Abstract
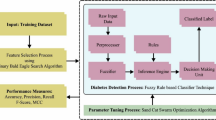
It is vitally important to establish a system that is able to provide an early detection of diabetes as a stealth disease of modern era. In order to achieve this goal, this manuscript proposes a novel framework for feature selection and extreme learning machine (ELM) hyper-parameter optimization applied to diabetes diagnostics. Feature selection and hyper-parameter optimization are two of the most important challenges in the domain of machine learning and they both belong to the group of NP-hard challenges. An upgraded version of the newly suggested sand cat swarm optimization (SCSO) is developed to address these issues, and adapted for ELM hyper-parameter tuning and feature selection. A preliminary set of biases and weights are established using the proposed approach, as well as the optimal (sub-optimal) no. of neurons for the ELM hidden layer, as well as to establish initial set of biases and weights. Furthermore, each swarm individual also tries to select the most relevant features for classification tasks against a widely utilized diabetes dataset. The performance of proposed methods was compared to other well-known state-of-the-art swarm intelligence algorithms in terms of accuracy, precision, recall and f1 score. Experimental findings demonstrate that the improved SCSO is more efficient than other algorithms in addressing both challenges.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacanin, N., et al.: Artificial neural networks hidden unit and weight connection optimization by quasi-refection-based learning artificial bee colony algorithm. IEEE Access 9, 169135–169155 (2021)
Bacanin, N., Bezdan, T., Zivkovic, M., Chhabra, A.: Weight optimization in artificial neural network training by improved monarch butterfly algorithm. In: Shakya, S., Bestak, R., Palanisamy, R., Kamel, K.A. (eds.) Mobile Computing and Sustainable Informatics. LNDECT, vol. 68, pp. 397–409. Springer, Singapore (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-1866-6_29
Bacanin, N., Petrovic, A., Zivkovic, M., Bezdan, T., Antonijevic, M.: Feature selection in machine learning by hybrid sine cosine metaheuristics. In: Singh, M., Tyagi, V., Gupta, P.K., Flusser, J., Ören, T., Sonawane, V.R. (eds.) ICACDS 2021. CCIS, vol. 1440, pp. 604–616. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81462-5_53
Beni, G., Wang, J.: Swarm intelligence in cellular robotic systems. In: Dario, P., Sandini, G., Aebischer, P. (eds.) Robots and Biological Systems: Towards a New Bionics? NATO ASI Series, vol. 102, pp. 703–712. Springer, Heidelberg (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-58069-7_38
Bezdan, T., Zivkovic, M., Bacanin, N., Chhabra, A., Suresh, M.: Feature selection by hybrid brain storm optimization algorithm for COVID-19 classification. J. Comput. Biol. 29, 515–529 (2022)
Butt, U.M., Letchmunan, S., Ali, M., Hassan, F.H., Baqir, A., Sherazi, H.H.R.: Machine learning based diabetes classification and prediction for healthcare applications. J. Healthc. Eng. (2021)
Chandrashekar, G., Sahin, F.: A survey on feature selection methods. Comput. Electr. Eng. 40, 16–28 (2014)
Dua, D., Graff, C.: UCI machine learning repository (2017). http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml
Eberhart, R., Kennedy, J.: Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Australia, vol. 1948 (1942)
Heidari, A.A., Mirjalili, S., Faris, H., Aljarah, I., Mafarja, M., Chen, H.: Harris hawks optimization: algorithm and applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 97, 849–872 (2019)
Huang, G.B., Zhou, H., Ding, X., Zhang, R.: Extreme learning machine for regression and multiclass classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B (Cybern.) 42, 513–529 (2012)
Huang, G.B.: Learning capability and storage capacity of two-hidden-layer feedforward networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 14, 274–281 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1109/TNN.2003.809401
Huang, G.B., Zhu, Q.Y., Siew, C.K.: Extreme learning machine: a new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks. In: 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37541), vol. 2, pp. 985–990 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/IJCNN.2004.1380068
Huang, G.B., Zhu, Q.Y., Siew, C.K.: Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70, 489–501 (2006)
Jovanovic, D., Antonijevic, M., Stankovic, M., Zivkovic, M., Tanaskovic, M., Bacanin, N.: Tuning machine learning models using a group search firefly algorithm for credit card fraud detection. Mathematics 10, 2272 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/math10132272
Jovanovic, D., Antonijevic, M., Stankovic, M., Zivkovic, M., Tanaskovic, M., Bacanin, N.: Tuning machine learning models using a group search firefly algorithm for credit card fraud detection. Mathematics 10(13) (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/math10132272, https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7390/10/13/2272
Karaboga, D., Akay, B.: A comparative study of artificial bee colony algorithm. Appl. Math. Comput. 214(1), 108–132 (2009)
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R.: Particle swarm optimization. In: Proceedings of ICNN 1995 - International Conference on Neural Networks, vol. 4, pp. 1942–1948 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1109/ICNN.1995.488968
American Diabetes Association: Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 37(Suppl 1), 81–90 (2014)
Mirjalili, S., Gandomi, A.H., Mirjalili, S.Z., Saremi, S., Faris, H., Mirjalili, S.M.: Salp swarm algorithm: a bio-inspired optimizer for engineering design problems. Adv. Eng. Softw. 114, 163–191 (2017)
Reynolds, C.W.: Flocks, herds and schools: a distributed behavioral model, vol. 21, pp. 25–34. Association for Computing Machinery, New York (1987). https://doi.org/10.1145/37402.37406
Serre, D.: Matrices. Graduate Texts in Mathematics, 2nd edn. Springer, New York (2010)
Seyyedabbasi, A., Kiani, F.: Sand cat swarm optimization: a nature-inspired algorithm to solve global optimization problems. Eng. Comput. 1–25 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-022-01604-x
Wang, G.G., Deb, S., Coelho, L.D.S.: Elephant herding optimization. In: 2015 3rd International Symposium on Computational and Business Intelligence (ISCBI), pp. 1–5. IEEE (2015)
Yang, X.-S.: Firefly algorithms for multimodal optimization. In: Watanabe, O., Zeugmann, T. (eds.) SAGA 2009. LNCS, vol. 5792, pp. 169–178. Springer, Heidelberg (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-04944-6_14
Yang, X.S., Gandomi, A.H.: Bat algorithm: a novel approach for global engineering optimization. Eng. Comput. 29, 464–483 (2012)
Zivkovic, M., et al.: COVID-19 cases prediction by using hybrid machine learning and beetle antennae search approach. Sustain. Urban Areas 66, 102669 (2021)
Zivkovic, M., Stoean, C., Chhabra, A., Budimirovic, N., Petrovic, A., Bacanin, N.: Novel improved salp swarm algorithm: an application for feature selection. Sensors 22(5), 1711 (2022)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Stankovic, M. et al. (2023). Feature Selection and Extreme Learning Machine Tuning by Hybrid Sand Cat Optimization Algorithm for Diabetes Classification. In: Simian, D., Stoica, L.F. (eds) Modelling and Development of Intelligent Systems. MDIS 2022. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 1761. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-27034-5_13
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-27034-5_13
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-27033-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-27034-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)