Abstract
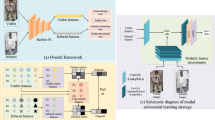
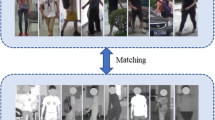
Visible-infrared person re-identification (ReID) aims to recognize a same person of interest across a network of RGB and IR cameras. Some deep learning (DL) models have directly incorporated both modalities to discriminate persons in a joint representation space. However, this cross-modal ReID problem remains challenging due to the large domain shift in data distributions between RGB and IR modalities. This paper introduces a novel approach for a creating intermediate virtual domain that acts as bridges between the two main domains (i.e., RGB and IR modalities) during training. This intermediate domain is considered as privileged information (PI) that is unavailable at test time, and allows formulating this cross-modal matching task as a problem in learning under privileged information (LUPI). We devised a new method to generate images between visible and infrared domains that provide additional information to train a deep ReID model through an intermediate domain adaptation. In particular, by employing color-free and multi-step triplet loss objectives during training, our method provides common feature representation spaces that are robust to large visible-infrared domain shifts. Experimental results on challenging visible-infrared ReID datasets indicate that our proposed approach consistently improves matching accuracy, without any computational overhead at test time. The code is available at: https://github.com/alehdaghi/Cross-Modal-Re-ID-via-LUPI.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, K., Pan, Z., Wang, J., Jiao, S., Zeng, Z., Miao, Z.: Joint feature learning network for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Peng, Y., et al. (eds.) PRCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12306, pp. 652–663. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-60639-8_54
Chen, Y., Wan, L., Li, Z., Jing, Q., Sun, Z.: Neural feature search for RGB-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 587–597 (2021)
Cho, J.W., Kim, D.J., Choi, J., Jung, Y., Kweon, I.S.: Dealing with missing modalities in the visual question answer-difference prediction task through knowledge distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 1592–1601 (2021)
Choi, C., Kim, S., Ramani, K.: Learning hand articulations by hallucinating heat distribution. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 3104–3113 (2017)
Choi, S., Lee, S., Kim, Y., Kim, T., Kim, C.: HI-CMD: hierarchical cross-modality disentanglement for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 10257–10266 (2020)
Crasto, N., Weinzaepfel, P., Alahari, K., Schmid, C.: Mars: motion-augmented RGB stream for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 7882–7891 (2019)
Dai, P., Ji, R., Wang, H., Wu, Q., Huang, Y.: Cross-modality person re-identification with generative adversarial training. In: IJCAI, vol. 1, p. 2 (2018)
Deng, J., Dong, W., Socher, R., Li, L.J., Li, K., Fei-Fei, L.: ImageNet: a large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 248–255. IEEE (2009)
Fan, X., Luo, H., Zhang, C., Jiang, W.: Cross-spectrum dual-subspace pairing for RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. ArXiv abs/2003.00213 (2020)
Fu, C., Hu, Y., Wu, X., Shi, H., Mei, T., He, R.: CM-NAS: cross-modality neural architecture search for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 11823–11832 (2021)
Gretton, A., Borgwardt, K.M., Rasch, M.J., Schölkopf, B., Smola, A.: A kernel two-sample test. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 13(1), 723–773 (2012)
Hao, Y., Li, J., Wang, N., Gao, X.: Modality adversarial neural network for visible-thermal person re-identification. Pattern Recogn. 107, 107533 (2020)
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., Sun, J.: Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 770–778 (2016)
Hoffman, J., Gupta, S., Darrell, T.: Learning with side information through modality hallucination. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 826–834 (2016)
Jia, M., Zhai, Y., Lu, S., Ma, S., Zhang, J.: A similarity inference metric for RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.01504 (2020)
Jiang, J., Jin, K., Qi, M., Wang, Q., Wu, J., Chen, C.: A cross-modal multi-granularity attention network for RGB-IR person re-identification. Neurocomputing 406, 59–67 (2020)
Kampffmeyer, M., Salberg, A.B., Jenssen, R.: Urban land cover classification with missing data modalities using deep convolutional neural networks. IEEE J. Sel. Topics Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 11(6), 1758–1768 (2018)
Kiran, M., Praveen, R.G., Nguyen-Meidine, L.T., Belharbi, S., Blais-Morin, L.A., Granger, E.: Holistic guidance for occluded person re-identification. In: British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC) (2021)
Kniaz, V.V., Knyaz, V.A., Hladůvka, J., Kropatsch, W.G., Mizginov, V.: ThermalGAN: multimodal color-to-thermal image translation for person re-identification in multispectral dataset. In: Leal-Taixé, L., Roth, S. (eds.) ECCV 2018. LNCS, vol. 11134, pp. 606–624. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-11024-6_46
Kumar, S., Banerjee, B., Chaudhuri, S.: Improved landcover classification using online spectral data hallucination. Neurocomputing 439, 316–326 (2021)
Lambert, J., Sener, O., Savarese, S.: Deep learning under privileged information using heteroscedastic dropout. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 8886–8895 (2018)
Lezama, J., Qiu, Q., Sapiro, G.: Not afraid of the dark: NIR-VIS face recognition via cross-spectral hallucination and low-rank embedding. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 6628–6637 (2017)
Li, D., Wei, X., Hong, X., Gong, Y.: Infrared-visible cross-modal person re-identification with an X modality. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 4610–4617 (2020)
Liu, H., Cheng, J.: Enhancing the discriminative feature learning for visible-thermal cross-modality person re-identification. CoRR abs/1907.09659 (2019). https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.09659
Liu, H., Ma, S., Xia, D., Li, S.: SFANet: a spectrum-aware feature augmentation network for visible-infrared person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:2102.12137 (2021)
Lu, Y., et al.: Cross-modality person re-identification with shared-specific feature transfer. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 13379–13389 (2020)
Mekhazni, D., Bhuiyan, A., Ekladious, G., Granger, E.: Unsupervised domain adaptation in the dissimilarity space for person re-identification. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12372, pp. 159–174. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58583-9_10
Nguyen, D.T., Hong, H.G., Kim, K.W., Park, K.R.: Person recognition system based on a combination of body images from visible light and thermal cameras. Sensors 17(3), 605 (2017)
Pande, S., Banerjee, A., Kumar, S., Banerjee, B., Chaudhuri, S.: An adversarial approach to discriminative modality distillation for remote sensing image classification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops (2019)
Park, H., Lee, S., Lee, J., Ham, B.: Learning by aligning: visible-infrared person re-identification using cross-modal correspondences. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 12046–12055 (2021)
Pechyony, D., Vapnik, V.: On the theory of learning with privileged information. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, vol. 23 (2010)
Saputra, M.R.U., et al.: DeepTIO: a deep thermal-inertial odometry with visual hallucination. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 5(2), 1672–1679 (2020)
Vapnik, V., Vashist, A.: A new learning paradigm: learning using privileged information. Neural Netw. 22(5–6), 544–557 (2009)
Wang, G.A., et al.: Cross-modality paired-images generation for RGB-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 34, pp. 12144–12151 (2020)
Wang, G., Zhang, T., Cheng, J., Liu, S., Yang, Y., Hou, Z.: RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification via joint pixel and feature alignment. In: The IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), October 2019
Wang, M., Deng, W.: Deep visual domain adaptation: a survey. Neurocomputing 312, 135–153 (2018)
Wang, Z., Wang, Z., Zheng, Y., Wu, Y., Zeng, W., Satoh, S.: Beyond intra-modality: a survey of heterogeneous person re-identification. arXiv preprint arXiv:1905.10048 (2019)
Wang, Z., Wang, Z., Zheng, Y., Chuang, Y.Y., Satoh, S.: Learning to reduce dual-level discrepancy for infrared-visible person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 618–626 (2019)
Wu, A., Zheng, W.S., Gong, S., Lai, J.: RGB-IR person re-identification by cross-modality similarity preservation. Int. J. Comput. Vision 128(6), 1765–1785 (2020)
Wu, A., Zheng, W.S., Yu, H.X., Gong, S., Lai, J.: RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 5380–5389 (2017)
Wu, Q., et al.: Discover cross-modality nuances for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 4330–4339 (2021)
Xu, X., Wu, S., Liu, S., Xiao, G.: Cross-modal based person re-identification via channel exchange and adversarial learning. In: Mantoro, T., Lee, M., Ayu, M.A., Wong, K.W., Hidayanto, A.N. (eds.) ICONIP 2021. LNCS, vol. 13108, pp. 500–511. Springer, Cham (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-92185-9_41
Yang, Y., Zhang, T., Cheng, J., Hou, Z., Tiwari, P., Pandey, H.M., et al.: Cross-modality paired-images generation and augmentation for RGB-infrared person re-identification. Neural Networks 128, 294–304 (2020)
Ye, M., Lan, X., Wang, Z., Yuen, P.C.: Bi-directional center-constrained top-ranking for visible thermal person re-identification. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 15, 407–419 (2020)
Ye, M., Lan, X., Li, J., Yuen, P.: Hierarchical discriminative learning for visible thermal person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 32 (2018)
Ye, M., Ruan, W., Du, B., Shou, M.Z.: Channel augmented joint learning for visible-infrared recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 13567–13576 (2021)
Ye, M., Shen, J., J. Crandall, D., Shao, L., Luo, J.: Dynamic dual-attentive aggregation learning for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Vedaldi, A., Bischof, H., Brox, T., Frahm, J.-M. (eds.) ECCV 2020. LNCS, vol. 12362, pp. 229–247. Springer, Cham (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-58520-4_14
Ye, M., Shen, J., Lin, G., Xiang, T., Shao, L., Hoi, S.C.H.: Deep learning for person re-identification: a survey and outlook. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.04193 (2020)
Ye, M., Shen, J., Shao, L.: Visible-infrared person re-identification via homogeneous augmented tri-modal learning. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 16, 728–739 (2020)
Zhang, Q., Cheng, H., Lai, J., Xie, X.: DHML: deep heterogeneous metric learning for VIS-NIR person re-identification. In: Sun, Z., He, R., Feng, J., Shan, S., Guo, Z. (eds.) CCBR 2019. LNCS, vol. 11818, pp. 455–465. Springer, Cham (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-31456-9_50
Zhang, Z., Jiang, S., Huang, C., Li, Y., Da, X., R.Y.: RGB-IR cross-modality person ReID based on teacher-student GAN model. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 150, 155–161 (2021)
Zhu, Y., Yang, Z., Wang, L., Zhao, S., Hu, X., Tao, D.: Hetero-center loss for cross-modality person re-identification. Neurocomputing 386, 97–109 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Nuvoola AI Inc., and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
1 Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Alehdaghi, M., Josi, A., Cruz, R.M.O., Granger, E. (2023). Visible-Infrared Person Re-Identification Using Privileged Intermediate Information. In: Karlinsky, L., Michaeli, T., Nishino, K. (eds) Computer Vision – ECCV 2022 Workshops. ECCV 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13805. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25072-9_48
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-25072-9_48
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-031-25071-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-031-25072-9
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)