Abstract
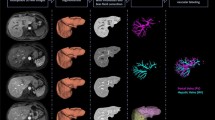
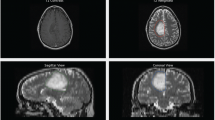
Often in neurosurgical planning a dual echo acquisition is performed that yields proton density (PD) and T2-weighted images to evaluate edema near a tumour or lesion. The development of vessel segmentation algorithms for PD images is of general interest since this type of acquisition is widespread and is entirely noninvasive. Whereas vessels are signaled by black blood contrast in such images, extracting them is a challenge because other anatomical structures also yield similar contrasts at their boundaries. In this paper we present a novel multi-scale geometric flow for segmenting vasculature from PD images which can also be applied to the easier cases of computed tomography (CT) angiography data or Gadolinium enhanced MRI. The key idea is to first apply Frangi’s vesselness measure [4] to find putative centerlines of tubular structures along with their estimated radii. This multi-scale measure is then distributed to create a vector field which is orthogonal to vessel boundaries so that the flux maximizing flow algorithm of [17] can be applied to recover them. We validate the approach qualitatively with PD, angiography and Gadolinium enhanced MRI volumes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez, L., Guichard, F., Lions, P.L., Morel, J.M.: Axiomes et équations fondamentales du traitement d’images. C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 315, 135–138 (1992)
Ambrosio, L., Soner, H.M.: Level set approach to mean curvature flow in arbitrary codimension. Journal of Differential Geometry 43, 693–737 (1996)
Aylward, S.R., Bullitt, E.: Initialization, noise, singularities, and scale in height ridge traversal for tubular object centerline extraction. IEEE Transactions On Medical Imaging 21(2), 61–75 (2002)
Frangi, W.N., Vincken, K.L., Viergever, M.A.: Multiscale vessel enhancement filtering. In: MICCAI 1998, pp. 130–137 (1998)
Gage, M., Hamilton, R.: The heat equation shrinking convex plane curves. Journal of Differential Geometry 23, 69–96 (1986)
Grayson, M.: The heat equation shrinks embedded plane curves to round points. Journal of Differential Geometry 26, 285–314 (1987)
Kimia, B.B., Tannenbaum, A., Zucker, S.W.: Shape, shocks, and deformations I: The components of two-dimensional shape and the reaction-diffusion space. International Journal of Computer Vision 15, 189–224 (1995)
Koller, T.M., Gerig, G., Székely, G., Dettwiler, D.: Multiscale detection of curvilinear structures in 2-d and 3-d image data. In: International Conference On Computer Vision, pp. 864–869 (1995)
Krissian, K., Malandain, G., Ayache, N.: Model-based detection of tubular structures in 3d images. Computer Vision and Image Understanding 80(2), 130–171 (2000)
Lindeberg, T.: Edge detection and ridge detection with automatic scale selection. International Journal of Computer Vision 30(2), 77–116 (1998)
Lorenz, C., Carlsen, I., Buzug, T., Fassnacht, C., Weese, J.: Multi-scale line segmentation with automatic estimation of width, contrast and tangential direction in 2d and 3d medical images. In: CVRMED-MRCAS 1997. LNCS, vol. 1205, pp. 233–242 (1997)
Lorigo, L.M., Faugeras, O.D., Grimson, E.L., Keriven, R., Kikinis, R., Nabavi, A., Westin, C.-F.: Curves: Curve evolution for vessel segmentation. Medical Image Analysis 5, 195–206 (2001)
McInerney, T., Terzopoulos, D.: T-snakes: Topology adaptive snakes. Medical Image Analysis 4, 73–91 (2000)
Osher, S.J., Sethian, J.A.: Fronts propagating with curvature dependent speed: Algorithms based on hamilton-jacobi formulations. Journal of Computational Physics 79, 12–49 (1988)
Ostergaard, L., Larsen, O., Goualher, G., Evans, A., Collins, D.: Extraction of cerebral vasculature from mri. In: 9th Danish Conference on Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis (August 2000)
Sato, Y., Nakajima, S., Shiraga, N., Atsumi, H., Yoshida, S., Koller, T., Gerig, G., Kikinis, R.: 3d multi-scale line filter for segmentation and visualization of curvilinear structures in medical images. Medical Image Analysis 2(2), 143–168 (1998)
Vasilevskyi, A., Siddiqi, K.: Flux maximizing geometric flows. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 24(12), 1–14 (2002)
Wilson, D.L., Noble, A.: Segmentation of cerebral vessels and aneurysms from mr aniography data. Information Processing in Medical Imaging, 423–428 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2004 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Descoteaux, M., Collins, L., Siddiqi, K. (2004). A Multi-scale Geometric Flow for Segmenting Vasculature in MRI. In: Sonka, M., Kakadiaris, I.A., Kybic, J. (eds) Computer Vision and Mathematical Methods in Medical and Biomedical Image Analysis. MMBIA CVAMIA 2004 2004. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 3117. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-27816-0_15
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-27816-0_15
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-22675-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-27816-0
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive