Abstract
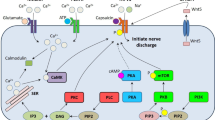
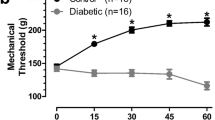
Pain-sensing sensory neurons (nociceptors) of the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) can become sensitized (hyperexcitable) in response to pathological conditions such as diabetes, which in turn may lead to the development of painful peripheral diabetic neuropathy (PDN). Because of insufficient knowledge about the mechanisms for this hypersensitization, current treatment for painful PDN has been limited to somewhat nonspecific systemic drugs having significant side effects or potential for abuse. Recent studies have established that the CaV3.2 isoform of T-channels makes a previously unrecognized contribution to sensitization of pain responses by enhancing excitability of nociceptors in animal models of type 1 and type 2 PDN. Furthermore, it has been reported that the glycosylation inhibitor neuraminidase can inhibit the native and recombinant CaV3.2 T-currents in vitro and completely reverse mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia in diabetic animals with PDN in vivo. Understanding details of posttranslational regulation of nociceptive channel activity via glycosylation may facilitate development of novel therapies for treatment of painful PDN. Pharmacological targeting the specific pathogenic mechanism rather than the channel per se may cause fewer side effects and reduce the potential for drug abuse in patients with diabetes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calcutt NA (2013) Location, location, location? Is the pain of diabetic neuropathy generated by hyperactive sensory neurons? Diabetes 62:3658–3660
Cao XH, Byun HS, Chen SR, Pan HL (2011) Diabetic neuropathy enhances voltage-activated Ca2+ channel activity and its control by M4 muscarinic receptors in primary sensory neurons. J Neurochem 119(3):594–603
Carbone E, Lux HD (1984) A low-voltage activated, fully inactivating Ca2+ channel in vertebrate sensory neurons. Nature 310:501–502
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2011) National diabetes fact sheet: national estimates and general information on diabetes and prediabetes in the United States. 2011 ed, Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, Center for Disease Control and Prevention. http://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/pdf/ndfs_2011.pdf
Cohen DM (2006) Regulation of TRP channels by N-linked glycosylation. Semin Cell Dev Biol 17(6):630–637
Dubreuil AS, Boukhaddaoui H, Desmadryl G, Martinez-Salgado C, Moshourab R, Lewin GR, Carroll P, Valmier J, Scamps F (2004) Role of T-type calcium current in identified d-hair mechanoreceptor neurons studied in vitro. J Neurosci 24:8480–8484
Edwards JL, Vincent AM, Cheng HT, Feldman EL (2008) Diabetic neuropathy: mechanisms to management. Pharmacol Ther 120:1–34
Gooch C, Podwall D (2004) The diabetic neuropathies. Neurologist 10:311–322
Gordois A, Scuffham P, Shearer A, Oglesby A, Tobian JA (2003) The health care cost of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in the US. Diabetes Care 26(6):1790–1795
Hall KE, Sima AA, Wiley JW (1995) Voltage-dependent calcium currents are enhanced in dorsal root ganglion neurones from the Bio Bred/Worchester diabetic rat. J Physiol (London) 486(Pt 2):313–322
Hong S, Wiley JW (2005) Early painful diabetic neuropathy is associated with differential changes in the expression and function of vanilloid receptor 1. J Biol Chem 280(1):618–627
Jack M, Wright D (2012) Role of advanced glycation end products and glyoxalase I in diabetic peripheral sensory neuropathy. Transl Res 159(5):355–365
Jacus MO, Uebele VN, Renger JJ, Todorovic SM (2012) Presynaptic CaV3.2 channels regulate excitatory neurotransmission in nociceptive dorsal horn neurons. J Neurosci 32(27):9374–9382
Jagodic MM, Pathirathna S, Nelson MT, Mancuso S, Joksovic PM, Rosenberg ER, Bayliss DA, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Todorovic SM (2007) Cell-specific alterations of T-type calcium current in painful diabetic neuropathy enhance excitability of sensory neurons. J Neurosci 27(12):3305–3316
Khomula EV, Viatchenko-Karpinski VY, Borisyuk AL, Duzhyy DE, Belan PV, Voitenko NV (2013) Specific functioning of Cav3.2 T-type calcium and TRPV1 channels under different types of STZ-diabetic neuropathy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832(5):636–649
Latham JR, Pathirathna S, Jagodic MM, Choe WJ, Levin ME, Nelson MT, Lee WY, Krishnan K, Covey D, Todorovic SM, Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2009) Selective T-type calcium channel blockade alleviates hyperalgesia in ob/ob mice. Diabetes 58(11):2656–2665
Messinger RB, Naik AK, Jagodic MM, Nelson MT, Lee WY, Choe WJ, Orestes P, Latham JR, Todorovic SM, Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2009) In vivo silencing of the Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels in sensory neurons alleviates hyperalgesia in rats with streptozocin-induced diabetic neuropathy. Pain 145(1–2):184–195
Moremen KW, Tiemeyer M, Naim AV (2012) Vertebrate protein glycosylation: diversity, synthesis, and function. Nat Rev 13:448–462
Nelson MT, Joksovic PM, Perez-Reyes E, Todorovic SM (2005) The endogenous redox agent L-cysteine induces T-type Ca2+ channel-dependent sensitization of a novel subpopulation of rat peripheral nociceptors. J Neurosci 25:8766–8775
Nelson MT, Woo J, Kang H-W, Barrett PQ, Vitko J, Perez-Reyes E, Lee J-H, Shin H-S, Todorovic SM (2007) Reducing agents sensitize C-type nociceptors by relieving high-affinity zinc inhibition of T-type calcium channels. J Neurosci 27(31):8250–8260
Obrosova IG (2009) Diabetic painful and insensate neuropathy: pathogenesis and potential treatments. Neurotherapeutics 6(4):638–647
Orestes P, Osuru HP, McIntire WE, Jacus MO, Salajegheh R, Jagodic MM, Choe W, Lee J, Lee SS, Rose KE, Poiro N, Digruccio MR, Krishnan K, Covey DF, Lee JH, Barrett PQ, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Todorovic SM (2013) Reversal of neuropathic pain by targeting glycosylation of CaV3.2 T-type calcium channels. Diabetes 62:3828–3838
Pabbidi RM, Cao DS, Parihar A, Pauza ME, Premkumar LS (2008) Direct role of streptozotocin in inducing thermal hyperalgesia by enhanced expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 in sensory neurons. Mol Pharmacol 73(3):995–1004
Pabbidi RM, Yu SQ, Peng S, Khardori R, Pauza ME, Premkumar LS (2008) Influence of TRPV1 on diabetes-induced alterations in thermal pain sensitivity. Mol Pain 1(4):9
Pertusa M, Madrid R, Morenilla-Palao C, Belmonte C, Viana F (2012) N-glycosylation of TRPM8 ion channels modulates temperature sensitivity of cold thermoreceptor neurons. J Biol Chem 287(22):18218–18229
Shankarappa SA, Piedras-Rentería ES, Stubbs EB Jr (2011) Forced-exercise delays neuropathic pain in experimental diabetes: effects on voltage-activated calcium channels. J Neurochem 118(2):224–236
Shin JB, Martinez-Salgado C, Heppenstall PA, Lewin GR (2003) A T-type calcium channel required for normal function of a mammalian mechanoreceptor. Nat Neurosci 6(7):724–730
Talley EM, Cribbs LL, Lee JH, Daud A, Perez-Reyes E, Bayliss DA (1999) Differential distribution of three members of a gene family encoding low voltage-activated (T-type) calcium channels. J Neurosci 19:1895–1911
Todorovic SM, Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2011) T-type voltage-gated calcium channels as targets for development of novel pain therapies. Br J Pharmacol 163(3):484–495
Veves A, Backonja M, Malik RA (2007) Painful diabetic neuropathy: epidemiology, natural history, early diagnosis, and treatment options. Pain Med 9:660–674
Weis N, Black SAG, Bladen C, Chen L, Zamponi GW (2013) Surface expression and function of CaV3.2 T-type calcium channels are controlled by asparagines-linked glycosylation. Pflugers Arch-Euro J Physiol 465(8):1159–1170
White G, Lovinger DM, Weight FF (1989) Transient low-threshold Ca2+ current triggers burst firing through an afterdepolarizing potential in an adult mammalian neuron. PNAS USA 86:6802–6806
Woolf CJ (2011) Central sensitization: implications for the diagnosis and treatment of pain. Pain 152(3 Suppl):S2–S15
Acknowledgments
Our research is supported by the American Diabetes Association National Award for Basic Research 7-09-BS-190 (to S.M.T.), Dr. Harold Carron Endowment fund (to V.J-T.), and research funds from the Department of Anesthesiology at the University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Todorovic, S.M., Jevtovic-Todorovic, V. Targeting of CaV3.2 T-type calcium channels in peripheral sensory neurons for the treatment of painful diabetic neuropathy. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 466, 701–706 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-014-1452-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-014-1452-z