Summary
Five normal men, aged 20–30 years, participated in three types of exercise (I, II, III) of equal duration (20 min) and total external work output (120–180 kJ) separated by ten days of rest. Exercises consisted of seven sets of squats with barbells on the shoulders (I; Maximal Power Output\(\dot W\) max=600−900 W), continuous cycling at 50 rev · min−1 (II;\(\dot W\) max=100−150 W) and seven bouts of intermittent cycling at 70 rev · min−1 (III;\(\dot W\) max=300−450 W).
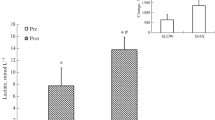
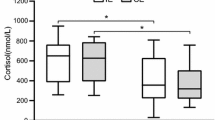
Plasma cortisol, glucagon and lactate increased significantly (P<0.05) during the exercise and recovery periods of the anaerobic, intermittent exercise (I and III) but not in the continuous, aerobic exercise (II). No consistent significant changes were found in plasma glucose. Plasma insulin levels decreased only during exercise II. The highest increase in cortisol and glucagon was not associated with the highest\(\dot V_E \),\(\dot V_{O_2 } \),\(\dot W\) max or HR; however it was associated with the anaerobic component of exercise (lactic acid). It is suggested that in exercises of equal duration and total external work output, the continuous, aerobic exercise (II) led to lowest levels of glucogenic hormones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahlborg G, Felig P, Hagenfeldt L, Hendler R, Wahren J (1974) Substrate turnover during prolonged exercise in man: Splanchnic and leg metabolism of glucose, free fatty acids and amino acids. J Clin Invest 53:1080–1090
Ahlborg G, Hagenfeldt L, Wahren J (1976) Influence of lactate infusion on glucose and free fatty acid metabolism in man. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 36:193–201
Berger M, Berchtold P, Cuppers HJ, Drost H, Drost HK, Muller WA, Wiegelmann W, Zimmermann H (1977) Metabolic and hormonal effects of muscular exercise in juvenile type diabetics. Diabetologia 13:355–365
DeLorme L, Watkins AL (1948) Techniques of progressive resistance exercise. Arch Phys Med 29:263–273
Durin JVGA, Womersley J (1974) Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: Measurements on 481 men and women aged from 16 to 72 years. Br J Nutr 34:77–97
Fischer O (1906) Theoretische Grundlagen für eine Mechanik des lebenden Körpers, Berlin
Follenius M, Brandenberger G (1975) Effect of muscular exercise on day-time variations of plasma cortisol and glucose. In: Howald H, Poortmans JR (eds) Metabolic adaptation to prolonged physical exercise. BirkhÄuser Verlag, Basel, pp 322–325
Galbo H, Richter EA, Hilsted J, Holst JJ, Christensen NJ, Henriksson J (1977) Hormonal regulation during prolonged exercise. Ann NY Acad Sci [USA] 310:72–80
Galbo H, Holst JJ, Christensen NJ (1979) The effect of different diets and of insulin on the hormonal response to prolonged exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 107:19–32
Harre D (1979) Trainingslehre. Sportsverlag, Berlin
Hilsted J, Galbo H, Somme B, Schwartz T, Fahrenkrug J, Schaffalitzky de Muckadell OB, Lauritsen KB, Tronier B (1980) Gastroenteropancreatic hormonal changes during exercise. Am J Physiol 239:G136-G140
Issekutz B, Miller H (1962) Plasma free fatty acids during exercise and the effect of lactic acid. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 110:237–239
Karagiorgos A, Garcia JF, Brooks GA (1979) Growth hormone response to continuous and intermittent exercise. Med Sci Sports 11:302–307
Kindermann W, Schnabel A, Schmitt WM, Biro G, Cassens J, Weber F (1982) Catecholamines, growth hormone, cortisol, insulin and sex hormones in anaerobic and aerobic exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 49:389–399
Kuoppasalmi K, Naveri H, Rehunen S, Karkonen M, Adlercreutz H (1976) Effect of strenuous anaerobic running exercise on plasma growth hormone, cortisol, luteinizing hormone, testosterone, androstenedione, estrone and estradiol. J Steroid Biochem 7:823–829
Rowell LB (1974) Human cardiovascular adjustments to exercise and thermal stress. Physiol Rev 54:75–159
Scheele K, Herzog W, Ritthaler G, Wirth A, Weicker H (1979) Metabolic adaptation to prolonged exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 41:101–108
Smith EW (1975) A new salting-out technique for calorimetric free fatty acids assays. Anal Biochem 67:531–539
Thorp GD (1975) The role of glucocorticoids in exercise. Med Sci Sports, vol 7, no. 1:6–11
Vanhelder WP, Sirek A, Sirek OV, Norwich KH, Policova Z, Vanhelder T (1980) Diurnal episodic pattern of insulin secretion in the dog. Diabetes 29:326–328
Vanhelder WP, Goode RC, Radomski MW (1984a) Effect of anaerobic and aerobic exercise of equal duration and work expenditure on plasma growth hormone levels. Eur J Appl Physiol 52:255–257
Vanhelder WP, Radomski MW, Goode RC (1984b) Growth hormone responses during intermittent weight lifting exercise in man. Eur J Appl Physiol 53:31–34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanhelder, W.P., Radomski, M.W., Goode, R.C. et al. Hormonal and metabolic response to three types of exercise of equal duration and external work output. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 54, 337–342 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02337175
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02337175