Abstract
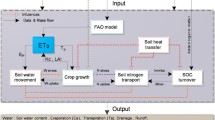
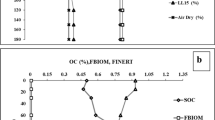
EPIC model has been evaluated and used world wide, however there is still some disagreements on the simulation results of nitrogen cycle. Based on field experimental data, simulation results of soil NO3-N was evaluated and the parameter sensitivity for simulated NO3-N was analyzed in irrigated winter wheat / summer maize field on the Loess Plateau of China. Results showed 1) EPIC model estimated soil NO3-N content and its movement among different soil layers well, with the mean RRMSE value of 0.46, for irrigated winter wheat / summer maize cropping system in the semi-humid region of the Loess Plateau. 2) Simulation results of soil NO3-N was more sensitive to soil parameters, compared with crop parameters and meteorological parameters. 3)To improve the parameter value of BN2, HI, TB, WA, CNDS, BD and FC was better to the EPIC model to simulate soil NO3-N on the Loess Plateau of China.
Chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouman, O.T., Mazzocca, M.A., Conrad, C.: Soil NO3-N leaching during growth of three grass–white-clover mixtures with mineral N applications. Agriculture Ecosystems and Environment 136, 111–115 (2010)
Wang, Q.J., Bai, Y.H., Gao, H.W., He, J., Chen, H., Chesney, R.C., Kuhn, N.J., Li, H.W.: Soil chemical properties and microbial biomass after 16 years of no-tillage farming on the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 144, 502–508 (2008)
Zhao, B.Z., Zhang, J.B., Flury, M., Zhu, A.N., Jiang, Q.A., Bi, J.W.: Groundwater contamination with NO3-N in a wheat-corn cropping system in the north china plain. Pedosphere 17(6), 721–731 (2007)
Guo, S.L., Zhu, H.H., Dang, T.H., Wu, J.S., Liu, W.Z., Hao, M.D., Li, Y., Keith, S.J.: Winter wheat grain yield associated with precipitation distribution under long-term nitrogen fertilization in the semiarid Loess Plateau in China. Geoderma 189, 442–450 (2012)
Dimitroulopoulou, C., Marshm, A.R.W.: Modeling studies of NO3-N nighttime chemistry and its effects on subsequent ozone formation. Atmospheric Emironment 31(18), 3041–3057 (1997)
Liu, X.J., Ju, X.T., Zhang, F.S., Pan, J.R., Peter, C.: Nitrogen dynamics and budgets in a winter wheat–maize cropping system in the North China Plain. Field Crops Research 83, 111–124 (2003)
Yvonne, O., Yvonne, K., Roland, B., Wolfgang, W.: Nitrate leaching in soil: Tracing the NO3 -N sources with the help of stable N and O isotopes. Soil Biology & Biochemistry 39, 3024–3033 (2007)
Wang, X.C., Li, J., Muhammad, N.T., Fang, X.Y.: Validation of the EPIC model and its utilization to research the sustainable recovery of soil desiccation after alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) by grain crop rotation system in the semi-humid region of the Loess Plateau. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 161, 152–160 (2012)
Wang, X.C., Li, J.: Evaluation of crop yield and soil water estimates using the EPIC model for the Loess Plateau of China. Mathematical and Computer Modeling 51, 1390–1397 (2010)
Niu, X.Z., William, E., Cynthia, J.H., Allyson, J., Linda, M.: Reliability and input-data induced uncertainty of the EPIC model to estimate climate change impact on sorghum yields in the U.S. Great Plains. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 129(1-3), 268–276 (2009)
Gaiser, T., de Barros, I., Sereke, F., Lange, F.M.: Validation and reliability of the EPIC model to simulate maize production in small-holder farming systems in tropical sub-humid West Africa and semi-arid Brazil. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 135, 318–327 (2010)
Cavero, J., Plant, R.E., Shennan, C., Williams, J.R., Kiniry, J.R., Benson, V.W.: Application of EPIC Model to Nitrogen Cycling in Irrigated Processing Tomatoes under Different Management Systems. Agriculture System 60, 123–135 (1997)
Cavero, J., Plant, R.E., Shennan, C., Williams, J.R., Kiniry, J.R., Benson, V.W.: Application of EPIC Model to Nitrogen Cycling in Irrigated Processing Tomatoes under Different Management Systems. Agriculture System 56(4), 391–414 (1998)
Chung, S.W., Gassman, P.W., Gu, R., Kanwar, R.S.: Evaluation of EPIC for Assessing Tile Flow and Nitrogen Losses for Alternative Agricultural Management Systems. Transactions of the ASABE 45(4), 1135–1146 (2002)
Wu, J., Yu, F.S., Chen, Z.X., Chen, J.: Global sensitivity analysis of growth simulation parameters of winter wheat based on EPIC model. Transactions of the CSAE 25(7), 136–142 (2009)
Saltelli, A., Tarantola, S., Chan, K.P.S.: A quantitative model-independent method for global sensitivity analysis of model output. Technometrics 41(1), 39–56 (1999)
Engelke, R., Fabrewitz, S.: Simulation Runs with the EPIC Model for Different Data Sets. In: Soil and Groundwater Report II: Nitrate in Soils, pp. 288–299 (1991)
Richter, J., Benbi, D.K.: Modeling of Nitrogen Transformations and Translocations. Plant Soil 181, 109–121 (1996)
Edwards, D.R., Benson, V.W., Williams, J.R., Daniel, T.C., Lemunyon, J., Gilbert, R.G.: Use of the EPIC Model to Predict Runoff Transport of Surface-Applied Inorganic Fertilizer and Poultry Manure Constituents. Transactions of the ASABE 37(2), 403–409 (1994)
Beckie, H.J., Moulin, A.P., Campbell, C.A., Brandt, S.A.: Testing Effectiveness of Four Simulation Models for Estimating Nitrates and Water in Two Soils. Canadian Journal of Soil Science 75, 135–143 (1992)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2014 IFIP International Federation for Information Processing
About this paper
Cite this paper
Wang, X., Tao, S., Li, J., Chen, Y. (2014). Evaluation of EPIC Model of Soil NO3-N in Irrigated and Wheat-Maize Rotation Field on the Loess Plateau of China. In: Li, D., Chen, Y. (eds) Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture VII. CCTA 2013. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, vol 420. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-54341-8_30
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-54341-8_30
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-54340-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-54341-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)