Abstract
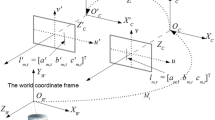
In this paper we study structure from motion problems for parallel cylinders. Using sparse keypoint correspondences is an efficient (and standard) way to solve the structure from motion problem. However, point features are sometimes unavailable and they can be unstable over time and viewing conditions. Instead, we propose a framework based on silhouettes of quadric surfaces, with special emphasis on parallel cylinders. Such structures are quite common, e.g. trees, lampposts, pillars, and furniture legs. Traditionally, the projection of the center lines of such cylinders have been considered and used in computer vision. Here, we demonstrate that the apparent width of the cylinders also contains useful information for structure and motion estimation. We provide mathematical analysis of relative structure and relative motion tensors, which is used to develop a number of minimal solvers for simultaneously estimating camera pose and scene structure from silhouette lines of cylinders. These solvers can be used efficiently in robust estimation schemes, such as RANSAC. We use Sampson-approximation methods for efficient estimation using over-determined data and develop averaging techniques. We also perform synthetic accuracy and robustness tests and evaluate our methods on a number of real-world scenarios.
This work was supported by the ADACORSA project with funding from ECSEL JU in the H2020 Framework Programme (H2020/2014-2020) and National Authorities, under GA 876019, the strategic research projects ELLIIT, the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research project, Semantic Mapping and Visual Navigation for Smart Robots (grant no. RIT15-0038) and by the Wallenberg AI, Autonomous Systems and Software Program (WASP) funded by the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akinlar, C., Topal, C.: EDlines: real-time line segment detection by edge drawing (ed). In: Proceedings of International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp. 2837–2840 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIP.2011.6116138
Åström, K., Oskarsson, M.: Solutions and ambiguities of the structure and motion problem for 1D retinal vision. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 12(2), 121–135 (2000)
Åström, K.: Invariancy Methods for Points, Curves and Surfaces in Computational Vision. Ph.D. thesis, Lund Unicersiry (1996)
Åström, K.: Using combinations of points, lines and conics to estimate structure and motion. In: Proceedings of Symposium on Image Analysis, pp. 61–64. SSBA (1998)
Åström, K., Cipolla, R., Giblin, P.J.: Generalised epipolar constraints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 33, 51–72 (1999)
Åström, K., Kahl, F.: Motion estimation in image sequences using the deformation of apparent contours. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 21(2), 114–127 (1999)
Åström, K., Kahl, F., Heyden, A., Berthilsson, R.: A statistical approach to structure and motion from image features. In: Amin, A., Dori, D., Pudil, P., Freeman, H. (eds.) SSPR /SPR 1998. LNCS, vol. 1451, pp. 929–936. Springer, Heidelberg (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0033321
Barath, D., Polic, M., Förstner, W., Sattler, T., Pajdla, T., Kukelova, Z.: Making affine correspondences work in camera geometry computation. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12356, pp. 723–740. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58621-8_42
Cho, N.G., Yuille, A., Lee, S.W.: A novel linelet-based representation for line segment detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 40(5), 1195–1208 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2703841
De Ma, S.: Conics-based stereo, motion estimation, and pose determination. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 10(1), 7–25 (1993)
Frosio, I., Alzati, A., Bertolini, M., Turrini, C., Borghese, N.A.: Linear pose estimate from corresponding conics. Pattern Recogn. 45(12), 4169–4181 (2012)
Frosio, I., Turrini, C., Alzati, A.: Camera re-calibration after zooming based on sets of conics. Vis. Comput. 32(5), 663–674 (2016)
Gillsjö, D., Flood, G., Åström, K.: Semantic room wireframe detection from a single view. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 1886–1893. IEEE (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR56361.2022.9956252
Grompone von Gioi, R., Jakubowicz, J., Morel, J.M., Randall, G.: LSD: a fast line segment detector with a false detection control. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 32(4), 722–732 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2008.300
Gu, G., Ko, B., Go, S., Lee, S.H., Lee, J., Shin, M.: Towards light-weight and real-time line segment detection. In: Proceedings of Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), pp. 726–734 (2022)
Gummeson, A., Engman, J., Åström, K., Oskarsson, M.: Fast and efficient minimal solvers for quadric based camera pose estimation. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), pp. 3973–3979. IEEE (2022)
Gummeson, A., Oskarsson, M.: Robust and accurate cylinder triangulation. In: Proceedings of Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis (SCIA). Springer (2023)
Hanek, R., Navab, N., Appel, M.: Yet another method for pose estimation: a probabilistic approach using points, lines, and cylinders. In: Proceedings of Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). vol. 2, pp. 544–550. IEEE (1999)
Huang, K., Wang, Y., Zhou, Z., Ding, T., Gao, S., Ma, Y.: Learning to parse wireframes in images of man-made environments. In: Proceedings of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 626–635. IEEE (2018)
Kahl, F., Heyden, A.: Structure and motion from points, lines and conics with affine cameras. In: Burkhardt, H., Neumann, B. (eds.) ECCV 1998. LNCS, vol. 1406, pp. 327–341. Springer, Heidelberg (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BFb0055676
Kahl, F., Heyden, A.: Using conic correspondences in two images to estimate the epipolar geometry. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 761–766. IEEE (1998)
Kaminski, J., Shashua, A.: Multiple view geometry of algebraic curves. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 56(3), 195–219 (2003)
Kuang, Y., Åström, K.: Pose estimation with unknown focal length using points, directions and lines. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), pp. 529–536. IEEE (2013)
Kuang, Y., Burgess, S., Torstensson, A., Åström, K.: A complete characterization and solution to the microphone position self-calibration problem. In: Proceedings of of International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), pp. 3875–3879. IEEE (2013)
Larsson, V., Åstrom, K., Oskarsson, M.: Efficient solvers for minimal problems by syzygy-based reduction. In: Proceedings of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 820–829. IEEE (2017)
Liu, C., Hu, W.: Real-time geometric fitting and pose estimation for surface of revolution. Pattern Recogn. 85, 90–108 (2019)
Lowe, D.G.: Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 60, 91–110 (2004)
Ma, S., Li, L.: Ellipsoid reconstruction from three perspective views. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR). vol. 1, pp. 344–348. IEEE (1996)
Mei, J., Zhang, D., Ding, Y.: Monocular vision for pose estimation in space based on cone projection. Opt. Eng. 56(10), 103108 (2017)
Mudigonda, P.K., Jawahar, C., Narayanan, P.: Geometric structure computation from conics. In: Proceedings of Indian Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics and Image Processing (ICVGIP), pp. 9–14. Citeseer (2004)
Mur-Artal, R., Montiel, J.M.M., Tardos, J.D.: ORB-SLAM: a versatile and accurate monocular SLAM system. IEEE Trans. Robot. 31(5), 1147–1163 (2015)
Navab, N., Appel, M.: Canonical representation and multi-view geometry of cylinders. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 70(2), 133–149 (2006)
Oskarsson, M., Åström, K.: Accurate and automatic surveying of beacon positions for a laser guided vehicle. In: Proceedings of European Consortium for Mathematics in Industry (ECMI) (1998)
Oskarsson, M., Åström, K., Overgaard, N.C.: Minimal cases of the structure and motion problem with missing data for one-dimensional retinae. In: Proceedings of Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis (SCIA), pp. 482–489. Springer (2001)
Oskarsson, M., Åström, K., Overgaard, N.C.: The minimal structure and motion problems with missing data for 1D retina vision. J. Math. Imaging Vis. 26(3), 327–343 (2006)
Pautrat, R., Lin, J.T., Larsson, V., Oswald, M.R., Pollefeys, M.: SOLD2: self-supervised occlusion-aware line description and detection. In: Proceedings of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 11368–11378. IEEE (2021)
Quan, L.: Invariant of a pair of non-coplanar conics in space: Definition, geometric interpretation and computation. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 926–931. IEEE (1995)
Quan, L.: Conic reconstruction and correspondence from two views. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 18(2), 151–160 (1996)
Quan, L.: Uncalibrated 1D projective camera and 3D affine reconstruction of lines. In: Proceedings of Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 60–65. IEEE (1997)
Raposo, C., Barreto, J.P.: Theory and practice of structure-from-motion using affine correspondences. In: Proceedings of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 5470–5478. IEEE (2016)
Rublee, E., Rabaud, V., Konolige, K., Bradski, G.: ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In: Proceedings of International conference on computer vision (ICCV), pp. 2564–2571. IEEE (2011)
Sattler, T., et al.: Benchmarking 6dof outdoor visual localization in changing conditions. In: Proceedings of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 8601–8610. IEEE (2018)
Schönberger, J.L., Frahm, J.M.: Structure-from-motion revisited. In: Proceedings of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4104–4113. IEEE (2016)
Schönberger, J.L., Zheng, E., Frahm, J.-M., Pollefeys, M.: Pixelwise view selection for unstructured multi-view stereo. In: Leibe, B., Matas, J., Sebe, N., Welling, M. (eds.) ECCV 2016. LNCS, vol. 9907, pp. 501–518. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46487-9_31
Stewénius, H.: Gröbner Basis Methods for Minimal Problems in Computer Vision. Ph.D. thesis, Lund University (2005)
Triggs, B., McLauchlan, P.F., Hartley, R.I., Fitzgibbon, A.W.: Bundle adjustment — a modern synthesis. In: Triggs, B., Zisserman, A., Szeliski, R. (eds.) IWVA 1999. LNCS, vol. 1883, pp. 298–372. Springer, Heidelberg (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44480-7_21
Xu, Y., Xu, W., Cheung, D., Tu, Z.: Line segment detection using transformers without edges. In: Proceedings of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 4257–4266. IEEE (2021)
Xue, N., et al.: Learning regional attraction for line segment detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 43(6), 1998–2013 (2019)
Xue, N., et al.: Holistically-attracted wireframe parsing. In: Proceedings of Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), pp. 2788–2797. IEEE (2020)
Zheng, J., Zhang, J., Li, J., Tang, R., Gao, S., Zhou, Z.: Structured3D: a large photo-realistic dataset for structured 3D modeling. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12354, pp. 519–535. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58545-7_30
Zhou, Y., Qi, H., Ma, Y.: End-to-end wireframe parsing. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 962–971. IEEE (2019)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Tegler, E. et al. (2023). The Multi-view Geometry of Parallel Cylinders. In: Gade, R., Felsberg, M., Kämäräinen, JK. (eds) Image Analysis. SCIA 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13886. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-31438-4_32
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-31438-4_32
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-31437-7
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-31438-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)