Abstract
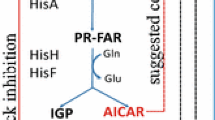
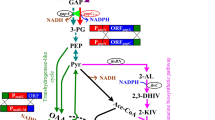
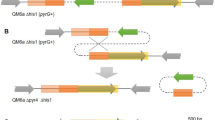
Histidine biosynthesis in Corynebacterium glutamicum is regulated not only by feedback inhibition by the first enzyme in the pathway, but also by repression control of the synthesis of the histidine enzymes. C. glutamicum histidine genes are located and transcribed in two unlinked loci, hisEG and hisDCB-orf1-orf2-hisHA-impA-hisFI. We constructed plasmid pK18hisDPtac to replace the native hisD promoter with the tac promoter, and overexpressed phosphoribosyl-ATP-pyrophosphohydrolase, encoded by hisE, and ATP-phosphoribosyltransferase, encoded by hisG. The l-histidine titer at 0.85 g l−1 was 80 % greater in the transformed bacterium and production of byproducts, l-alanine and l-tryptophan, was significantly decreased. However, accumulation of glutamic acid increased by 58 % (2.8 g l−1). This study represents the first attempt to substitute the histidine biosynthesis pathway promoter in the chromosome with a stronger promoter to increase histidine production.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araki K, Nakayama K (1974) Histidine production by Corynebacterium glutamicum mutants, multiresistant to analogs of histidine, tryptophan, purine and pyrimidine. Agric Biol Chem 38:2209–2218
Bongaerts J, Krämer M, Müller U et al (2001) Metabolic engineering for microbial production of aromatic amino acids and derived compounds. Metab Eng 3:289–300
Cheng LK, Wang J, Xu QY et al (2012) Effect of feeding strategy on l-tryptophan production by recombinant Escherichia coli. Ann Microbiol 62:1625–1634
Fu Y, Luo G, Spellberg BJ et al (2008) Gene overexpression/suppression analysis of candidate virulence factors of Candida albicans. Eukaryot Cell 7:483–492
Grant SG, Jessee J, Bloom FR et al (1990) Differential plasmid rescue from transgenic mouse DNAs into Escherichia coli methylation-restriction mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4645–4649
Jakoby M, Ngoutou-Nkili CE, Burkovski A (1999) Construction and application of new Corynebacterium glutamicum vectors. Biotechnol Tech 13:437–441
Jung S, Chun JY, Yim SH et al (2010) Transcriptional regulation of histidine biosynthesis genes in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Can J Microbiol 56:178–187
Keilhauer C, Eggeling L, Sahm H (1993) Isoleucine synthesis in Corynebacterium glutamicum: molecular analysis of the ilvB-ilvN-ilvC operon. J Bacteriol 175:5595–5603
Lange N, Steinbüchel A (2011) β-Carotene production by Saccharomyces cerevisiae with regard to plasmid stability and culture media. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 91:1611–1622
Liebl W, Bayerl A, Schein B et al (1989) High efficiency electroporation of intact Corynebacterium glutamicum cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett 65:299–303
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression date using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408
Mizukami T, Hamu A, Ikeda M et al (1994) Cloning of the ATP phosphoribosyl transferase gene of Corynebacterium glutamicum and application of the gene to l-histidine production. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58:635–638
Peters-Wendisch PG, Wendisch VF, Paul S et al (1997) Pyruvate carboxylase as an anaplerotic enzyme in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Microbiology 143:1095–1103
Schäfer A, Tauch A, Jäger W et al (1994) Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene 145:69–73
Tauch A, Kirchner O, Löffler B et al (2002) Efficient electrotransformation of Corynebacterium diphtheriae with a mini-replicon derived from the Corynebacterium glutamicum plasmid pGA1. Curr Microbiol 45:362–367
Verde P, Frunzio R, Dinocera PP et al (1981) Identification, nucleotide sequence and expression of the regulatory region of the histidine operon of Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res 9:2075–2086
Vitreschak AG, Lyubetskaya EV, Shirshin MA et al (2004) Attenuation regulation of amino acid biosynthetic operons in proteobacteria: comparative genomics analysis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 234:357–370
Zhang Y, Shang XL, Deng AH et al (2012) Genetic and biochemical characterization of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATP phosphoribosyltransferase and its three mutants resistant to feedback inhibition by histidine. Biochimie 94:829–838
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Tianjin Committee of Science and Technology (Grant No. 12ZCZDSY01900, 12ZXCXSY05900), and by the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in Universities (IRT 1166).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
Supplementary material 2 (DOCX 10 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Supplementary material 4 (DOCX 10 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Supplementary material 6 (DOCX 10 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Y., Zhou, Y., Yang, L. et al. Modification of histidine biosynthesis pathway genes and the impact on production of l-histidine in Corynebacterium glutamicum . Biotechnol Lett 35, 735–741 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1138-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-013-1138-1