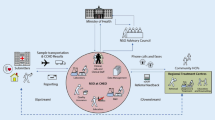
Abstract
In this paper, we established a newborn screening system under the HL7/Web Services frameworks. We rebuilt the NTUH Newborn Screening Laboratory’s original standalone architecture, having various heterogeneous systems operating individually, and restructured it into a Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA), distributed platform for further integrity and enhancements of sample collections, testing, diagnoses, evaluations, treatments or follow-up services, screening database management, as well as collaboration, communication among hospitals; decision supports and improving screening accuracy over the Taiwan neonatal systems are also addressed. In addition, the new system not only integrates the newborn screening procedures among phlebotomy clinics, referral hospitals, as well as the newborn screening center in Taiwan, but also introduces new models of screening procedures for the associated, medical practitioners. Furthermore, it reduces the burden of manual operations, especially the reporting services, those were heavily dependent upon previously. The new system can accelerate the whole procedures effectively and efficiently. It improves the accuracy and the reliability of the screening by ensuring the quality control during the processing as well.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Therrell, B.L., US newborn screening policy dilemmas for the twenty-first century. Mol. Genet. Metab. 74, 64–74 (2001). doi:10.1006/mgme.2001.3238
Ohkubo, S., Shimozawa, K., Matsumoto, M., Kitagawa, T., Analysis of blood spot 17α-hydroxyprogesterone concentration in premature infants -proposal for cut-off limits in screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia-. Acta. Paediatr. Jpn. 34, 126–133 (1992)
John, A., Age-dependent cutoff values in screening newborns for Hypothyroidism. Clin. Biochem. 37(9), 791–797 (2004)
Lindner, M., et al., Neonatal screen for glutaric aciduria type I: Strategies to proceed. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 29, 378–382 (2006). doi:10.1007/s10545-006-0284-1
Weng, Y. –C., Hsieh, S. –L., Hsieh, S. –H., Lai, F., Design and Enhance a Dynamic Healthcare Portal Site. Web Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology Workshops, 2007 IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conferences, pp. 173–176, 2007.
Stoddard, J.J., Farrell, P.M., State-to-state variations in newborn screening policies. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 151, 561–564 (1997)
Expanded Newborn Screening using Tandem Mass Spectrometry Financial, Ethical, Legal and Social Issues (FELSI), http://www.newbornscreening.info.
http://www.susps.org/overview/birthrates.html, “U.S. Birth Rates and Population Growth.
http://content.healthaffairs.org/cgi/content/abstract/26/2/559?ck=nck as of 08/09/2008.
http://content.healthaffairs.org, Newborn Screening: Current Status, Pamela H. Arn.
http://www.nlm.nih.gov/, Medical Encyclopedia: Newborn screening tests.
http://www.drgreene.org, Newborn Screening Tests.
Georgia Newborn Screening Manual for Metabolic Diseases and Hemoglobinopathies. Georgia Department of Human Resources: Division of Public Health, 2007.
http://www.slh.wisc.edu/wps/scm/connect/extranet/newborn, Wisconsin Newborn Screening Laboratory.
Wisconsin Newborn Screening Laboratory Newsletter, No. 63, “2006 Testing Summary”, July 2007.
http://www.foxnews.com, “States Doubled Number of Newborns Tested for Genetic Diseases” as of 07/11/2006
http://www.healthsystem.virgina.edu, “Newborn Screening Tests”, University of Virginia Health System, as of 10/23/2007
http://www.kidshealth.org/parent/system/medical/newborn_screening_tests.html as of 27/08/2008
http://www.marchofdimes.com/printable Articles/298_834.asp as of 10/23/2007, Testing the newborn for Metabolic Birth Defects, March of Dimes
Hinman, A.R., Eichwald, J., Linzer, D., Saarlas, K. N., Integrating child health information systems. Am. J. Public Health 95(11), 1923–1927 (2006). doi:10.2105/AJPH.2004.051466
http://las.perkinelmer.com, Wallac LifeCycle for Neonatal Screening–Design Principles–USA
Therrell, B.L., Hannon, W.H., National evaluation of US newborn screening system components. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 12, 236–245 (2006). doi:10.1002/mrdd.20124
National Newborn Screening Information System, NNSIS, http://www2.uthscsa.edu/nnsis
NNSGRC, http://genes-r-us.uthscsa.edu/resources/newborn/00/2000report.pdf a) National Newborn Screening and Genetics Resources Center
Padilla, C.D., Therrell, B.L., Newborn screening in the Asia Pacific region. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 30, 490–506 (2007). doi:10.1007/s10545-007-0687-7
http://www.health.vic.gov.au/genetics/strategy.htm Genetics Services Strategy for Victoria 2005–2009
Bodamer, O.A., Hoffmann, G.F., Lindner, M., Expanded newborn screening in Europe 2007. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 30, 439–444 (2007). doi:10.1007/s10545-007-0666-z
http://www.atlab.com/Neomate.php as of 08/30/2008.
http://www.perkinelmer.com/ as of 08/28/2008.
Liu, N., Marenco, L., Miller, P.L., ResourceLog: An Embeddable Tool for Dynamically Monitoring the Usage of Web-Based Bioscience Resources. J. Am. Med. Inform. Assoc. 2006 13(4), 432–437 (2006). doi:10.1197/jamia.M2013
Sean, A., McGhee, E. Stiehm, R., Cowan, M., Krogstad, P. McCabe, E. R. B., “Two-tiered universal newborn screening strategy for severe combined immunodeficiency”, Nov. 2, 2005; http: www.sciencedirect.com
Webster, D., Quality performance of newborn screening systems: Strategies for improvement. J. Inherit. Meta. Dis. 30, 576–584 (2007)
Olgemoller, B., et al., Screening for congenital adrenal hyperplasia: adjustment of 17-Hydroxyprogesterone cut-off values to both age and birth weight markedly improves the predictive value. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88(12), 5790–5794 (2003). doi:10.1210/jc.2002-021732
Microsoft Developer Network (MSDN), http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa480482.aspx as of 02/09/2008.
Ko, L. F., Lin, J. C., et al., “HL7 middleware framework for healthcare information system”, IEEE Healthcare, pp 152–156, 2006.
Hsieh, S. L., Feipei Lai, S. H., Hsieh et al., “An Integrated Healthcare Enterprise Information Portal and Healthcare Information System Framework”. IEEE EMBC, pp 4731–4734, 2006.
Hsieh, S. H., Hsieh, S. L., Weng, Y. C., et al., “Middleware based Inpatient Healthcare Information System”, Bioinformatics and Bioengineering, BIBE 2007, Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference, pp. 1230–1234, 2007.
Yang, T. H., Cheng, P. H., et al., “A Scalable Multi-tier Architecture for the National Taiwan University Hospital Information System based on HL7 Standard”, CBMS August 2006, Proceedings of the 19th IEEE Symposium on Computer-Based Medical Systems, pp. 99–104, 2006.
Pierce, M., Fox, G., Youn, C., Mock, S., Mueller, K., Balsoy, O., Interoperable Web Services for Computational Portals. Proceedings of Supercomputing 2002, Baltimore.
Murray, M., “Strategies for the successful implementation of workflow systems within healthcare: a cross case comparison”, System Sciences, 2003. Proceedings of the 36th Annual Hawaii International Conference, pp. 10, 2003.
Bunge, R., Chung, S., Endicott-Popovsky, B., McLane, D., “An operational framework for service oriented architecture network security”, Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Proceedings of the 41st Annual, pp. 312–312, 2008.
Lewis, G. A., Morris, E., Simanta, S., et al., “Common Misconceptions about Service-Oriented Architecture”, Commercial-off-the-Shelf (COTS)-Based Software Systems, ICCBSS ‘07, Sixth International IEEE Conference, pp. 123–130, 2007
Millington, D. S., Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Diagnosis.
Pinheiro, M., Oliveira, J. L., Santos, M. A. S., Rocha, H., Cardoso, M. L., Vilarinho, L., “NeoScreen: A software application for MS/MS newborn screening analysis”, in Biological and Medical Data Analysis (ISBMDA'2004), Lecture Notes in Computer Science - Volume 3337, Barcelona, Spain, 2004.
Pinheiro, M., Oliveira, J.L., Santos, M.A.S., Rocha, H., Cardoso, M.L., Vilarinho, L., A computer-based solution for screening of inherited metabolic diseases. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis 27(1), 4 (2004). abstract
Michael, J., Maranda, PhD, Brian Gugerty, DNS, MS, RN. “CISIES: An Informatics Measurement Instrument”. http://cisevaluation.com/
Hurley, A.C., Lancaster, D., Hayes, J., Wilson-Chase, C., Bane, A., Griffin, M., Warden, V., Duffy, M.E., Poon, E.G., Gandhi, T.K., The medication administration system—nurses assessment of satisfaction (MAS—NAS) scale. J. Nurs. Scholarsh. 38, 298–300 (2006). doi:10.1111/j.1547-5069.2006.00117.x
Staggers, N., Kobus, D., Brown, C., Nurses’ Evaluations of a Novel Design for an Electronic Medication Administration Record. Comput. Inform. Nurs. 25, 67–75 (2007). doi:10.1097/01.NCN.0000263981.38801.be
www.google.com/health as of 08/30/2008
Knights, M., “Web 2.0”, Communications Engineer, 5(1), 30–35, 2007.
Schroth, C., Janner, T., “Web 2.0 and SOA: Converging concepts enabling the internet of services”. IT Professional 9(3), 36–41 (2007)
Ping, X.-O., Ko, L.-F., Shang, R.-J., Lai, F., et al., “Dynamic messages creation method for HL7 based healthcare information system”, 9th International Conference on e-Health Networking, Application and Services, June 2007, pp. 150–155.
Hsieh, S.-H., Hsieh, S.-L., et al., “Web services based newborn screening system with support vector machines”, ICITA 2008, June, 2008.
Tu, C. -M., Chang, H. -Y., Tang, M. -Y., Lai, F., et al., “The design and implementation of a next generation information system for newborn Screening”, HEALTHCOM 2007, June, 2007.
Tu, C.-M., The new generation of information system for newborn screening—A case study of National Taiwan University Hospital. Dept. of Computer Science and Information Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taiwan, Master Thesis, June (2007)
Chace, D.H., Kalas, T.A., Naylor, E.W., Use of tandem mass spectrometry for multianalyte screening of dried blood specimens from newborns. Clin. Chem. 49, 1797–1817 (2003). doi:10.1373/clinchem.2003.022178
Expanded Newborn Screening using Tandem Mass Spectrometry Financial, Ethical, Legal and Social Issues (FELSI), http://www.newbornscreening.info.
Michie, D., Spiegelhalter, D. J., Taylor, C. C., Campbell, J., “Machine learning, neural and statistical classification”, 1995.
Cortes, C., Vapnik, V., Support-vector network, 1995.
Ward, J.J., McGuffin, L.J., Buxton, B.F., Jones, D.T., Secondary structure prediction with support vector machine. Bioinformatics 19, 1650–1655 (2003). doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btg223
Chen, P. H., Fan, R. E., Lin, C. J., “A Study on SMO-type Decomposition Methods for Support Vector Machines,” January 2005.
Papazoglou, M.P., van den Heuvel, W.-J., Service-oriented architectures: approaches, technologies and research issues. VLDB J 16(3), 389–415 (2007). doi:10.1007/s00778-007-0044-3
Mike, P., Papazoglou, “Service -Oriented Computing: Concepts, Characteristics and Directions”, Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Web Information Systems Engineering, p. 3, December 10–12, 2003.
Krafzig, D., Banke, K., Slama, D., Enterprise SOA: Service Oriented Architecture Best Practices. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs (2005)
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to acknowledge members of the Pediatrics and Medical Genetics Office, the Information Systems Office at NTUH for their kindly assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsieh, SH., Hsieh, SL., Chien, YH. et al. Newborn Screening Healthcare Information System Based on Service-Oriented Architecture. J Med Syst 34, 519–530 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-009-9265-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-009-9265-x