Abstract
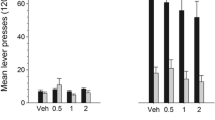
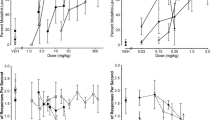
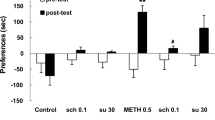
Rationale: Recent data suggest that dopamine (DA) D1-like receptor full agonists may be potential pharmacotherapeutic agents for treating cocaine abuse. The structurally novel isochroman D1-like agonist, A-77636, has not been well characterized and may prove to be useful as such an agent. Objectives: The interactions of cocaine and A-77636 were compared to those obtained with the better investigated benzazepine D1-like dopamine agonists, SKF 82958 and SKF 81297. The alterations in the locomotor stimulant and discriminative-stimulus effects of cocaine by the full D1-like dopamine receptor agonists were investigated across a full range of doses in order to characterize their interactions. Methods: Drug-naive Swiss-Webster mice were pretreated with SKF 81297, SKF 82958 or A-77636 (1–10 mg/kg) and cocaine (5–56 mg/kg) prior to a 30-min period in which locomotor activity was assessed. Rats were trained on a fixed ratio 20 (FR20) schedule to discriminate IP saline from cocaine (10 mg/kg) injections. Cocaine alone (1–10 mg/kg) and with either A-77636 (0.56–1.7 mg/kg), SKF 82958 (0.01–0.1 mg/kg) or SKF 81297 (0.1–0.56) were injected IP 5 min prior to a 15-min test session. Results: Cocaine maximally stimulated activity at 20–40 mg/kg with higher and lower doses stimulating activity less. Each D1-like agonist produced a dose-related decrease in cocaine-induced locomotor activity and lowered its maximal rate. Each of the D1-like agonists partially substituted for cocaine, with maximal substitution approximating 49, 35, and 24% for SKF 81297, SKF 82958, and A-77636, respectively. SKF 82958 significantly shifted the cocaine dose-effect curve approximately 3-fold to the left. With SKF 81297, there was a trend towards a leftward shift of cocaine dose effects, however the change was not statistically significant. In contrast to the other two D1-like agonists, A-77636 either did not affect the cocaine dose-effect curve or shifted it to the right. Conclusions: All three agonists produced similar effects on cocaine-induced locomotor activity, however the discriminative-stimulus effects of cocaine were affected differently by the D1 agonists. These results suggest fundamental differences in the actions of these D1 agonists. Because A-77636 consistently attenuated the present effects of cocaine, it may prove more useful than the others as a pharmacotherapy to treat cocaine abuse.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chausmer, A.L., Katz, J.L. Comparison of interactions of D1-like agonists, SKF 81297, SKF 82958 and A-77636, with cocaine: locomotor activity and drug discrimination studies in rodents. Psychopharmacology 159, 145–153 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100896
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100896