Abstract
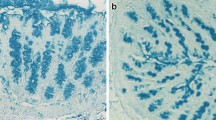
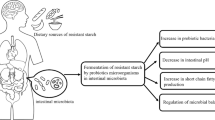
Resistant starch is by definition that part of starch that escapes digestion in the small bowel. Cecal fermentation of resistant starch into short-chain fatty acids will result subsequently in a decrease in pH. Thus, resistant starch may have the same effect on colonic luminal contents and mucosa as some fiber components. We studied the effects of adding 45 g native amylomaize (Hylon-VII) to a standardized diet in 14 healthy volunteers on fermentation and colonic mucosal proliferation. Hylon-VII is a high amylose maize starch, containing 62% resistant starch. During amylomaize consumption, breath hydrogen excretion rose 85% and fecal short chain fatty acid output increased 35% (P<0.01). Excretion of primary bile acids increased and the soluble deoxycholic acid concentration decreased by 50% (P=0.002). Subsequently, cytotoxicity of the aqueous phase of feces—as measured on a colon cancer cell line—decreased (P=0.007). Colonic mucosal proliferation in rectal biopsies (proliferating cell nuclear antigen immunostaining) decreased from 6.7 to 5.4% (P=0.05). We speculate that resistant starch consumption decreases colonic mucosal proliferation as a result of the decreased formation of cytotoxic secondary bile acids, which is possibly mediated through acidification of the large bowel by production of short-chain fatty acids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kashtan H, Stern HS, Jenkins DJ, Jenkins AL, Thompson LU, Hay K, Marcon N, Minkin S, Bruce WR: Colonic fermentation and markers of colorectal-cancer risk. Am J Clin Nutr 55:723–728, 1992
Clausen MR, Bonnen H, Mortensen PB: Colonic fermentation of dietary fibre to short chain fatty acids in patients with adenomatous polyps and colonic cancer. Gut 32:923–928, 1991
Weaver GA, Krause JA, Miller TL, Wolin MJ: Short chain fatty acid distributions of enema samples from a sigmoidoscopy population: An association of high acetate and low butyrate ratios with adenomatous polyps and colon cancer. Gut 29:1539–1543, 1988
Dexter DL, Lev R, McKendall GR, Mitchell P, Calabres P: Sodium butyrate-induced alteration of growth properties and glycogen levels in cultured human colon carcinoma cells. Histochem J 16:137–149, 1984
Friedman E, Lightdale C, Winawer S: Effects of psyllium fiber and short-chain organic acids derived from fiber breakdown on colonic epithelial cells from high-risk patients. Cancer Lett 43:121–124, 1988
MacDonald IA, Singh G, Mahony DE, Meier CE: Effect of pH on bile salt degradation by mixed fecal cultures. Steroids 32:245–256, 1978
Nagengast FM, Hectors MP, Buys WA, van Tongeren JH: Inhibition of secondary bile acid formation in the large intestine by lactulose in healthy subjects of two different age groups. Eur J Clin Invest 18:56–61, 1988
Rafter JJ, Eng VW, Furrer R, Medline A, Bruce WR: Effects of calcium and pH on the mucosal damage produced by deoxycholic acid in the rat colon. Gut 27:1320–1329, 1986
Lapre JA, van der Meer R: Diet-induced increase of colonic bile acids stimulates lytic activity of fecal water and proliferation of colonic cells. Carcinogenesis 13:41–44, 1992
Deschner EE, Long FC, Hakissan M, Herrman SL: Differential susceptibility of AKR, C57BL/6J, and CF1 mice to 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colonic tumor formation predicted by proliferative characteristics of colonic epithelial cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 70:279–282, 1983
Lipkin M, Enker WE, Winawer SJ: Tritiated-thymidine labeling of rectal epithelial cells in “non-prep” biopsies of individuals at increased risk for colonic neoplasia. Cancer Lett 37:153–161, 1987
Terpstra OT, van-Blankenstein M, Dees J, Eilers GA: Abnormal pattern of cell proliferation in the entire colonic mucosa of patients with colon adenoma or cancer. Gastroenterology 92:704–708, 1987
Cohen BI, Raicht RF, Deschner EE, et al: Effect of cholic acid feeding onN-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced colon tumors and cell kinetics in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst 64:573–578, 1980
Weisburger JH, Reddy BS, Barnes WS, Wynder EL: Bile acids, but not neutral sterols, are tumor promoters in the colon in man and in rodents. Environ Health Perspect 50:101–107, 1983
Hill MJ: Bile acids and colorectal cancer: Hypothesis. Eur J Cancer Prev 1(suppl 2):69–72, 1991
Steimetz KA, Potter JD: Vegetables, fruit, and cancer. I. Epidemiology. Cancer Causes Control 2:325–357, 1991
Vargas PA, Alberts DS, Ritenbauch C, Atwood JR, Sampliner R, Earnest D, Clark LC, Emerson SS: Dietary fiber and colon cancer prevention. Cancer Bull 43:549–561, 1991
Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Rosner BA, Speizer FE: Relation of meat, fat, and fiber intake to the risk of colon cancer in a prospective study among women. N Engl J Med 323:1664–1672, 1990
Giovannucci E, Stampfer MJ, Colditz G, Rimm EB, Willett WC: Relationship of diet to risk of colorectal adenoma in men. J Natl Cancer Inst 84:91–98, 1992
Alberts DS, Einspahr J, Rees-McGee S, Ramanujam P, Buller MK, Clark L, Ritenbaugh C, Atwood J, Pethigal P, Earnest D, et al: Effects of dietary wheat bran fiber on rectal epithelial cell proliferation in patients with resection for colorectal cancers. J Natl Cancer Inst 82:1280–1285, 1990
McIntyre A, Young GP, Taranto T, Gibson PR, Ward PB: Different fibers have different regional effects on luminal contents of rat colon. Gastroenterology 101:1274–1281, 1991
van Munster IP, Nagengast FM: The influence of dietary fibre on bile acid metabolism. Eur J Cancer Prev 1(suppl 2):35–44, 1991
Reddy BS, Engle A, Simi B, Goldman M: Effect of dietary fiber on colonic bacterial enzymes and bile acids in relation to colon cancer. Gastroenterology 102:1475–1482, 1992
Trock B, Lanza E, Greenwald P: Dietary fiber, vegetables, and colon cancer: Critical review and meta-analysis of the epidemiological evidence. J Natl Cancer Inst 83:650–661, 1990
Cummings JH, Englyst HN: Fermentation in the human large intestine and the available substrates. Am J Clin Nutr 45:1243–1255, 1987
Chapman RW, Sillery JK, Graham MM, Saunders DR: Absorption of starch by healthy ileostomates: Effect of transit time and of carbohydrate load. Am J Clin Nutr 41:1244–1248, 1985
Englyst HN, Cummings JH: Digestion of the polysaccharides of some cereal foods in the human small intestine. Am J Clin Nutr 42:778–787, 1985
Thornton JR, Dryden A, Kelleher J, Losowsky MS: Super-efficient starch absorption. A risk factor for colonic neoplasia? Dig Dis Sci 32:1088–1091, 1987
Nordgaard I, Rumessen JJ, Damgaard Nielsen A, Gudmand-Hoyer E: Absorption of wheat starch in patients resected for left-sided colonic cancer. Scand J Gastroenterol 27:632–634, 1992
Englyst HN, Kingman SM, Cummings JH: Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions. Eur J Clin Nutr 46 (suppl 2):S33-S50, 1992
Tangerman A, van Schaik A, Meuwese-Arends MT, van Tongeren JHM: Quantitative determination of C2–C8 volatile fatty acids in human serum by vacuum distillation and gas chromatography. Clin Chim Acta 133:341–348, 1983
Tangerman A, van Schaik A, van der Hoek EW: Analysis of conjugated and unconjugated bile acids in serum and jejunal fluid of normal subjects. Clin Chim Acta 159:123–132, 1986
van Faassen A, Nagengast FM, Hectors MPC, Van den Broek WJM, Huijbregts AWM, van der Werf SDJ, van Berge Henegouwen GP, van Tongeren JHM: Determination of individual human faecal bile acids by gas-liquid chromatography after enzymatic deconjugation and simultaneous solvolysis and methylation using dimethoxypropane. Clin Chim Acta 152:231–239, 1985
Bjork I, Nyman M, Pedersen B, Siljestrom M, Asp N-G, Eggum BO: Formation of enzyme resistant starch during autoclaving of wheat starch: Studiesin vitro andin vivo. J Cereal Sci 6:159–172, 1987
van Munster IP, Tangerman A, de Haan AJF, Nagengast FM: A new method for the determination of cytotoxicity of bile acids and the aqueous phase of stool; the effect of calcium. Eur J Clin Invest 23:773–777, 1993
Park JG, Kramer BS, Steinberg SM, Carmichael J, Collins JM, Minna JD, Gazdar AF: Chemosensitivity testing of human colorectal carcinoma cell lines using a tetrazolium-based colorimetric assay. Cancer Res 47:5875–5879, 1987
Hansen MB, Nielsen SE, Berg K: Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye method for measuring cell growth/cell kill. J Immunol Methods 119:203–210, 1989
Mosman T: Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63, 1983
Florent C, Flourie B, Leblond A, Rautureau M, Bernier JJ, Rambaud JC: Influence of chronic lactulose ingestion on the colonic metabolism of lactulose in man (anin vivo study). J Clin Invest 75:608–613, 1985
Perman JA, Modler S, Olson C: Role of pH in production of hydrogen from carbohydrates by colonic bacterial flora. J Clin Invest 67:643–650, 1981
Peters SG, Pomare EW, Fisher CA: Portal and peripheral blood short chain fatty acid concentrations after caecal lactulose installation at surgery. Gut 33:1249–1252, 1992
Cummings JH, Pomare EW, Branch WJ, Naylor CP, Macfarlane GT: Short chain fatty acids in human large intestine, portal, hepatic and venous blood. Gut 28:1221–1227, 1987
Flourie B, Florent C, Jouany JP: Colonic metabolism of wheat starch in healthy humans. Effects of fecal outputs and clinical symptoms. Gastroenterology 90:111–119, 1986
Gum JR, Kam WK, Byrd JC, Hicks JW, Sleisenger MH, Kim YS: Effects of sodium butyrate on human colonic adenocarcinoma cells. Induction of placental-like alkaline phosphatase. J Biol Chem 262:1092–1097, 1987
Scheppach W, Sommer H, Kirchner T, Paganelli GM, Bartram P, Christl S, Richter F, Dusel G, Kasper H: Effect of butyrate enemas on the colonic mucosa in distal ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 103:51–56, 1992
Caderni G, Bianchini F, Dolara P, Kriebel D: Starchy foods and colon proliferation in mice. Nutr Cancer 15:33–40, 1991
Scheppach W, Fabian C, Ahrens F, Spengler M, Kasper H: Effect of starch malabsorption on colonic function and metabolism in humans. Gastroenterology 95:1549–1555, 1988
Weaver GA, Krause JA, Miller TL, Wolin MJ: Cornstarch fermentation by the colonic microbial community yields more butyrate than does cabbage fiber fermentation; cornstarch fermentation rates correlate negatively with methanogenesis. Am J Clin Nutr 55:70–77, 1992
Flourie B, Florent C, Etanchaud F, Evard D, Franchisseur C, Rambaud JC: Starch absorption by healthy man evaluated by lactulose hydrogen breath test. Am J Clin Nutr 47:61–66, 1988
Fallingborg J, Christensen LA, Ingeman-Nielsen M, Jacobseb BA, Abildgaard K, Rasmussen HH: pH-profile and regional transit times of the normal gut by a radiotelemetry device. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 3:605–613, 1989
Hofmann AF, Cravetto C, Molino G, Belforte G, Bona B: Simulation of the metabolism and enterohepatic circulation of endogeneous deoxycholic acid in humans using a physiologic pharmacokinetic model for bile acid metabolism. Gastroenterology 93:693–709, 1987
Okhuysen-Young C, Kellog TF: The effect of cecectomy on fecal bile acid and neutral steroid excretion of the rat. Comp Biochem Physiol (B) 70B:345–347, 1981
Yahiro K, Setoguchi T, Katsuki T: Effect of cecum and appendix on 7α-dehydroxylation and 7β-epimerisation of chenodeoxycholic acid in the rabbit. J Lipid Res 21:215–222, 1980
Fini A, Roda A: Chemical properties of bile acids. IV. Acidity constants of glycine-conjugated bile acids. J Lipid Res 28:755–759, 1987
Geltner-Allinger U, Johansson GK, Gustafsson J, Rafter JJ: Shift from a mixed to a lactovegetarian diet: Influence on acidic lipids in fecal water—a potential risk factor for colon cancer. Am J Clin Nutr 50:992–996, 1989
van Berge Henegouwen GP, van der Werf SD, Ruben AT: Effect of long term lactulose ingestion on secondary bile salt metabolism in man: Potential protective effect of lactulose in colonic carcinogenesis. Gut 28:675–680, 1987
Thornton JR, Heaton KW: Do colonic bacteria contribute to cholesterol gall-stone formation? Effects of lactulose on bile. Br Med J 282:1018–1020, 1981
Andrieux C, Gadelle D, Leprince C, Sacquet E: Effects of some poorly digestible carbohydrates on bile acid bacterial transformations in the rat. Br J Nutr 62:103–119, 1989
Bartram HP, Scheppach W, Heid C, Fabian C, Kasper H: Effect of starch malabsorption on fecal bile acids and neutral sterols in humans: Possible implications for colonic carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 51:4238–4242, 1991
Macfarlane GT, Cummings JH: The colonic flora, fermentation, and large bowel digestive function.In The Large Intestine: Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Disease. SF Phillips, JH Pemberton, RG Shorter (eds). New York, Raven Press, 1991, p 51
Heitman DW, Ord VA, Hunter KE, Cameron IL: Effect of dietary cellulose on cell proliferation and progression of 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colon carcinogenesis in rats. Cancer Res 49:5581–5585, 1989
Jacobs LR, Lupton JR: Relationship between colonic luminal pH, cell proliferation, and colon carcinogenesis in 1,2-dimethylhydrazine treated rats fed high fiber diets. Cancer Res 46:1727–1734, 1986
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was financially supported by the Dutch Cancer Foundation, grant 89-04.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Munster, I.P., Tangerman, A. & Nagengast, F.M. Effect of resistant starch on colonic fermentation, bile acid metabolism, and mucosal proliferation. Digest Dis Sci 39, 834–842 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02087431
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02087431