Abstract
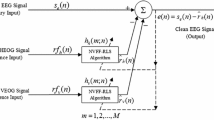
The electro-encephalogram (EEG) is useful for clinical diagnosts and in biomedical research. EEG signals, however, especially those recorded from frontal channels, often contain strong electro-oculogram (EOG) artifacts produced by eye movements. Existing regression-based methods for removing EOG artifacts require various procedures for preprocessing and calibration that are inconvenient and timeconsuming. The paper describes a method for removing ocular artifacts based on adaptive filtering. The method uses separately recorded vertical EOG and horizontal EOG signals as two reference inputs. Each reference input is first processed by a finite impulse response filter of length M (M=3 in this application) and then subtracted from the original EEG. The method is implemented by a recursive leastsquares algorithm that includes a forgetting factor (λ=0.9999 in this application) to track the non-stationary portion of the EOG signals. Results from experimental data demonstrate that the method is easy to implement and stable, converges fast and is suitable for on-line removal of EOG artifacts. The first three coefficients (up to M=3) were significantly larger than any remaining coefficients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Comstock, J. R., andArnegard, R. J. (1992): ‘The multi-attribute task battery for human operator and strategic behavior research’. NASA Technical Memorandum 104174.
Croft, R. J., andBarry, R. J. (2000): ‘Removal of ocular artifact from the EEG: a review’,Neurophysiologie Clinique,30, pp. 5–19
Gratton, G., Coles, M. G. H., andDonchin, E. (1983): ‘A new method for off-line removal of ocular artifacts’,Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,55, pp. 468–484.
Hankins, T. C., andWilson, G. F. (1998): ‘A comparison of heart rate, eye activity, EEG and subjective measures of pilot mental workload during flight’,Aviat. Space Environ. Med.,69, pp. 360–367
Haykin, S. (1996): ‘Adaptive filter theory, 3rd edn’ (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, USA, 1996)
Jasper, H. H. (1958): ‘The ten-twenty electrode system of the International Federation’,Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,10, pp. 371–375.
Jung, T. P., Makeig, S., Westerfield, M., Townsend, J., Courchesne, E., andSejnowski, T. J. (2000): ‘Removal of eye activity artifacts from visual event-related potential in normal and clinical subjects’,Clin. Neurophysiol.,111, pp. 1745–1758
Kenemans, J. L., Molenaar, P. C. M., Verbaten, M. N., andSlangen, J. L. (1991): ‘Removal of the ocular artifact from the EEG: A comparison of time and frequency domain methods with simulated and real data’,Psychophysiology,28, pp. 115–121
Vaseghi, S. V. (1996): ‘Advanced signal processing and digital noise reduction’ (John Wiley & Sons and B. G. Teubner, New York, USA, 1996), pp. 172–177.
Verleger, R., Gasser, T., andMöcks, J. (1982): ‘Correction of EOG artifacts in event-related potentials of the EEG: Aspects of reliability and validity’,Psychophysiology,19, pp. 472–480
Whitton, J. L., Lue, F., andMoldofsky, H. (1978): ‘A spectral method for removing eye movement artifacts from the EEG’,Electroenceph. Clin. Neurophysiol.,44, pp. 735–741
Widrow, B., Glover, J. R., McCool, J. M., Kaunitz, J., Williams, C. S., Hearn, R. H., Zeidler, J. R., Dong, E., andGoodlin, R. C. (1975): ‘Adaptive noise canceling: Principles and applications’,Proc. IEEE,63, pp. 1692–1716
Wilson, G. F., andRussell, C. (1999): ‘Operator functional state classification using neural networks with combined physiological and performance features’,Proc. Human Factors and Ergonomics Society, 43rd, Annual Meeting, pp. 1099–1101
Wilson, G. F. (2002). ‘An analysis of mental workload in pilots during flight using multiple psychophysiological measures’,Int. J. Aviat. Psychol.,12, pp. 3–18
Wilson, G. F., andRussell, C. (2003): ‘Real-time assessment of mental workload using psychophysiological measures’,Human Factors,45, pp. 635–643
Woestenburg, J. C., Verbaten, M. N., andSlanger, J. L. (1983): ‘The removal of the eye-movement artifact from the EEG by regression analysis in the frequency domain’,Biological Psychology,16, pp. 127–147
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, P., Wilson, G. & Russell, C. Removal of ocular artifacts from electro-encephalogram by adaptive filtering. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 42, 407–412 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344717
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02344717