Abstract
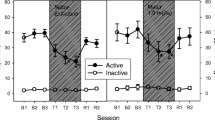
Recently, a rodent model of nicotine abstinence syndrome has been developed based on continuous subcutaneous infusion of nicotine tartrate and observing the frequency of spontaneous behavioral signs following termination of infusion. The observed signs closely resemble those commonly seen in rat opiate abstinence syndrome, raising the possibility that there is an endogenous opioid component in nicotine dependence. The present study demonstrates that the opiate antagonist naloxone can precipitate an abstinence syndrome in nicotine-dependent rats. Fourteen rats were infused for 7 days with 9 mg/kg/day nicotine tartrate in saline via an Alzet osmotic minipump. Fourteen rats were sham-operated and remained nicotine-naive. Half of each group received 4.5 mg/kg naloxone SC immediately before a “blind” 15-min observation, while the other half received saline alone. ANOVA revealed significant nicotine infusion, naloxone injection and interaction effects. Post-hoc analysis showed that the nicotine-infused rats injected with naloxone had significantly more signs than all other groups (P<0.01). In a second experiment, 2 mg/kg morphine sulfate SC produced a significant (P<0.01) 91.2% reduction of spontaneous abstinence signs observed 21 h after termination of nicotine infusion. These results are consistent with the hypothesized endogenous opioid component in nicotine dependence and abstinence syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK (1978) Tolerance of locus coeruleus neurones to morphine and suppression of withdrawal response by clonidine. Nature 276:186–188
Akil H, Mayer DJ, Liebeskind JC (1976) Antagonism of stimulation-produced analgesia by naloxone, narcotic antagonist. Science 191:961–962
Bodnar RJ, Kelly DD, Spiaggia A, Ehrenberg C, Glusman M (1978) Dose-dependent reductions by naloxone of analgesia induced by cold-water stress. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 8:667–672
Chait LD, Griffiths RR (1984) Effects of methadone on human cigarette smoking and subjective ratings. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 229:636–640
Corrigall WA, Herling S, Coen KM (1988) Evidence for opioid mechanisms in the behavioral effects of nicotine. Psychopharmacology 96:29–35
Davenport KE, Houdi AA, VanLoon GR (1990) Nicotine protects against mu-opioid receptor antagonism by beta-funaltrexamine:evidence for nicotine-induced release of endogenous opioid. Neurosci Lett 113:40–46
Fanselow MS (1986) Conditioned fear-induced opiate analgesia: a competing motivational state theory of stress analgesia. Ann NY Acad Sci 467:40–54
Fennesy MR, Lee JR (1975) Experimental evaluation of narcotic analgesics. In: Ehrenpreis S, Neidle A (eds) Methods in narcotic research Dekker, New York, pp 73–99
Fielding S, Wilker J, Hynes M, Szewczak M, Novick WJ, Lal H (1978) A comparison of clonidine with morphine for antinociceptive and antiwithdrawal actions. J. Pharmacol Exp Ther 207:899–205
Gianutsos G, Drawbaugh R, Hynes M, Lal H (1975) The narcotic withdrawal syndrome in the rat. In: Ehrenpreis S, Neidle A (eds) Methods in narcotic research. Dekker, New York, pp 293–309
Glassman AH, Jackson WK, Walsh T, Roose SP, Rosenfeld B (1984) Cigarette craving, smoking withdrawal and clonidine. Science 226:864–866
Glassman AH, Stetner F, Walsh BT, Raizman PS, Fleiss JL, Cooper TB, Covey LS (1988) Heavy smokers, smoking cessation, and clonidine: results of a double-blind, randomized trial. JAMA 259:2863–2866
Gold MS, Redmond DE, Kleber HD (1978) Clonidine blocks acute opiate withdrawal symptoms. Lancet 2:599–602
Gossop M, Powell J, Grey S, Hajek P (1990) What do opiate addicts and cigarette smokers mean by “craving”? A pilot study. Drug Alcohol Depend 26:85–87
Gray WD, Osterberg AC, Scuto TJ (1970) Measurement of the analgesic efficacy and potency of pentazocine by the D'Amour and Smith method. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 172:154–162
Hatsukami DK, Hughes JR, Pickens RW, Svikis D (1984) Tobacco withdrawal symptoms: an experimental analysis. Psychopharmacology 84:231–236
Hexum TD, Russett LR (1987) Plasma enkephalin-like peptide response to chronic nicotine infusion in guinea pig. Brain Res 406:370–372
Hughes JR, Gust SW, Skoog K, Keenan RM, Fenwick JW (1991) Symptoms of tobacco withdrawal: a replication and extension. Arch Gen Psychiatry 48:52–59
Jensen RA, Gilbert DG, Meliska CJ, Landrum TA (1990) Characterization of a dose-response curve for nicotine-induced conditioned taste aversion in rats: relationship to elevation of plasmaβ-endorphin concentration. Behav Neural Biol 53:428–440
Karras A, Kane JM (1980) Naloxone reduces cigarette smoking. Life Sci 27:1541–1545
Malin DH, Murray JB, Crucian GP, Schweitzer FC, Cook RE, Skolnick MH (1988) Auricular micro-electrostimulation: naloxone reversible attenuation of opiate abstinence syndrome. Biol Psychiatry 24:886–890
Malin DH, Lake RJ, Hammond MV, Fowler DE, Rogillio RB, Brown SL, Sims JL, Leecraft BM, Yang H-YT (1991) FMRF-NH2-Like mammalian octapeptide: possible role in opiate dependence and abstinence. Peptides 11:969–972
Malin DH, Lake JR, Newlin-Maultsby P, Roberts LK, Lanier JG, Carter VA, Cunningham JS, Wilson OB (1992) A rodent model of nicotine abstinence syndrome. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 43:119–184
Mello NK, Mendelson JH (1986) Cigarette smoking: interactions with alcohol, opiates, and marijuana. NIDA Res Monogr 68:154–180
Nemeth-Coslett R, Griffiths RR (1986) Naloxone does not affect cigarette smoking. Psychopharmacology 89:261–264
Ornish SA, Zisook S, McAdams LA (1988) Effects of transdermal clonidine treatment on withdrawal symptoms associated with smoking cessation. Arch Int Med 148:2027–2031
Pierzchala K, Houdi AA, VanLoon GR (1987) Nicotine-induced alterations in brain regional concentrations of native and cryptic met- and leu-enkephalin. Peptides 8:1035–1043
Pomerleau OF (1992) Nicotine and the central nervous system: biobehavioral effects of cigarette smoking. Am J Med 93 [1A]:2–8
Pomerleau OF, Rosecrans J (1989) Neuroregulatory effects of nicotine. Psychoneuroendocrinology 14:407–423
Pomerleau OF, Fertig JB, Seyler E, Jaffe J (1983) Neuroendocrine reactivity to nicotine in smokers. Psychopharmacology 81:61–67
Rosecrans JA, Hendry JS, Hong JS (1985) Biphasic effects of chronic nicotine treatment on hypothalamic immunoreactive beta-endorphin in the mouse. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23:141–143
Shiffman SM, Jarvik ME (1976) Smoking withdrawal symptoms in two weeks of abstinence. Psychopharmacology 50:35–39
Tobin MJ, Jenouri G, Sackner MA (1982) Effect of naloxone on change in breathing pattern with smoking. Chest 82:530–537
Tseng L, Loh HH, Wei ET (1975) Effects of clonidine on withdrawal signs in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 30:93–99
US Department of Health and Human Services (1988) The health consequences of smoking: nicotine addiction. A report of the Surgeon General. DHHS Publication (CDC) 88-8406
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malin, D.H., Lake, J.R., Carter, V.A. et al. Naloxone precipitates nicotine abstinence syndrome in the rat. Psychopharmacology 112, 339–342 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244930
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244930