Abstract
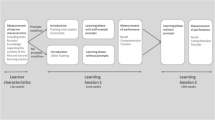
This work explores the role of students’ motivation and metacognitive skills as moderating factors that influence the impact of an instructional method in the ill-structured domain of Software Project Management (SPM). In order to teach aspects of the SPM domain, we developed a web environment for case-based learning and implemented additionally a questioning strategy to help students focus on important parts of the case material. The paper presents the results from three studies revealing how students’ motivation and metacognitive awareness influenced their engagement in the cognitively challenging situations induced by the method. The implication for instructors and designers is that implementing a promising method, to help students efficiently process the complex material in an ill-structured domain, might not always lead to the desired learning outcomes. Students’ motivation and metacognitive skills should also be addressed, in order to maximize the potential benefits of instruction.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jonassen, D.H.: Instructional design models for well-structured and ill-structured problem-solving learning outcomes. Educational Technology: Research and Development 45, 65–94 (1997)
Shin, N., Jonassen, D.H., McGee, S.: Predictors of well-structured and ill-structured problem solving in an astronomy simulation. Journal of Research in Science Teaching 40(1), 6–33 (2003)
Voss, J.F., Post, T.A.: On the solving of ill-structured problems. In: Chi, M.H., Glaser, R., Farr, M.J. (eds.) The nature of expertise, pp. 261–285. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Hillsdale (1988)
Spiro, R.J., Feltovich, P.J., Jacobson, M.J., Coulson, R.L.: Cognitive flexibility, constructivism, and hypertext: Random access instruction for advanced knowledge acquisition in ill-structured domains. In: Duffy, T., Jonassen, D. (eds.) Constructivism and the technology of instruction, pp. 57–75. Erlbaum, Hillsdale (1992)
Chi, M.T.H., Feltovich, P.J., Glaser, R.: Categorization and representation of physics problems by experts and novices. Cognitive Science 5, 121–152 (1981)
Azevedo, R., Hadwin, A.F.: Scaffolding self-regulated learning and metacognition – Implications for the design of computer-based scaffolds. Instructional Science 33, 367–379 (2005)
Ge, X.: Scaffolding students’ problem-solving processes on an ill-structured task using question prompts and peer interactions. Unpublished Doctoral Thesis (2001), http://etda.libraries.psu.edu/theses/approved/WorldWideIndex/ETD-75/index.html
Craig, S.D., Sullins, J., Witherspoon, A., Gholson, B.: The Deep-Level-Reasoning-Question Effect: The Role of Dialogue and Deep-Level-Reasoning Questions During Vicarious Learning. Cognition and Instruction 24(4), 565–591 (2006)
Hmelo, C., Day, R.: Contextualized questioning to scaffold learning from simulations. Computers & Education 32, 151–164 (1999)
Feltovich, P.J., Spiro, R.J., Coulson, R.L., Feltovich, J.: Collaboration within and among minds: Mastering complexity, individuality and in groups. In: Koschmann, T. (ed.) CSCL: Theory and practice of an emerging paradigm, pp. 25–44. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah (1996)
Kolodner, J.: Case-Based Reasoning. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., San Mateo (1993)
Kokinov, B.: Dynamics and Automaticity of Context: A Cognitive Modeling Approach. In: Bouquet, P., Serafini, L., Brezillon, P., Benerecetti, M., Castellani, F. (eds.) CONTEXT 1999. LNCS (LNAI), vol. 1688, p. 200. Springer, Heidelberg (1999)
Keller, J.M.: Development and use of the ARCS model of instructional design. Journal of Instructional Development 10(3), 2–10 (1987)
Keller, J.M., Kopp, T.W.: Application of the ARCS model to motivational design. In: Reigeluth, C.M. (ed.) Instructional Theories in Action: Lessons Illustrating Selected Theories, pp. 289–320. Lawrence Erlbaum Publishers, New York (1987)
Flavell, J.: Metacognitive aspects of problem solving. In: Resnick, B. (ed.) The nature of intelligence. Erlbaum, Hillsdale (1976)
Jehng, S.D., Johnson, S.D., Anderson, R.C.: Schooling and students’ logical beliefs about learning. Contemporary Educational Psychology 18, 45–56 (1993)
Tyler, S.W., Voss, J.F.: Attitude and knowledge effects in prose processing. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior 21, 524–538 (1982)
Brabeck, M.M., Wood, P.K.: Cross-sectional and longitudinal evidence for differences between well-structured and ill-structured problem-solving abilities. In: Commons, M.L., Armon, C., Kohlberg, L., Richards, F.A., Grotzer, T.A., Sinnott, J.D. (eds.) Adult development. Models and methods in the study of adolescent and adult thought, vol. 2, pp. 133–146. Praeger, New York (1990)
Sommerville, I.: Software Engineering, 7th edn. Addison-Wesley, Reading (2004)
Kitchenham, B., Budgen, D., Brereton, P., Woodall, P.: An investigation of software engineering curricula. Journal of Systems and Software 74(3), 325–335 (2005)
Ewusi-Mensah, K.: Software Development Failures. MIT Press, Cambridge (2003)
Tynjälä, P.: Writing as a tool for constructive learning: Students’ learning experiences during an experiment. Higher Education 36, 209–230 (1998)
Quitadamo, I.J., Kurtz, M.J.: Learning to Improve: Using Writing to Increase Critical Thinking Performance in General Education Biology. CBE-Life Sciences Education 6, 140–154 (2007)
Greene, B.A., Land, S.M.: A qualitative analysis of scaffolding use in a resource-based learning environment involving the World Wide Web. Journal of Educational Computing Research 23(2), 151–179 (2000)
Clark, R.C., Mayer, R.E.: e-Learning and the Science of Instruction. Pfeiffer, San Francisco (2003)
Papadopoulos, P.M., Demetriadis, S.N., Stamelos, I.G.: Analyzing the Role of Students’ Self-Organization in a Case of Scripted Collaboration. In: O’Maley, C., Suthers, D., Reimann, P., Dimitracopoulou, A. (eds.) Computer Supported Collaborative Learning Practices: CSCL 2009 Conference Proceedings, pp. 487–496. International Society of Learning Sciences, ISLS (2009)
Berge, Z.L., Collins, M.: Computer-mediated scholarly discussion groups. Computers & Education 24, 183–189 (1995)
Liu, C., Tsai, C.: An analysis of peer interaction patterns as discoursed by on-line small group problem-solving activity. Computers & Education 50, 627–639 (2008)
Dillenbourg, P., Tchounikine, P.: Flexibility in macro-scripts for computer-supported collaborative learning. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning 23(1), 1–13 (2007)
Kollar, I., Fischer, F., Hesse, F.W.: Collaboration Scripts – A Conceptual Analysis. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 18, 159–185 (2006)
Dillenbourg, P. (ed.): Framework for Integrated Learning. Deliverable D23-05-01-F of Kaleidoscope Network of Excellence (2004), http://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/docs/00/19/01/07/PDF/Dillenbourg-Kaleidoscope-2004.pdf
Kalyuga, S.: Prior knowledge principle in multimedia learning. In: Mayer, R.E. (ed.) The Cambridge handbook of multimedia learning, pp. 325–337. Cambridge University Press, New York (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Papadopoulos, P.M., Demetriadis, S.N., Stamelos, I.G. (2009). The Impact of Prompting in Technology-Enhanced Learning as Moderated by Students’ Motivation and Metacognitive Skills. In: Cress, U., Dimitrova, V., Specht, M. (eds) Learning in the Synergy of Multiple Disciplines. EC-TEL 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5794. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04636-0_49
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04636-0_49
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-04635-3
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-04636-0
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)