Abstract
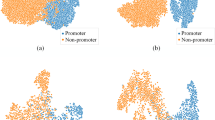
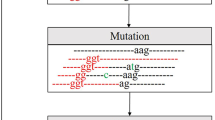
Accurate prediction and recognition of promoters remains a challenge in DNA sequence analysis. In this paper, the gene set firstly can be divided into two parts by CpG-island analysis. Then, in each part, a set of statistical divergence (SD) algorithms and sparse auto-encoders (SAEs) are integrated to optimize a series kinds of kmers and get multiple deep divergence features which compromises the merits of signal and context features. Extracted from the total possible combinations of kmers, the informative kmers can be selected by optimizing the differentiating extents of four sparse distributions based on promoter and non-promoters training samples. SAE in deep learning can convert the kmer feature based on SD into multiple deep divergence feature and reduce the dimension. Finally, multiple support vector machines and a bilevel decision model construct a human promoter recognition method called DSD-SVMs. Framework is flexible that it can integrate new features or new classification models freely. Experimental result shows the method has high sensitivity and specificity.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajic, V.B., Chong, A., Seah, S.H., et al.: An intelligent system for vertebrate promoter recognition. IEEE Intell. Syst. 17(4), 64–70 (2002)
Fickett, J.W., Hatzigeorgiou, A.G.: Eukaryotic promoter recognition. Genome Res. 7, 861–878 (1997)
Zeng, J., et al.: SCS: signal, context, and structure features for genome-wide human promoter recognition. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 7(3), 550–562 (2010)
Saxonov, S., Berg, P., Brutlag, D.L.: A genome-wide analysis of CpG dinucleotides in the human genome distinguishes two distinct classes of promoters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 103(5), 1412–1417 (2006)
Werner, T.: The state of the art of mammalian promoter recognition. Brief Bioinform. 2014 (2014)
Setty, M., Leslie, C.S.: SeqGL Identifies Context-Dependent Binding Signals in Genome-Wide Regulatory Element Maps. PLoS Comput. Biol. 11(5), e1004271 (2015)
Ghandi, M., Lee, D., Mohammad-Noori, M., et al.: Enhanced regulatory sequence prediction using gapped k-mer features. PLoS Comput. Biol. 10(12), e1003711 (2014)
Vinga, S.: Information theory applications for biological sequence analysis. Brief. Bioinform. 15(3), 376–389 (2014)
Zeng, J., Cao, X.Q., Yan, H.: Human promoter recognition using Kullback-Leibler divergence. In: IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, pp. 3319–3325 (2007)
Zhao, X.Y., et al.: Promoter recognition based on the maximum entropy hidden markov model. Comput. Biol. Med. 51(15), 73–81 (2014)
Neelakanta, P., et al.: Information-theoretic algorithms in bioinformatics and bio-/medical-imaging: a review. In: IEEE International Conference on Recent Trends in Information Technology, pp. 183–188 (2011)
Nielsen, F., Nock, R.: Sided and symmetrized Bregman centroids. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 55(6), 2882–2904 (2009)
Anwar, F., et al.: Pol II promoter prediction using characteristic 4-mer motifs: a machine learning approach. BMC Bioinformatics 9(1), 414 (2008)
Ng, A.: Sparse autoencoder. CS294A Lecture Notes for Stanford University (2011)
Baldi, P., Lu, Z.: Complex-valued autoencoders. Neural Netw. 33(3), 136–147 (2014)
Ng, A., Ngiam, J., Foo, C.Y., Mai, Y., Suen, C.: UFLDL tutorial: building deep networks for classification. An online tutorial (2013)
Suzuki, Y., et al.: DBTSS, DataBase of Transcriptional Start Sites: progress report 2004. Nucleic Acids Res. 32(Database issue D), 78–81 (2004)
Goddard, N.L., et al.: Sequence dependent rigidity of single stranded DNA. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85(11), 2400–2403 (2000)
Liu, W., Kou, Q.B., Wei, L.H., et al.: Plant promoter recognition based on analysis of base bias and SVM. J. Liaoning Normal Univ. (2012)
Vapnik, V., Cortes, C.: Support vector networks. Mach. Learn. 20(3), 273–297 (1995)
Platt, J.C.: Probabilistic outputs for support vector machines and comparisons to regularized likelihood methods. Adv. Large Margin Classif. 10(4), 61–74 (1999)
Saxonov, S., Daizadeh, I., Fedorov, A., Gillbert, W.: EID: the exon-intron database—an exhaustive database of protein-coding intron-containing genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28(1), 185–190 (2000)
Pesole, G., Liuni, S., Grillo, G., et al.: UTRdb and UTRsite: specialized databases of sequences and functional elements of 5’ and 3’ untranslated regions of eukaryotic mRNAs. Update 2002. Nucleic Acids Res. 30(1), 335 (2002)
Bajić, V.B.: Comparing the success of different prediction software in sequence analysis: a review. Brief. Bioinform. 1(3), 214 (2000)
Zhu, L., Guo, W.L., Lu, C., Huang, D.S.: Collaborative completion of transcription factor binding profiles via local sensitive unified embedding. IEEE Trans. Nanobiosci. 99, 1 (2016)
Liang, X., Zhu, L., Huang, DS.: Multi-task ranking SVM for image cosegmentaiton. Neurocomputing (2017)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the grants of the National Science Foundation of China, Nos. 61520106006, 31571364, U1611265, 61532008, 61672203, 61402334, 61472282, 61472280, 61472173, 61572447, 61373098 and 61672382, China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Grant, Nos. 2016M601646.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2017 Springer International Publishing AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Xu, W., Bao, W., Yuan, L., Jiang, Z. (2017). DSD-SVMs: Human Promoter Recognition Based on Multiple Deep Divergence Features. In: Huang, DS., Bevilacqua, V., Premaratne, P., Gupta, P. (eds) Intelligent Computing Theories and Application. ICIC 2017. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 10361. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63309-1_46
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-63309-1_46
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-63308-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-63309-1
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)