Abstract
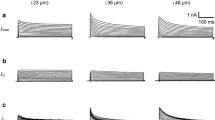
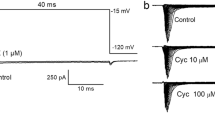
In the nucleus of the tractus solitarii (NTS), a large proportion of neurones express transient A-type potassium currents (I KA) having deep influence on the fidelity of the synaptic transmission of the visceral primary afferent inputs to second-order neurones. Up to now, the strong impact of I KA within the NTS was considered to result exclusively from its variation in amplitude, and its molecular correlate(s) remained unknown. In order to identify which Kv channels underlie I KA in NTS neurones, the gating properties and the pharmacology of this current were determined using whole cell patch clamp recordings in slices. Complementary information was brought by immunohistochemistry. Strikingly, two neurone subpopulations characterized by fast or slow inactivation time courses (respectively about 50 and 200 ms) were discriminated. Both characteristics matched those of the Kv4 channel subfamily. The other gating properties, also matching the Kv4 channel ones, were homogeneous through the NTS. The activation and inactivation occurred at membrane potentials around the threshold for generating action potentials, and the time course of recovery from inactivation was rapid. Pharmacologically, I KA in NTS neurones was found to be resistant to tetraethylammonium (TEA), sea anemone toxin blood-depressing substance (BDS) and dendrotoxin (DTX), whereas Androctonus mauretanicus mauretanicus toxin 3 (AmmTX3), a scorpion toxin of the α-KTX 15 family that has been shown to block all the members of the Kv4 family, inhibited 80 % of I KA irrespectively of its inactivation time course. Finally, immunohistochemistry data suggested that, among the Kv4 channel subfamily, Kv4.3 is the prevalent subunit expressed in the NTS.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amarillo Y, De Santiago-Castillo JA, Dougherty K, Maffie J, Kwon E, Covarrubias M, Rudy B (2008) Ternary Kv4.2 channels recapitulate voltage-dependent inactivation kinetics of A-type K+ channels in cerebellar granule neurons. J Physiol 586:2093–2106. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2007.150540, PMID: 18276729
Amendola J, Woodhouse A, Martin-Eauclaire M-F, Goaillard J-M (2012) Ca2+/cAMP-sensitive covariation of IA and IH voltage dependences tunes rebound firing in dopaminergic neurons. J Neurosci 32:2166–2181. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5297-11.2012, PMID: 22323729
Appleyard SM, Marks D, Kobayashi K, Okano H, Low MJ, Andresen MC (2007) Visceral afferents directly activate catecholamine neurons in the solitary tract nucleus. J Neurosci 27:13292–13302, PMID: 18045923
Bailey TW, Hermes SM, Whittier KL, Aicher SA, Andresen MC (2007) A-type potassium channels differentially tune afferent pathways from rat solitary tract nucleus to caudal ventrolateral medulla or paraventricular hypothalamus. J Physiol 582:613–628, PMID: 17510187
Bailey TW, Jin Y-H, Doyle MW, Andresen MC (2002) Vanilloid-sensitive afferents activate neurons with prominent A-type potassium currents in nucleus tractus solitarius. J Neurosci 22:8230–8237, PMID: 12223577
Balland B, Lachamp P, Strube C, Kessler J-P, Tell F (2006) Glutamatergic synapses in the rat nucleus tractus solitarii develop by direct insertion of calcium-impermeable AMPA receptors and without activation of NMDA receptors. J Physiol 574:245–261, PMID: 16690712
Baude A, Strube C, Tell F, Kessler J-P (2009) Glutamatergic neurotransmission in the nucleus tractus solitarii: structural and functional characteristics. J Chem Neuroanat 38:145–153. doi:10.1016/j.jchemneu.2009.03.004, PMID: 19778680
Belugin S, Mifflin S (2005) Transient voltage-dependent potassium currents are reduced in NTS neurons isolated from renal wrap hypertensive rats. J Neurophysiol 94:3849–3859, PMID: 16293589
Bonham AC, Sekizawa S, Chen C-Y, Joad JP (2006) Plasticity of brainstem mechanisms of cough. Resp Physiol Neur 152:312–319, PMID: 16484366
Brooke RE, Atkinson L, Batten TF, Deuchars SA, Deuchars J (2004) Association of potassium channel Kv3 subunits with pre- and post-synaptic structures in brainstem and spinal cord. Neurosci 126:1001–1010, PMID: 15207333
Brooke RE, Atkinson L, Edwards I, Parson SH, Deuchars J (2006) Immunohistochemical localisation of the voltage gated potassium channel subunit Kv3.3 in the rat medulla oblongata and thoracic spinal cord. Brain Res 1070:101–115, PMID: 16403474
Burkhalter A, Gonchar Y, Mellor RL, Nerbonne JM (2006) Differential expression of IA channel subunits Kv4.2 and Kv4.3 in mouse visual cortical neurons and synapses. J Neurosci 26:12274–12282, PMID: 17122053
Castelfranco AM, Hartline DK (2004) Corrections for space-clamp errors in measured parameters of voltage-dependent conductances in a cylindrical neurite. Biol Cybern 90:280–290, PMID: 15085347
Coetzee WA, Amarillo Y, Chiu J, Chow A, Lau D, McCormack T, Morena H, Nadal MS, Ozaita A, Pountney D, Saganich M, Vega-Saenz de Miera E, Rudy B (1999) Molecular diversity of K+ channels. Ann N Y Acad Sci 868:233–255, PMID: 10414301
Dekin MS, Getting PA (1987) In vitro characterization of neurons in the ventral part of the nucleus tractus solitarius. II. Ionic basis for repetitive firing patterns. J Neurophysiol 58:215–229, PMID: 3612224
Dufour A, Tell F, Baude A (2010) Perinatal development of inhibitory synapses in the nucleus tractus solitarii of the rat. Eur J Neurosci 32:538–549. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07309.x, PMID: 20718854
Hartline DK, Castelfranco AM (2003) Simulations of voltage clamping poorly space-clamped voltage-dependent conductances in a uniform cylindrical neurite. J Comput Neurosci 14:253–269, PMID: 12766427
Hermes SM, Mitchell JL, Aicher SA (2006) Most neurons in the nucleus tractus solitarii do not send collateral projections to multiple autonomic targets in the rat brain. Exp Neurol 198:539–551, PMID: 16487517
Hines ML, Carnevale NT (1997) The NEURON simulation environment. Neural Comput 9:1179–1209, PMID: 9248061
Hoffman DA, Magee JC, Colbert CM, Johnston D (1997) K+ channel regulation of signal propagation in dendrites of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Nature 387:869–875, PMID: 9202119
Holmqvist MH, Cao J, Knoppers MH, Jurman ME, Distefano PS, Rhodes KJ, Xie Y, An WF (2001) Kinetic modulation of Kv4-mediated A-current by arachidonic acid is dependent on potassium channel interacting proteins. J Neurosci 21:4154–4161, PMID: 11404400
Holmqvist MH, Cao J, Hernadez-Pineda R, Jacobson MD, Caroll KI, Sung MA, Betty M, Ge P, Gilbride KJ, Brown ME, Jurman ME, Lawson D, Silos-Santigo I, Xie Y, Covarrubias M, Rhodes KJ, Ps D, An WF (2002) Elimination of fast inactivation in Kv4 A-type potassium channels by an auxiliary subunit domain. PNAS 99:1035–1040, PMID: 9202119
Jerng HH, Kunjilwar K, Pfaffinger PJ (2005) Multiprotein assembly of Kv4.2, KChIP3 and DPP10 produces ternary channel complexes with ISA-like properties. J Physiol 568:767–788, PMID: 16123112
Jerng HH, Lauver AD, Pfaffinger PJ (2007) DPP10 splice variants are localized in distinct neuronal populations and act to differentially regulate the inactivation properties of Kv4-based ion channels. Mol Cell Neurosci 35:604–624, PMID: 17475505
Jerng HH, Pfaffinger PJ (2012) Incorporation of DPP6a and DPP6K variants in ternary Kv4 channel complex reconstitutes properties of A-type K current in rat cerebellar granule cells. Bondarenko VE, ed. PLoS ONE 7:e38205. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0038205. PMID: 22675523
Jerng HH, Pfaffinger PJ, Covarrubias M (2004) Molecular physiology and modulation of somatodendritic A-type potassium channels. Mol Cell Neurosci 27:343–369, PMID: 15555915
Johnston D, Brown TH (1983) Interpretation of voltage-clamp measurements in hippocampal neurons. J Neurophysiol 50:464–486, PMID: 6310063
Kim J, Hoffman DA (2008) Potassium channels: newly found players in synaptic plasticity. Neuroscientist 14:276–286. doi:10.1177/1073858408315041, PMID: 18413784
King MS, Bradley RM (1994) Relationship between structure and function of neurons in the rat rostral nucleus tractus solitarii. J Comp Neurol 344:50–64, PMID: 8063955
Maffie J, Rudy B (2008) Weighing the evidence for a ternary protein complex mediating A-type K + currents in neurons. J Physiol 586:5609–5623. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2008.161620, PMID: 18845608
Maffie JK, Dvoretskova E, Bougis PE, Martin-Eauclaire M-F, Rudy B (2013) Dipeptidyl-peptidase-like-proteins confer high sensitivity to the scorpion toxin AmmTX3 to Kv4-mediated A-type K+ channels. J Physiol 591:2419–2427. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2012.248831, PMID: 23440961
Moak JP, Kunze DL (1993) Potassium currents of neurons isolated from medical nucleus tractus solitarius. Am J Physiol 265:1596–1602, PMID: 7694508
Nakamura TY, Pountney DJ, Ozaita A, Nandi S, Ueda S, Rudy B, Coetzee WA (2001) A role for frequenin, a Ca2+-binding protein, as a regulator of Kv4 K+-currents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:12808–12813, PMID: 11606724
Norris AJ, Nerbonne JM (2010) Molecular dissection of IA in cortical pyramidal neurons reveals three distinct components encoded by Kv4.2, Kv4.3, and Kv1.4 α-subunits. J Neurosci 30:5092–5101. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2010.08.067, PMID: 20813163
Pan Y, Weng J, Kabaleeswaran V, Li H, Cao Y, Bhosle RC, Zhou M (2008) Cortisone dissociates the Shaker family K+ channels from their beta subunits. Nat Chem Biol 4:708–714. doi:10.1038/nchembio.114, PMID: 18806782
Paton JF, Foster WR, Schwaber JS (1993) Characteristic firing behavior of cell types in the cardiorespiratory region of the nucleus tractus solitarii of the rat. Brain Res 604:112–125, PMID: 8457840
Pongs O (1999) Voltage-gated potassium channels: from hyperexcitability to excitement. FEBS Lett 452:31–35, PMID: 10376673
Pongs O, Schwarz JR (2010) Ancillary subunits associated with voltage-dependent K+ channels. Physiol Rev 90:755–796. doi:10.1152/physrev.00020.2009, PMID: 20393197
Rasmusson RL, Morales MJ, Castellino RC, Zhang Y, Campbell DL, Strauss HC (1995) C-type inactivation controls recovery in a fast inactivating cardiac K+ channel (Kv1.4) expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol 489:709–721, PMID: 7890764
Riazanski V, Becker A, Chen J, Sochivko D, Lie A, Wiestler OD, Elger CE, Beck H (2001) Functional and molecular analysis of transient voltage-dependent K+ currents in rat hippocampal granule cells. J Physiol Lond 537:391–406, PMID: 11731573
Rybak IA, Paton JFR, Schwaber JS (1997) Modeling neural mechanisms for genesis of respiratory rhythm and pattern. I. models of respiratory neurons. J Neurophysiol 77:1994–2006, PMID: 9114250
Schaefer AT, Helmstaedter M, Sakmann B, Korngreen A (2003) Correction of conductance measurements in non-space-clamped structures: 1. Voltage-gated K+ channels. Biophys J 84:3508–3528, PMID: 12770864
Schild JH, Khushalani S, Clark JW, Andresen MC, Kunze DL, Yang M (1993) An ionic current model for neurons in the rat medial nucleus tractus solitarii receiving sensory afferent input. J Physiol 469:341–363, PMID: 7505824
Sekizawa S, Joad JP, Pinkerton KE, Bonham AC (2010) Secondhand smoke exposure alters K+ channel function and intrinsic cell excitability in a subset of second-order airway neurons in the nucleus tractus solitarius of young guinea pigs. Eur J Neurosci 31:673–684. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2009.10.009, PMID: 19850058
Serôdio P, Rudy B (1998) Differential expression of Kv4 K+ channel subunits mediating subthreshold transient K+ (A-type) currents in rat brain. J Neurophysiol 79:1081–1091, PMID: 9463463
Shi W, Wymore RS, Wang H-S, Pan Z, Cohen IS, McKinnon D, Dixon JE (1997) Identification of two nervous system-specific members of the erg potassium channel gene family. J Neurosci 17:9423–9432, PMID: 9390998
Sutton GM, Patterson LM, Berthoud H-R (2004) Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signaling pathway in solitary nucleus mediates cholecystokinin-induced suppression of food intake in rats. J Neurosci 24:10240–10247, PMID: 15537896
Suwabe T, Bradley RM (2009) Characteristics of rostral solitary tract nucleus neurons with identified afferent connections that project to the parabrachial nucleus in rats. J Neurophysiol 102:546–555. doi:10.1152/jn.91182.2008, PMID: 19439671
Tell F, Bradley RM (1994) Whole-cell analysis of ionic currents underlying the firing pattern of neurons in the gustatory zone of the nucleus tractus solitarii. J Neurophysiol 71:479–492, PMID: 7513751
Travagli RA, Hermann GE, Browning KN, Rogers RC (2006) Brainstem circuits regulating functions. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 68:279–305, PMID: 16460274
Vacher H, Alami M, Crest M, Possani LD, Bougis PE, Martin-Eauclaire M-F (2002) Expanding the scorpion toxin α-KTX 15 family with AmmTX3 from Androctonus mauretanicus: expanding the scorpion toxin α-KTX 15 family. Eur J Biochem 269:6037–6041, PMID: 12473099
Vacher H, Diochot S, Bougis PE, Martin-Eauclaire M-F, Mourre C (2006) Kv4 channels sensitive to BmTX3 in rat nervous system: autoradiographic analysis of their distribution during brain ontogenesis . Eur J Neurosci 24:1325–1340. PMID: 16987219
Vincent A, Tell F (1997) Postnatal changes in electrophysiological properties of rat nucleus tractus solitarii neurons. Eur J Neurosci 9:1612–1624, PMID: 9283816
Vincent A, Tell D (1999) Postnatal development of rat nucleus tractus solitarius neurons: morphological and electrophysiological evidence. Neuroscience 93:293–305, PMID: 10430493
Wang M, Bradley RM (2010) Properties of GABAergic neurons in the rostral solitary tract nucleus in mice. J Neurophysiol 103:3205–3218. doi:10.1152/jn.00971.2009, PMID: 20375246
Yeung SY, Thompson D, Wang Z, Fedida D, Robertson B (2005) Modulation of Kv3 subfamily potassium currents by the sea anemone toxin BDS: significance for CNS and biophysical studies. J Neurosci 25:8735–8745, PMID: 16177043
Zagha E, Ozaita A, Chang SY, Nadal MS, Lin U, Saganich MJ, McCornmack T, Akinsanya KO, Qi SY, Rudy B (2005) DPP10 modulates Kv4-mediated A-type potassium channels. J Biol Chem 280:18853–18861, PMID: 15671030
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS), Aix Marseille Université (AMU), Agence De l’Environnement et de la Maîtrise de l‘Energie and Région Provence-Alpes-Côte d’Azur (ADEME/Région PACA, fellowship to LS).
We are grateful to Jean-Pierre Kessler for performing immunohistochemical experiments. We also thank Dr. Brigitte Céard for her technical assistance in the production of the toxin AmmTX3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strube, C., Saliba, L., Moubarak, E. et al. Kv4 channels underlie A-currents with highly variable inactivation time courses but homogeneous other gating properties in the nucleus tractus solitarii. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 467, 789–803 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-014-1533-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-014-1533-z