9. Photosynthesis: physiology and metabolism. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Mayaudon J (1957) Study of association between the main nucleoprotein of green leaves and carboxydismutase. Enzymologia 18:345–354
McGowan RE, Gibbs M (1974) Comparative enzymology of the glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenases from Pisum sativum. Plant Physiol 54:312–319
Meyerhof O, Junowicz-Kocholaty R (1943) The equilibria of isomerase and aldolase, and the problem of the phosphorylation of glyceraldehyde phosphate. J Biol Chem 149:71–92
Mouille G, Maddelein ML, Libessart N, Talaga P, Decq A, Delrue B, Ball S (1996) Preamylopectin processing: a mandatory step for starch biosynthesis in plants. Plant Cell 8:1353–1366
Neuhaus HE, Schulte N (1996) Starch degradation in chloroplasts isolated from C3 or CAM (crassulacean acid metabolism)-induced Mesembryanthemum crystallinum L. Biochem J 318:945–953
Niewiadomski P, Knappe S, Geimer S, Fischer K, Schulz B, Unte US, Rosso MG, Ache P, Flugge UI, Schneider A (2005) The Arabidopsis plastidic glucose 6-phosphate/phosphate translocator GPT1 is essential for pollen maturation and embryo sac development. Plant Cell 17:760–775
Ölçer H, Lloyd JC, Raines CA (2001) Photosynthetic capacity is differentially affected by reductions in sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase activity during leaf development in transgenic tobacco plants. Plant Physiol 125:982–989
Preiss J, Ghosh HP, Wittkop J (1967) Regulation of the biosynthersis of starch in spinach leaf chloroplasts. In: Goodwin TW (ed) Biochemistry of chloroplasts. Academic Press, London, pp 131–153
Quayle JR, Fuller RC, Benson AA, Calvin M (1954) Enzymatic carboxylation of ribulose diphosphate. J Am Chem Soc 76(13):3610–3611. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01642a089
Racker E, Haba GDL, Leder IG (1953) Thiamine pyrophosphate, a coenzyme of transketolase. J Am Chem Soc 75(4):1010–1011. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01100a526
Raines CA, Lloyd JC, Dyer TA (1999) New insights into the structure and function of sedoheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase; an important but neglected Calvin cycle enzyme. J Exp Bot 50:1–8
Rosenthal DM, Locke AM, Khozaei M, Raines CA, Long SP, Ort DR (2011) Over-expressing the C3 photosynthesis cycle enzyme sedoheptulose-1-7 bisphosphatase improves photosynthetic carbon gain and yield under fully open air CO2 fumigation (FACE). BMC Plant Biol 11:123. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-11-123
Ruben S, Kamen MD (1940) Radioactive carbon of long half-life. Phys Rev 57(6):549–549. https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.57.549
Ruben S, Kamen MD, Hassid WZ, Devault DC (1939) Photosynthesis with radio-carbon. Science 90(2346):570
Schleucher J, Vanderveer P, Markley JL, Sharkey TD (1999) Intramolecular deuterium distributions reveal disequilibrium of chloroplast phosphoglucose isomerase. Plant Cell Environ 22:525–533
Schloss JV, Lorimer GH (1982) The stereochemical course of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. Reductive trapping of the 6-carbon reaction-intermediate. J Biol Chem 257(9):4691–4694
Schnarrenberger C, Oeser A (1974) Two isoenzymes of glucosephosphate isomerase from spinach leaves and their intracellular compartmentation. Eur J Biochem 45(1):77–82. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03531.x
Schnitzler JP, Graus M, Kreuzwieser J, Heizmann U, Rennenberg H, Wisthaler A, Hansel A (2004) Contribution of different carbon sources to isoprene biosynthesis in poplar leaves. Plant Physiol 135:152–160
Sharkey TD, Vassey TL (1989) Low oxygen inhibition of photosynthesis is caused by inhibition of starch synthesis. Plant Physiol 90:385–387
Sharkey TD, Weise SE (2012) Autotrophic carbon dioxide fixation. In: Eaton-Rye JJ, Tripathy B, Sharkey TD (eds) Photosynthesis: plastid biology, energy conversion and carbon assimilation. advances in photosynthesis and respiration, vol 34. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 649–672
Sharkey TD, Weise SE (2016) The glucose 6-phosphate shunt around the Calvin–Benson cycle. J Exp Bot 67(14):4067–4077. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erv484
Stitt M, Huber S, Kerr P, Stumpf PK, Conn EE (1987) Control of photosynthetic sucrose formation. In: The biochemistry of plants. Academic Press, New York, pp 327–409
Strand DD, Livingston AK, Satoh-Cruz M, Froehlich JE, Maurino VG, Kramer DM (2015) Activation of cyclic electron flow by hydrogen peroxide in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112(17):5539–5544. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1418223112
Strand DD, Fisher N, Davis GA, Kramer DM (2016) Redox regulation of the antimycin A sensitive pathway of cyclic electron flow around photosystem I in higher plant thylakoids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1857:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2015.07.012
Streb S, Delatte T, Umhang M, Eicke S, Schorderet M, Reinhardt D, Zeeman SC (2008) Starch granule biosynthesis in Arabidopsis is abolished by removal of all debranching enzymes but restored by the subsequent removal of an endoamylase. Plant Cell 20(12):3448–3466. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.063487
Szecowka M, Heise R, Tohge T, Nunes-Nesi A, Vosloh D, Huege J, Feil R, Lunn J, Nikoloski Z, Stitt M, Fernie AR, Arrivault S (2013) Metabolic fluxes in an illuminated Arabidopsis rosette. Plant Cell Online 25:694–714. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.106989
Tcherkez G, Cornic G, Bligny R, Gout E, Ghashghaie J (2005) In vivo respiratory metabolism of illuminated leaves. Plant Physiol 138(3):1596. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.062141
Tcherkez G, Gauthier P, Buckley TN, Busch FA, Barbour MM, Bruhn D, Heskel MA, Gong XY, Crous KY, Griffin K, Way D, Turnbull M, Adams MA, Atkin OK, Farquhar GD, Cornic G (2017) Leaf day respiration: low CO2 flux but high significance for metabolism and carbon balance. New Phytol 216(4):986–1001. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14816
Tolmach LJ (1951) Effects of triphosphopyridine nucleotide upon oxygen evolution and carbon dioxide fixation by illuminated chloroplasts. Nature 167:946–948
Uematsu K, Suzuki N, Iwamae T, Inui M, Yukawa H (2012) Expression of Arabidopsis plastidial phosphoglucomutase in tobacco stimulates photosynthetic carbon flow into starch synthesis. J Plant Physiol 169(15):1454–1462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2012.05.008
Vishniac W, Ochoa S (1951) Photochemical reductionof pyridine nucleotides by spinach grana and coupled carbon dioxide fixation. Nature 167:768–769
Weissbach A, Horecker BL, Hurwitz J (1956) The enzymatic formation of phosphoglyceric acid from ribulose diphosphate and carbon dioxide. J Biol Chem 218(2):795–810
Wildman SG (1981) Molecular aspects of wheat evolution: rubisco composition. In: Evans LT, Peacock WJ (eds) Wheat science, today and tomorrow. Cambridge, New York, pp 61–74
Wildman SG (2002) Along the trail from Fraction I protein to Rubisco (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase). Photosynth Res 73:243–250
Wilson AT, Calvin M (1955) The photosynthetic cycle. CO2 dependent transients. J Am Chem Soc 77(22):5948–5957. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01627a050
Acknowledgements
My research on the carbon metabolism of photosynthesis is supported by U.S. Department of Energy Grant DE-FG02-91ER2002. Partial salary support came from Michigan AgBioResearch. I thank Sean Weise for finding the original use of “rubisco”, Joe Berry for telling me about the fisherman in Fig. 6, and Christoph Benning for the loan of the lollipop from Ed Tolbert’s lab.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharkey, T.D. Discovery of the canonical Calvin–Benson cycle. Photosynth Res 140, 235–252 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-018-0600-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-018-0600-2