Abstract
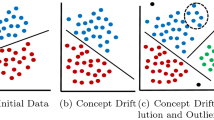
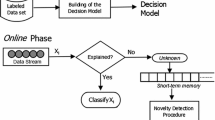
The presence of anomalies in data compromises data quality and can reduce the effectiveness of learning algorithms. Standard data mining methodologies refer to data cleaning as a pre-processing before the learning task. The problem of data cleaning is exacerbated when learning in the computational model of data streams. In this paper we present a streaming algorithm for learning classification rules able to detect contextual anomalies in the data. Contextual anomalies are surprising attribute values in the context defined by the conditional part of the rule. For each example we compute the degree of anomaliness based on the probability of the attribute-values given the conditional part of the rule covering the example. The examples with high degree of anomaliness are signaled to the user and not used to train the classifier. The experimental evaluation in real-world data sets shows the ability to discover anomalous examples in the data. The main advantage of the proposed method is the ability to inform the context and explain why the anomaly occurs.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barateiro, J., Galhardas, H.: A survey of data quality tools. Datenbank-Spektrum 14, 15–21 (2005)
Chandola, V., Banerjee, A., Kumar, V.: Anomaly detection: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. 41(3) (2009)
Clark, P., Boswell, R.: Rule induction with cn2: Some recent improvements, pp. 151–163. Springer (1991)
Domingos, P., Hulten, G.: Mining high-speed data streams. In: Ramakrishnan, R., Stolfo, S.J., Bayardo, R.J., Parsa, I. (eds.) KDD, pp. 71–80. ACM (2000)
Frank, A., Asuncion, A.: UCI machine learning repository (2010)
Gama, J., Fernandes, R., Rocha, R.: Decision trees for mining data streams. Intelligent Data Analysis 10, 23–45 (2006)
Gama, J., Rocha, R., Medas, P.: Accurate decision trees for mining high-speed data streams. In: Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. ACM Press, New York (2003)
Gama, J., Kosina, P.: Learning decision rules from data streams. In: Walsh, T. (ed.) IJCAI, pp. 1255–1260. IJCAI/AAAI (2011)
Han, J., Kamber, M., Pei, J.: Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Morgan Kaufmann (2012)
Harries, M., Sammut, C., Horn, K.: Extracting hidden context. Machine Learning 32, 101–126 (1998)
Hodge, V.J., Austin, J.: A survey of outlier detection methodologies. Artificial Intelligence Review 22(2), 85–126 (2004)
Ikonomovska, E., Gama, J., Dzeroski, S.: Learning model trees from evolving data streams. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 23(1), 128–168 (2011)
Knorr, E.M., Ng, R.T., Tucakov, V.: Distance-based outliers: algorithms and applications. The VLDB Journal 8(3-4), 237–253 (2000)
Kosina, P., Gama, J.: Handling time changing data with adaptive very fast decision rules. In: Flach, P.A., De Bie, T., Cristianini, N. (eds.) ECML PKDD 2012, Part I. LNCS, vol. 7523, pp. 827–842. Springer, Heidelberg (2012)
Pham, D.-S., Venkatesh, S., Lazarescu, M., Budhaditya, S.: Anomaly detection in large-scale data stream networks. Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery (to appear)
Ross Quinlan, J.: Kdd-99 panel on last 10 and next 10 years. SIGKDD Explorations 1(2), 62 (2000)
Nick Street, W., Kim, Y.: A streaming ensemble algorithm (sea) for large-scale classification. In: KDD, pp. 377–382 (2001)
Tukey, J.W.: Exploratory Data Analysis. Addison-Wesley (1977)
Zliobaite, I., Gabrys, B.: Adaptive preprocessing for streaming data. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 99(PrePrints), 1 (2012)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2013 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Gama, J., Kosina, P., Almeida, E. (2013). Avoiding Anomalies in Data Stream Learning. In: Fürnkranz, J., Hüllermeier, E., Higuchi, T. (eds) Discovery Science. DS 2013. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 8140. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40897-7_4
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-40897-7_4
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-40896-0
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-40897-7
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)