Abstract
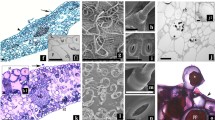
Submergence of the stem induces rapid internodal elongation in deepwater rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. “Habiganj Aman II”). A comparative anatomical study of internodes isolated from airgrown and partially submerged rice plants was undertaken to localize and characterize regions of growth and differentiation in rice stems. Longitudinal sections were examined by light and scanning-electron microscopy. Based on cell-size analysis, three zones of internodal development were recognized: a zone of cell division and elongation at the base of the internode, designated the intercalary meristem (IM); a zone of cell elongation without concomitant cell division; and a zone of cell differentiation where neither cell division nor elongation occur. The primary effects of submergence on internodal development were a threefold increase in the number of cells per cell file resulting from a decrease in the cell-cycle time from 24 to 7 h within the IM; an expansion of the cell-elongation zone from 5 to 15 mm leading to a threefold greater final cell length; and a suppression of tissue differentiation as indicated by reduced chlorophyll content and a lack of secondary wall formation in xylem and cortical sclerenchyma. These data indicate that growth of deepwater-rice internoes involves a balance between elongation and differentiation of the stem. Submergence shifts this balance in favor of growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GA:
-
gibberellin
- IM:
-
intercalary meristem
References
Adams, P.A., Montague, M.J., Tepfer, M., Rayle, D.L., Ikuma, H. Kaufman, P.B. (1975) Effect of gibberellic acid on the plasticity and elasticity of Avena stem segments. Plant Physiol. 56, 757–760
Arnon, D.I. (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24, 1–15
Bleecker, A.B., Rose-John, S., Kende, H. (1985) Ethylene action in rice: reversible inhibition by 2,5-norbornadiene. (Abstr.) Plant Physiol. (Suppl.) 77, 157
Buchholz, M. (1921) Über die Wasserleitungsbahnen in den interkalaren Wachstumszonen monokotyler Sprosse. Flora 114, 119–186
Cohen, E., Kende, H. (1986) The effect of submergence, ethylene and gibberellin on polyamines and their biosynthetic enzymes in deepwater-rice internodes. Planta 169, 498–504
Esau, K. (1965) Plant anatomy. Wiley, New York
Fisher, J.B. (1970a) Development of the intercalary meristem of Cyperus alternifolius. Am. J. Bot. 57, 691–703
Fisher, J.B. (1970b) Control of the internodal intercalary meristem of Cyperus alternifolius. Am. J. Bot. 57, 1017–1026
Green, P.B. (1976) Growth and cell pattern formation on an axis: critique of concepts, terminology, and modes of study. Bot. Gaz. 137, 187–202
Johansen, D.A. (1940) Plant microtechnique. McGraw-Hill, New York
Jones, R.L. (1983) The role of gibberellins in plant cell elongation. CRC Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1, 23–47
Juliano, J.B., Aldama, M.J. (1937) Morphology of Oryza sativa Linnaeus. Philipp. Agric. 26, 1–136
Kaufman, P.B. (1965) The effects of growth substances on intercalary growth and cellular differentiation in developing internodes of Avena sativa. II. The effects of gibberellic acid. Physiol. Plant. 18, 703–724
Kaufman, P.B., Cassell, S.J., Adams P.A. (1965) On the nature of intercalary growth and cellular differentiation in internodes of Avena sativa. Bot. Gaz. 126, 1–13
Liu, P.B., Loy, J.B. (1976) Action of gibberellic acid on cell proliferation in the subapical shoot meristem of watermelon seedlings. Am. J. Bot. 63, 700–704
Loy, J.B. (1977) Hormonal regulation of cell division in the primary elongating meristems of shoots. In: Mechanisms and control of cell division, pp. 92–110, Rost, T.L., Gifford, E.M., Jr., eds. Dowden Hutchinson and Ross, Stroudsburg, Pa., USA
Mayfield, S.P., Taylor, W.C. (1984) The appearance of photosynthetic proteins in developing maize leaves. Planta 161, 481–486
Métraux, J.-P., Kende, H. (1983) The role of ethylene in the growth response of submerged deep water rice. Plant Physiol. 72, 441–446
Métraux, J.-P., Kende, H. (1984) The cellular basis of the elongation response in submerged deep-water rice. Planta 160, 73–77
Raskin, I., Kende, H. (1984a) Regulation of growth in stem sections of deep-water rice. Planta 160, 66–72
Raskin, I., Kende, H. (1984b) Role of gibberelin in the growth response of deep water rice. Plant Physiol. 76, 947–950
Rose-John, S., Kende, H. (1984) Effect of submergence on the cell wall composition of deep-water rice internodes. Plant Physiol. 76, 106–111
Sharman, B.C. (1942) Developmental anatomy of the shoot of Zea mays L. Ann. Bot. 6, 245–282
Stuart, D.A., Durnam, D.J., Jones, R.L. (1977) Cell elongation and cell division in elongating lettuce hypocotyl sections. Planta 135, 249–255
Suge, H. (1985) Ethylene and gibberellin: regulation of internodal elongation and nodal root development in floating rice. Plant Cell Physiol. 26, 607–614
Vergara, B.S., Jackson, B., DeDatta, S.K. (1976) Deep-water rice and its response to deep-water stress. In: Climate and rice, pp. 301–319. International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, Philippines
Wellburn, A.R. (1984) Ultrastructural, respiratory and metabolic changes associated with chloroplast development. In: Chloroplast biogenesis. pp. 253–304, Baker, N.R., Barber, J., eds. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bleecker, A.B., Schuette, J.L. & Kende, H. Anatomical analysis of growth and developmental patterns in the internode of deepwater rice. Planta 169, 490–497 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392097
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00392097