Abstract
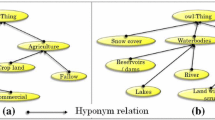
This paper presents an approach to measure the semantic similarity between digital elevation model (DEMs). We compute a semantic “distance” between concepts in hierarchical structure of geomorphologic application ontology. The method is composed of two stages: analysis and measurement. Analysis stage is focused on performing a geomorphometric analysis: a qualitative value (descriptor) representing a concept in ontology is assigned to each DEM’s cell. Measurement stage is based on a comparison between the descriptors of two DEMs. In other words, we measure the semantic “distance” (called herein confusion) between two ontology concepts. The similarity is defined at two levels of measurement: local and global. The first one is defined at cell-level value and the second one considers the entire cells in a DEM. Thus, the similarity between two DEMs at the conceptual level is established. For instance, our methodology can detect that two DEMs share the same or similar geomorphologic features: plateau, downhill, etc.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rudner M, Biedermann R, Schroder B, Kleyer B, (2007) Integrated Grid Based Ecological and Economic (INGRID) landscape model. A tool to support landscape management decisions. J Environmental Modelling & Software 22(2): 177-187
Saadat H, Bonnell R, Sharifi F, Mehuys G, Namdar M, Ale-Ebrahim S (2008) Landform classification from a digital elevation model and satellite imagery, Geomorphology, In Press
Wilson JP, Gallant JC (2000) Terrain Analysis- Principles and Applications. John Willey & Sons, USA
Chaplot V, Darboux F, Bourennane H, Leguedois S Silvera N, Phachomphon K (2006) Accuracy of interpolation techniques for the derivation of digital elevation models in relation to landform types and data density. J Geomorphology 77(1-2): 126-141
Bonk R (2002) Scale-dependent Geomorphometric Analysis for Glacier Mapping at Nanga Parbat: GRASS GIS Approach. In: Proceedings of the Open source GIS - GRASS User’s conference 2002, Italy
Rodríguez A and Egenhofer M (2004) Comparing Geospatial Entity Classes: An Asymmetric and Context-Dependent Similarity Measure. J International Journal of Geographical Information Science 18(3): 229-256
Ahlqvist O (2005) Using semantic similarity metrics to uncover category and land cover change. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3799, pp 107-119
Hirtle S (2007) Similarity Matching for Emergency Evacuation Workshop on Semantic Similarity Measurement at the Conference on Spatial Information Theory (COSIT 2007), Melbourne, Australia
Levachkine S and Guzman A (2004) Hierarchies Measuring Qualitative Variables. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2945: 262-274
Riley SJ, DeGloria SD, and Elliot R (1999) A terrain ruggedness index that quantifies topographic heterogeneity. J Intermountain Journal of Sciences 5: 23-27
Moreno M, Levachkine S, Torres M and Quintero R (2004) Landform Classification in Raster Geo-Images. In: Progress in Pattern Recognition, Image Analysis and Applications. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 3287: 558-565
Levachkine S and Guzman-Arenas A (2007) Hierarchy as a new data type for qualitative variables. J Expert Systems with Applications 32(3): 899-910
Resnik P (1995) Using information content to evaluate semantic similarity in a taxonomy. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, pp 448-453
Guarino N (1995) Formal ontology, conceptual analysis, and knowledge representation. J International Journal Human and Computer Studies 43: 625-640
Moreno-Ibarra M (2007) Semantic Similarity Applied to Generalization of Geospatial Data. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 4853: 247-255
Project Agent (1998) Selection of basic measures. http://agent.ign.fr/
Resnik P (1999) Semantic Similarity in a Taxonomy: An Information-Based Measure and Its Application to Problems of Ambiguity in Natural Language. J Artificial Intelligence Research 11: 95-130
Goni A, Mena E and Illarramendi A (1998) Querying heterogeneous and distributed data repositories using ontologies. In: Charrel PJ and Jaakkola H (eds), Information Modeling and Knowledge Base IX, IOS Press, pp 19-34
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Moreno-Ibarra, M., Levachkine, S., Torres, M., Quintero, R., Guzman, G. (2009). Semantic Similarity Applied to Geomorphometric Analysis of Digital Elevation Model. In: Popovich, V.V., Claramunt, C., Schrenk, M., Korolenko, K.V. (eds) Information Fusion and Geographic Information Systems. Lecture Notes in Geoinformation and Cartography. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00304-2_10
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-00304-2_10
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-00303-5
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-00304-2
eBook Packages: Earth and Environmental ScienceEarth and Environmental Science (R0)