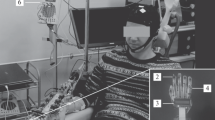
Abstract
In this experimental we investigated the cortical neuromodulation during a tDCS (transcranial direct current stimulation) section to induce a temporary inhibition of the frontal area. The induced effect of brain modulation was tested on the EEG (electroencephalography) and ERPs (event-related potentials) profile when subjects performed a task in which they had to respond if the object represented in the sequence was correctly or incorrectly used. It was shown that an increased negative peak deflection (N400) is observable in case of semantic anomalies. We attended a significant reduction of this ERPs deflections when tDCS was applied to frontal area. During the detection task, participants were asked to evaluate the semantic correctness of some motor sequences that manipulated simple objects. EEG were registered during the tDCS or no tDCS stimulation. Significant differences between the two conditions and a reduction of the peak amplitude were observed in case of tDCS stimulation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoruso, L., Gelormini, C., Aboitiz, F., González, M.A., Manes, F., Cardona, J.F., Agustín, I.: N400 ERPs for actions: building meaning in context. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 4, 7–57 (2013)
Balconi, M., Caldiroli, C.L.: Semantic violation effect on object-related action comprehension. N400-like ERP in a non linguistic task. Neurosci. 197, 191–199 (2011)
Balconi, M., Vitaloni, S.: The tDCS effect on alpha brain oscillation for correct vs. incorrect object use. The contribution of the left DLPFC. Neurosci. Lett. 517, 25–29 (2012)
Balconi, M., Canavesio, Y., Vitaloni, S.: Activation of the prefrontal cortex and posterior parietal cortex increases the recognition of semantic violations in action representation. Brain Stimul. 7, 435–442 (2014)
Bach, P., Gunter, T.C., Knoblich, G., Prinz, W., Friederici, A.D.: N400-like negativities in action perception reflect the activation of two components of an action representation. Soc. Neurosci. 4, 212–232 (2009)
Ganis, G., Kutas, M.: An electrophysiological study of scene effects on object identification. Cogn. Brain. Res. 16, 123–144 (2003)
Maffongelli, L., Bartoli, E., Sammler, D., Kölsch, S., Campus, C., Olivier, E., Fadiga, L., D’Ausilio, A.: Distinct brain signatures of content and structure violation during action observation. Neuropsychologia 75, 30–39 (2015)
Proverbio, M.A., Riva, F., Zani, A.: When neurons do not mirror the agentʼs intentions: Sex differences in neural coding of goal-directed actions. Neuropsychologia 48, 1454–1463 (2010)
Reid, V.M., Hoehl, S., Grigutsch, M., Groendahl, A., Parise, E., Striano, T.: The neural correlates of infant and adult goal prediction: evidence for semantic processing systems. Dev. Psychol. 45, 620–629 (2008)
Rizzolatti, G., Craighero, L.: The Mirror-neuron system. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 27, 169–192 (2004)
Salmaso, D., Longoni, A.M.: Problems in the assessment of hand preference. Cortex 21, 533–549 (1985)
Sitnikova, T., Holcomb, P.J., Kiyonaga, K.A., Kuperberg, G.R.: Two neurocognitive mechanisms of semantic integration during the comprehension of visual real-world events. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 20, 2037–2057 (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2016 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Caldiroli, C.L., Balconi, M. (2016). The Effect of tDCS on EEG Profile During a Semantic Motor Task Divided in a Correct and Incorrect Ways. In: Serino, S., Matic, A., Giakoumis, D., Lopez, G., Cipresso, P. (eds) Pervasive Computing Paradigms for Mental Health. MindCare 2015. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 604. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32270-4_27
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-32270-4_27
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-32269-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-32270-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)