Abstract
Topology optimization has undergone a tremendous development since its introduction in the seminal paper by Bendsøe and Kikuchi in 1988. By now, the concept is developing in many different directions, including “density”, “level set”, “topological derivative”, “phase field”, “evolutionary” and several others. The paper gives an overview, comparison and critical review of the different approaches, their strengths, weaknesses, similarities and dissimilarities and suggests guidelines for future research.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Although the discretized optimization problem (2) is a solid-void optimization problem it is for computational reasons common to treat it as a “solid-almost void” problem, meaning that void is mimicked by a very soft material, hence avoiding to have to remesh or renumber the finite element mesh in between iterations. Hence throughout the paper, unless otherwise noted, \(\rho =0\) must be read as \(\rho =\rho _{min}\), where \(\rho _{min}\) is a small number.
Actually, topology optimization approaches often work best with active volume constraints. Depending on the physical problem considered, superfluous material may create non-physical effects or may obstruct the free movement of structural boundaries in turn restricting convergence to (near)global minima.
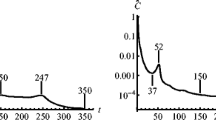
The compliance increases until the volume fraction has been reached and decreases after. Hence, if the average energy before and after feasibility becomes equal the algorithm terminates prematurely.
These problems can partially be avoided by performing the optimization on consecutively refined meshes, however, for many physical problems that are more complex than simple compliance minimization (c.f. wave propagation problems as e.g. reviewed in Jensen andSigmund 2011) and electrostatic actuators (Qian and Sigmund 2012) this is not a viable approach.
Note that without filtering the boundaries will not move and hence the design cannot move away from the solid bar starting guess.
References
Aage N, Sigmund O (2013) Density interpolations for electromagnetic topology optimization schemes. in preparation
Aage N, Nobel-Jørgensen M, Andreasen C, Sigmund O (2013) Interactive topology optimization on hand-held devices. Struct Multidiscip Optim 47:1–6. doi:10.1007/s00158-012-0827-z
Allaire G, Francfort GA (1993) A numerical algorithm for topology and shape optimization. In: Bendsøe MP, Soares Mota CA (eds) Topology optimization of structures. Kluwer, Boston, pp 239–248
Allaire G, Kohn RV (1993) Topology optimization and optimal shape design using homogenization. In: Bendsøe MP, Soares Mota CA (eds) Topology design of structures. Kluwer, Boston, pp 207–218
Allaire G, Jouve F (2008) Minimum stress optimal design with the level set method. Eng AnalBound Elemen 32(11):909–918. doi:10.1016/j.enganabound.2007.05.007
Allaire G, Jouve F, Toader AM (2002) A level-set method for shape optimization. C R Math 334(12):1125–1130. doi:10.1016/S1631-073X(02)02412-3
Allaire G, Jouve F, Toader AM (2004) Structural optimization using sensitivity analysis and a level-set method. J Comput Phys 194(1):363–393
Allaire G, de Gournay F, Jouve F, Toader A (2005) Structural optimization using topological and shape sensitivity via a level set method. Control Cybern 34(1):59–80
Ambrosio L, Buttazzo G (1993) An optimal design problem with perimeter penalization. Calc Var 1:55–69
Amstutz S (2011) Connections between topological sensitivity analysis and material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43(6):755–765. doi:10.1007/s00158-010-0607-6
Amstutz S, Novotny A (2010) Topological optimization of structures subject to von mises stress constraints. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41:407–420. doi:10.1007/s00158-009-0425-x
Andreassen E, Clausen A, Schevenels M, Lazarov B, Sigmund O (2011) Efficient topology optimization in matlab using 88 lines of code. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43:1–16. doi:10.1007/s00158-010-0594-7. MATLAB code available online at: www.topopt.dtu.dk
Ansola R, Vegueria E, Canales J, Tarrago J (2007) A simple evolutionary topology optimization procedure for compliant mechanism design. Finite Elem Anal Des 44(1–2):53–62. doi:10.1016/j.finel.2007.09.002
Ansola R, Vegueria E, Canales J (2010) 3d compliant mechanisms synthesis by a finite element addition procedure. Finite Elem Anal Des 46(9):760–769. doi:10.1016/j.finel.2010.04.006
Arnout S, Firl M, Bletzinger KU (2012) Parameter free shape and thickness optimisation considering stress response. Struct Multidiscip Optim 45:801–814. doi:10.1007/s00158-011-0742-8
Beckers M (1999) Topology optimization using a dual method with discrete variables. Struct Optim 17(1):14–24
Beckers M (2000) Dual methods for discrete structural optimization problems. Int J Numer Meth Eng 48:1761–1784
Bendsøe MP (1989) Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct Optim 1:193–202
Bendsøe MP, Kikuchi N (1988) Generating optimal topologies in structural design using a homogenization method. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 71(2):197–224
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (1999) Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Arch Appl Mech 69(9–10):635–654
Bendsøe MP, Sigmund O (2004) Topology optimization-theory, methods and applications. Springer, Berlin
Bendsøe MP, Díaz AR, Kikuchi N (1993) Topology and generalized layout optimization of elastic structures. In: Bendsøe MP, Soares Mota CA (eds) Topology design of structures. Kluwer, Boston, pp 159–206
Bendsøe MP, Guedes JM, Haber RB, Pedersen P, Taylor JE (1994) An analytical model to predict optimal material properties in the context of optimal structural design. Trans ASME J Appl Mech 61(4):930–937
Bletzinger KU, Maute K (1997) Towards generalized shape and topology optimization. Eng Optim 29(1–4):201–216
Bonnet M, Guzina B (2004) Sounding of finite solid bodies by way of topological derivative. Int J Numer Methods Eng 61(13):2344–2373
Borrvall T (2001) Topology optimization of elastic continua using restriction. Arch Comput Methods Eng 8(4):351– 385
Borrvall T, Petersson J (2001) Topology optimization using regularized intermediate density control. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190:4911–4928
Borrvall T, Petersson J (2003) Topology optimization of fluids in stokes flow. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 41:77–107. doi:10.1002/fld.426
Bourdin B (2001) Filters in topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 50(9):2143–2158
Bourdin B, Chambolle A (2003) Design-dependent loads in topology optimization. ESAIM Control Optim Calc Var 9:19–48
Bruns TE, Tortorelli DA (2001) Topology optimization of non-linear elastic structures and compliant mechanisms. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190(26–27):3443–3459
Burger M, Osher S (2005) A survey in mathematics for industry—a survey on level set methods for inverse problems and optimal design. Eur J Appl Math 16:263–301. doi:10.1017/S0956792505006182
Burger M, Stainko R (2006) Phase-field relaxation of topology optimization with local stress constraints. SIAM J Control Optim 45(4):1447–1466. doi:10.1137/05062723X
Burger M, Hackl B, Ring W (2004) Incorporating topological derivatives into level set methods. J Comput Phys 194(1):344–362. doi:10.1016/j.jcp.2003.09.033
Cea J, Garreau S, Guillaume P, Masmoudi M (2000) The shape and topological optimizations connection. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 188:713–726
Challis V, Guest J (2009) Level set topology optimization of fluids in Stokes flow. Int J Numer Methods Eng 79(10):1284–1308. doi:10.1002/nme.2616
Challis V, Roberts A, Wilkins A (2008) Design of three dimensional isotropic microstructures for maximized stiffness and conductivity. Int J Solids Struct 45(14–15):4130–4146. doi:10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2008.02.025
Challis VJ (2010) A discrete level-set topology optimization code written in matlab. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41(3):453–464. doi:10.1007/s00158-009-0430-0
Chen B, Kikuchi N (2001) Topolgy optimization with design-dependent loads. Finite Elem Anal Des 37:57–70
Chen S, Chen W (2011) A new level-set based approach to shape and topology optimization under geometric uncertainty. Struct Multidiscip Optim 44(1):1–18. doi:10.1007/s00158-011-0660-9
Cheng GD, Guo X (1997) 𝜖-relaxed approach in topology optimization. Struct Optim 13:258–266
Cheng GD, Jiang Z (1992) Study on topology optimization with stress constraints. Eng Optim 20:129–148
Cho S, Ha SH (2009) Isogeometric shape design optimization: exact geometry and enhanced sensitivity. Struct Multidiscip Optim 38:53–70. doi:10.1007/s00158-008-0266-z
Christiansen A, Nobel-Jørgensen M, Aage N, Sigmund O, Bærentzen J (2013) Topology optimization using an explicit interface representation. in preparation
de Ruiter M, van Keulen F (2004) Topology optimization using a topology description function. Struct Multidiscip Optim 26(6):406–416. doi:10.1007/s00158-003-0375-7
Deaton J, Grandhi R (2013) A survey of structural and multidisciplinary continuum topology optimization: post 2000. Struct Multidiscip Optim 1–38. doi:10.1007/s00158-013-0956-z
Díaz AR, Sigmund O (1995) Checkerboard patterns in layout optimization. Struct Optim 10(1):40–45
Du J, Olhoff N (2004a) Topological optimization of continuum structures with design-dependent surface loading-Part I: new computational approach for 2D problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 27:151–165
Du J, Olhoff N (2004b) Topological optimization of continuum structures with design-dependent surface loading—Part II: algorithm and examples for 3D problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 27:166–177
Dühring MB, Sigmund O, Feurer T (2010) Design of photonic-bandgap fibers by topology optimization. J Opt Soc Am B 27:51–58
Duysinx P, Bendsøe MP (1998) Topology optimization of continuum structures with local stress coinstraints. Int J Numer Methods Eng 43(8):1453–1478
Duysinx P, Sigmund O (1998) New developments in handling stress constraints in optimal material distributions. In: 7th symposium on multidiciplinary analysis and optimization, AIAA/USAF/NASA/ISSMO, AIAA-98-4906, pp 1501–1509
Erentok A, Sigmund O (2011) Topology optimization of sub-wavelength antennas. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 59(1):58–69. doi:10.1109/TAP.2010.2090451
Eringen A (1983) On differential equations of nonlocal elasticity and solutions of screw dislocation and surface waves. J Appl Phys 54:4703. doi:10.1063/1.332803
Eschenauer HA, Kobelev VV, Schumacher A (1994) Bubble method for topology and shape optimization of structures. Struct Optim 8:42–51
FE-Design (2011) Tosca structure manual. FE-Design GMBH, version 7.1 edn., www.fe-design.com
Fuchs MB, Shemesh NNY (2004) Density-based topological design of structures subjected to water pressure using a parametric loading surface. Struct Multidiscip Optim 28(1):11–19
Gersborg-Hansen A, Sigmund O, Haber RB (2005) Topology optimization of channel flow problems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 30(3):181–192. doi:10.1007/s00158-004-0508-7
Gill P, Murray W, Saunders MA (2005) SNOPT: an SQP algorithm for large-scale constrained optimization. SIAM Rev 47(1):99–131
Gomes A, Suleman A (2006) Application of spectral level set methodology in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 31(6):430–443. doi:10.1007/s00158-006-0005-2
Guest J (2009a) Imposing maximum length scale in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 37(5):463–473. doi:10.1007/s00158-008-0250-7
Guest J (2009b) Topology optimization with multiple phase projection. Comput Method Appl Mech Eng 199(1–4):123–135. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2009.09.023
Guest J, Prevost J, Belytschko T (2004) Achieving minimum length scale in topology optimization using nodal design variables and projection functions. Int J Numer Methods Eng 61(2):238–254
Guest J, Asadpoure A, Ha SH (2011) Eliminating beta-continuation from heaviside projection and density filter algorithms. Struct Multidiscip Optim 44(4):443–453. doi:10.1007/s00158-011-0676-1
Guo X, Zhang W, Zhang L (2013) Robust structural topology optimization considering boundary uncertainties. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 253:356–368. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2012.09.005
Haber RB, Bendsøe MP, Jog CS (1996) Perimeter constrained topology optimization of continuum structures. In: IUTAM symposium on optimization of mechanical systems (Stuttgart, 1995). Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 113–120
Hammer VB, Olhoff N (2000) Topology optimization of continuum structures subjected to pressure loading. Struct Multidiscip Optim 19:85–92
Huang X, Xie YM (2010a) A further review of ESO type methods for topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41:671–683. doi:10.1007/s00158-010-0487-9
Huang Y, Xie YM (2010b) Evolutionary topology optimization of geometrically and materially nonlinear structures under prescribed design load. Struct Eng Mech 34(5):581–595
Jansen M, Lazarov B, Schevenels M, Sigmund O (2013) On the similarities between micro/nano lithography and topology optimization projection methods. Struct Multidiscip Optim 1–14. doi:10.1007/s00158-013-0941-6
Jensen JS, Sigmund O (2005) Topology optimization of photonic crystal structures: a high-bandwidth low-loss T-junction waveguide. J Opt Soc Am B 22(6):1191–1198
Jensen JS, Sigmund O (2011) Topology optimization for nano-photonics. Laser Photonics Rev 5(2):308–321. doi:10.1002/lpor.201000014
Jog CS, Haber RB (1996) Stability of finite element models for distributed-parameter optimization and topology design. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 130(3–4):203–226
Kawamoto A, Matsumori T, Yamasaki S, Nomura T, Kondoh T, Nishiwaki S (2011) Heaviside projection based topology optimization by a PDE-filtered scalar function. Struct Multidiscip Optim:1–6. doi:10.1007/s00158-010-0562-2
Kawamoto A, Matsumori T, Yamasaki S, Nomura T, Kondoh T, Yamasaki S, Nishiwaki S (2013) Topology optimization by a time-dependent diffusion equation. Int J Numer Methods Eng 93(8):795–817. doi:10.1002/nme.4407
Kim DH, Lee SB, Kwak BM, Kim HG, Lowther D (2008) Smooth boundary topology optimization for electrostatic problems through the combination of shape and topological design sensitivities. IEEE Trans Magn 44(6):1002–1005
Kita E, Toyoda T (2000) Structural design using cellular automata. Struct Multidiscip Optim 19(1):64–73
Klarbring A, Torstenfelt B (2010) Dynamical systems and topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 42(2):179–192. doi:10.1007/s00158-010-0479-9
Kocvara M, Stingl M, Zowe J (2008) Free material optimization: recent progress. Optimization 57(1):79–100. doi:10.1080/02331930701778908
Kreissl S, Maute K (2012) Levelset based fluid topology optimization using the extended finite element method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 3:311–326. doi:10.1007/s00158-012-0782-8
Kreissl S, Pingen G, Evgrafov A, Maute K (2010) Topology optimization of flexible micro-fluidic devices. Struct Multidiscip Optim 42(4):495–516
Lazarov B, Sigmund O (2011) Filters in topology optimization as a solution to Helmholtz type differential equation. Int J Numer Methods Eng 86(6):765–781. doi:10.1002/nme.3072
Lazarov B, Schevenels M, Sigmund O (2012a) Topology optimization considering material and geometric uncertainties using sparse grid stochastic collocation method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 46:597–612. doi:10.1007/s00158-012-0791-7
Lazarov B, Schevenels M, Sigmund O (2012b) Topology optimization with geometric uncertainties by perturbation techniques. Int J Numer Methods Eng 90(11):1321–1336. doi:10.1002/nme.3361
Le C, Norato J, Bruns T, Ha C, Tortorelli D (2010) Stress-based topology optimization for continua. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41:605–620. doi:10.1007/s00158-009-0440-y
Le C, Bruns T, Tortorelli D (2011) A gradient-based, parameter-free approach to shape optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 200(9–12):985–996. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2010.10.004
Liu Z, Korvink JG, Huang R (2005) Structure topology optimization: fully coupled level set method via FEMLAB. Struct Multidiscip Optim 29(6):407–417
Luo Z, Tong L, Wang M, Wang S (2007) Shape and topology optimization of compliant mechanisms using a parameterization level set method. J Comput Phys 227(1):680–705. doi:10.1016/j.jcp.2007.08.011
Luo J, Luo Z, Chen S, Tong L, Wang MY (2008a) A new level set method for systematic design of hinge-free compliant mechanisms. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 198(2):318–331
Luo Z, Wang M, Wang S, Wei P (2008b) A level set-based parameterization method for structural shape and topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 76(1):1–26. doi:10.1002/nme.2092
Luo Y, Wang M, Kang Z (2013) An enhanced aggregation method for topology optimization with local stress constraints. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 254:31–41. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2012.10.019
Mattheck C, Burkhardt S (1990) A new method of structural shape optimization based on biological growth. Int J Fatigue 12(3):185–190
Maute K, Ramm E (1995) General shape optimizationan integrated model for topology and shape optimization. In: Olhoff N, Rozvany G (eds) Proceedings of the first world congress of structural and multidisciplinary optimization. Pergamon, Oxford, pp 299–306
Maute K, Kreissl S, Makhija D, Yang R (2011) Topology optimization of heat conduction in nanocomposites. In: 9th world congress on structural and multidisciplinary optimization. Shizuoka, Japan
Mei Y (2004) A level set method for structural topology optimization and its applications. Adv Eng Softw 35(7):415–441. doi:10.1016/j.advengsoft.2004.06.004
Michell AGM (1904) The limit of economy of material in frame structures. Philos Mag 8(6):589–597
Missoum S, Gurdal Z, Setoodeh S (2005) Study of a new local update scheme for cellular automata in structural design. Struct Multidiscip Optim 29(2):103–112. doi:10.1007/s00158-004-0464-2
Misztal M, Bærentzen J (2012) Topology adaptive interface tracking using the deformable simplicial complex. ACM Trans Graph 31(3):24:1–24:12. doi:10.1145/2167076.2167082
Mlejnek HP (1992) Some aspects of the genesis of structures. Struct Optim 5:64–69
Niordson FI (1983) Optimal design of plates with a constraint on the slope of the thickness function. Int J Solids Struct 19:141–151
Norato J, Haber R, Tortorelli D, Bendsoe M (2004) A geometry projection method for shape optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 60(14):2289–2312
Norato J, Bendsøe M, Haber R, Tortorelli D (2007) A topological derivative method for topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 33:375–386. doi:10.1007/s00158-007-0094-6
Novotny A, Feijoo R, Taroco E, Padra C (2003) Topological sensitivity analysis. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192(7–8):803–829. doi:10.1016/S0045-7825(02)00599-6
Novotny A, Feijoo R, Taroco E, Padra C (2007) Topological sensitivity analysis for three-dimensional linear elasticity problem. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 196(41):4354–4364
Olhoff N, Bendsøe MP, Rasmussen J (1992) On CAD-integrated structural topology and design optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 89:259–279
Olsson E, Kreiss G (2005) A conservative level set method for two phase flow. J Comput Phys 210(1):225–246. doi:10.1016/j.jcp.2005.04.007
Olsson E, Kreiss G, Zahedi S (2007) A conservative level set method for two phase flow ii. J Comput Phys 225(1):785–807. doi:10.1016/j.jcp.2006.12.027
Osher S, Fedkiw R (2003) Level set methods and dynamic implicit surfaces. Springer, New York
Osher S, Sethian J (1988) Fronts propagating with curvature-dependent speed-algorithms based on hamilton-jacobi formulations. J Comput Phys 79(1):12–49
Otomori M, Yamada T, Izui K, Nishiwaki S (2011) Level set-based topology optimisation of a compliant mechanism design using mathematical programming. Mech Sci 2(1):91–98
Papalambros PY, Chirehdast M (1993) Integrated structural optimization system. In: Bendsøe MP, Mota Soares CA (eds) Topology design of structures. Kluwer, Boston, pp 501–514
Pedersen CBW, Buhl T, Sigmund O (2001) Topology synthesis of large-displacement compliant mechanisms. Int J Numer Methods Eng 50(12):2683–2705
Pedersen NL (2000) Maximization of eigenvalues using topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 20(1):2–11
Petersson J (1999) A finite element analysis of optimal variable thickness sheets. SIAM J Num Anal 36:1759–1778
Petersson J, Sigmund O (1998) Slope constrained topology optimization. IInt J Numer Methods Eng 41(8):1417–1434
Pingen G, Waidmann M, Evgrafov A, Maute K (2010) A parametric level-set approach for topology optimization of flow domains. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41:117–131
Qian X, Sigmund O (2012) Topological design of electromechanical actuators with robustness toward over-and under-etching. Comput Method Appl Mech Eng 253:237–251
Raulli M, Maute K (2005) Topology optimization of electrostatically actuated microsystems. Struct Multidiscip Optim 30(5):342–359
Rozvany G (2009) A critical review of established methods of structural topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 37:217–237. doi:10.1007/s00158-007-0217-0
Rozvany G, Sobieszczanski-Sobieski J (1992) New optimality criteria methods: forcing uniqueness of the adjoint strains by corner-rounding at constraint intersections. Struct Optim 4:244–246. doi:10.1007/BF01742752
Ru C, Aifantis E (1993) A simple approach to solve boundary-value problems in gradient elasticity. Acta Mech 101:59–68. doi:10.1007/BF01175597
Schevenels M, Lazarov B, Sigmund O (2011) Robust topology optimization accounting for spatially varying manufacturing errors. Comput Method Appl Mech Eng 200(49–52):3613–3627. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2011.08.006
Schury F, Stingl M, Wein F (2012) Slope constrained material design. Struct Multidiscip Optim 46:813–827. doi:10.1007/s00158-012-0795-3
Seo YD, Kim HJ, Youn SK (2010) Isogeometric topology optimization using trimmed spline surfaces. Comput Method Appl Mech Eng 199(49–52):3270–3296. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2010.06.033
Sethian JA (1999) Level set methods and fast marching methods. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sethian JA, Wiegmann A (2000) Structural boundary design via level set and immersed interface methods. J Comput Phys 163(2):489–528
Sigmund O (1997) On the design of compliant mechanisms using topology optimization. Mech Struct Mach 25(4):493–524
Sigmund O (2001a) A 99 line topology optimization code written in MATLAB. Struct Multidiscip Optim 21:120–127. doi:10.1007/s001580050176. MATLAB code available online at: www.topopt.dtu.dk
Sigmund O (2001b) Design of multiphysics actuators using topology optimization-part II: two-material structures. Comput Method Appl Mech Eng 190(49–50):6605–6627. doi:10.1016/S0045-7825(01)00252-3
Sigmund O (2007) Morphology-based black and white filters for topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 33(4–5):401–424
Sigmund O (2009) Manufacturing tolerant topology optimization. Acta Mech Sinica 25(2):227–239. doi:10.1007/s10409-009-0240-z
Sigmund O (2011) On the usefulness of non-gradient approaches in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43(5):589–596. doi:10.1007/s00158-011-0638-7
Sigmund O, Clausen P (2007) Topology optimization using a mixed formulation: an alternative way to solve pressure load problems. Comput Method Appl Mech Eng 196(13–16):1874–1889
Sigmund O, Maute K (2012) Sensitivity filtering from a continuum mechanics perspective. Struct Multidiscip Optim 46(4):471–475. doi:10.1007/s00158-012-0814-4
Sigmund O, Petersson J (1998) Numerical instabilities in topology optimization: a survey on procedures dealing with checkerboards, mesh-dependencies and local minima. Struct Optim 16(1):68–75
Sigmund O, Torquato S (1997) Design of materials with extreme thermal expansion using a three-phase topology optimization method. J Mech Phys Solids 45(6):1037–1067
Sokołowski J, Zochowski A (1999) On the topological derivative in shape optimization. SIAM J Control Opt 37:1251–1272
Stolpe M, Bendsøe M (2010) Global optima for the Zhou-Rozvany problem. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43:151–164. doi:10.1007/10.1007
Stolpe M, Svanberg K (2001a) An alternative interpolation scheme for minimum compliance optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 22(2):116–124. doi:10.1007/s001580100129
Stolpe M, Svanberg K (2001b) On the trajectories of penalization methods for topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 21:128–139
Suresh K (2010) A 199-line matlab code for pareto-optimal tracing in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 42:665–679. doi:10.1007/s00158-010-0534-6
Svanberg K (1987) The method of moving asymptotes-a new method for structural optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 24:359–373
Svanberg K (2002) A class of globally convergent optimization methods based on conservative convex separable approximations. SIAM J Optim 12(2):555–573. doi:10.1137/S1052623499362822
Svanberg K, Werme M (2006) Topology optimization by a neighbourhood search method based on efficient sensitivity calculations. Int J Numer Methods Eng 67(12):1670–1699. doi:10.1002/nme.1677
Talischi C, Paulino G, Pereira A, Menezes I (2012) Polytop: a matlab implementation of a general topology optimization framework using unstructured polygonal finite element meshes. Struct Multidiscip Optim 45:329–357. doi:10.1007/s00158-011-0696-x
van Dijk N, Langelaar M, van Keulen F (2012) Explicit level-set-based topology optimization using an exact heaviside function and consistent sensitivity analysis. Int J Numer Methods Eng 91(1):67–97. doi:10.1002/nme.4258
van Dijk N, Maute K, Langelaar M, van Keulen F (2013) Level-set methods for structural topology optimization: a review. Struct Multidiscip Optim 1–36. doi:10.1007/s00158-013-0912-y
Van Miegroet L, Duysinx P (2007) Stress concentration minimization of 2d filets using x-fem and level set description. Struct Multidiscip Optim 33(4–5):425–438. doi:10.1007/s00158-006-0091-1
Vigdergauz SB (1999) Energy-minimizing inclusions in a planar elastic structure with macroisotropy. Struct Optim 17(2–3):104–112
Wächter A, Biegler L (2006) On the implementation of an interior-point filter line-search algorithm for large-scale nonlinear programming. Math Program 106(1):25–57
Wall W, Frenzel M, Cyron C (2008) Isogeometric structural shape optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197(33–40):2976–2988. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2008.01.025
Wallin M, Ristinmaa M, Askfelt H (2012) Optimal topologies derived from a phase-field method. Struct Multidiscip Optim 45(2):171–183. doi:10.1007/s00158-011-0688-x
Wang M, Wang X (2004a) Color level sets: a multi-phase method for structural topology optimization with multiple materials. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 193(6–8):469–496. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2003.10.008
Wang M, Wang X (2004b) Pde-driven level sets, shape sensitivity and curvature flow for structural topology optimization. Comput Model Eng Sci 6(4):373–395
Wang M, Zhou S (2004) Phase field: a variational method for structural topology optimization. Comput Model Eng Sci 6(6):547–566
Wang S, Wang M (2006a) A moving superimposed finite element method for structural topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 65(11):1892–1922
Wang S, Wang M (2006b) Radial basis functions and level set method for structural topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 65(12). doi:10.1002/nme.1536
Wang M, Wang X, Guo D (2003) A level set method for structural topology optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 192(1–2):227–246
Wang M, Zhou S, Ding H (2004a) Nonlinear diffusions in topology optimization. Struct Multidicip Optim 28(4):262–276. doi:10.1007/s00158-004-0436-6
Wang X, Wang M, Guo D (2004b) Structural shape and topology optimization in a level-set-based framework of region representation. Struct Multidiscip Optim 27(1–2):1–19. doi:10.1007/s00158-003-0363-y
Wang SY, Lim KM, Khoo BC, Wang MY (2007) An unconditionally time-stable level set method and its application to shape and topology optimization. Comput Model Eng Sci 21(1):1–40
Wang F, Lazarov B, Sigmund O (2011) On projection methods, convergence and robust formulations in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 43(6):767–784. doi:10.1007/s00158-010-0602-y
Wei P, Wang M (2009) Piecewise constant level set method for structural topology optimization. Int J Numer Methods Eng 78(4):379–402. doi:10.1002/nme.2478
Wei P, Wang M, Xing X (2010) A study on x-fem in continuum structural optimization using a level set model. Comput Aided Des 42(8):708–719. doi:10.1016/j.cad.2009.12.001
Wu CH, Tseng KY (2010) Topology optimization of structures using modified binary differential evolution. Struct Multidiscip Optim 42:939–953
Xia Q, Shi T, Liu S, Wang M (2012) A level set solution to the stress-based structural shape and topology optimization. Comput Struct 90–91:55–64. doi:10.1016/j.compstruc.2011.10.009
Xie YM, Steven GP (1993) A simple evolutionary procedure for structural optimization. Comput Struct 49:885–896
Xu S, Cai Y, Cheng G (2010) Volume preserving nonlinear density filter based on heaviside funtions. Struct Mulidiscip Optim 41:495–505
Yamada T, Izui K, Nishiwaki S, Takezawa A (2010) A topology optimization method based on the level set method incorporating a fictitious interface energy. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 199(45–48):2876–2891. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2010.05.013
Yamada T, Izui K, Nishiwaki S (2011) A level set-based topology optimization method for maximizing thermal diffusivity in problems including design-dependent effects. J Mech Des 133(3):031011. doi:10.1115/1.4003684
Yamasaki S, Nomura T, Kawamoto A, Sato K, Izui K, Nishiwaki S (2010) A level set based topology optimization method using the discretized signed distance function as the design variables. Struct Multidiscip Optim 41(5):685–698
Yamasaki S, Nomura T, Kawamoto A, Sato K, Nishiwaki S (2011) A level set-based topology optimization method targeting metallic waveguide design problems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 87(9):844–868. doi:10.1002/nme.3135
Yoon GH, Sigmund O (2008) A monolithic approach for topology optimization of electrostatically actuated devices. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 197:4062–4075. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2008.04.004
Yoon GH, Jensen JS, Sigmund O (2007) Topology optimization for acoustic structure interaction problems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 70(9):1049–1075
Young V, Querin OM, Steven GP, Xie YM (1999) 3D and multiple load case bi-directional evolutionary structural optimization (BESO). Struct Optim 18(2–3):183–192
Zhou M, Rozvany GIN (1991) The COC algorithm, part II: topological, geometry and generalized shape optimization. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 89(1–3):309–336
Zhou M, Rozvany GIN (2001) On the validity of ESO type methods in topology optimization. Struct Multidiscip Optim 21:80–83
Zuo Z, Xie Y, Huang X (2012) Evolutionary topology optimization of structures with multiple displacement and frequency constraints. Adv Struct Eng 15(2):359–372
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Grants: The first author appreciates the support from the Villum Foundation through the grant: “NextTop”. The second author acknowledges the support of the National Science Foundation under grant EFRI-1038305. The opinions and conclusions presented in this paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the sponsoring organization. This work was partially performed during the first authors sabbatical leave at University of Colorado Boulder.
Appendix
Appendix
1.1 A Matlab threshold code
The Matlab script shown below is intended as a post-processing step that converts a grey scale design obtained with the 99-line code (Sigmund 2001a) to a discrete design satisfying the volume fraction constraint.

In the script, the total volume includes the volume taken up by low-density elements. If the discrete approach does not include low-density elements, the third line above can simply be changed to

‘For the more compact 88-line code (Andreassen et al. 2011) the FE-part of above script should be substituted with the following

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sigmund, O., Maute, K. Topology optimization approaches. Struct Multidisc Optim 48, 1031–1055 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-013-0978-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00158-013-0978-6