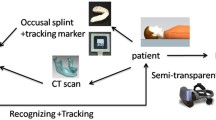
Abstract
Recently, in the field of surgical visualization, augmented reality technology has shown incomparable advantages in oral and maxillofacial surgery. However, the current augmented reality methods need to develop personalized occlusal splints and perform secondary Computed Tomography (CT) scanning. These unnecessary preparations lead to high cost and extend the time of preoperative preparation. In this paper, we propose an augmented reality surgery guidance system based on 3D scanning. The system innovatively designs a universal occlusal splint for all patients and reconstructs the virtual model of patients with occlusal splints through 3D scanning. During the surgery, the pose relationship between the virtual model and the markers is computed through the marker on the occlusal splint. The proposed method can replace the wearing of occlusal splints for the secondary CT scanning during surgery. Experimental results show that the average target registration error of the proposed method is \(\text{1.38}\pm \text{0.43 mm}\), which is comparable to the accuracy of the secondary CT scanning method. This result suggests the great application potential and value of the proposed method in oral and maxillofacial surgery.
L. Ding and L. Shao—These authors contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chana, J.S., Chang, Y.M., Wei, F.C.: Segmental mandibulectomy and immediate free fibula osteoseptocutaneous flap reconstruction with endosteal implants: an ideal treatment method for mandibular ameloblastoma. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 113(1), 80–87 (2004)
Ma, L., et al.: Augmented reality surgical navigation with accurate CBCT-patient registration for dental implant placement. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 57(1), 47–57 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-018-1861-9
Gao, Y., Lin, L., Chai, G.: A feasibility study of a new method to enhance the augmented reality navigation effect in mandibular angle split osteotomy. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. (2019)
Badiali, G., Ferrari, V., Cutolo, F.: Augmented reality as an aid in maxillofacial surgery: Validation of a wearable system allowing maxillary repositioning. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 42(8), 1970–1976 (2014)
Mamone, V., Ferrari, V., Condino, S.: Projected augmented reality to drive osteotomy surgery: implementation and comparison with video see-through technology. IEEE Access 8, 169024–169035 (2020)
Azimi, E., Song, T., Yang, C., et al.: Endodontic Guided treatment using augmented reality on a head-mounted display system. Healthc. Technol. Lett. 5(5), 201–207 (2018)
Wang, J., Suenaga, H., Liao, H.: Real-time computer-generated integral imaging and 3D image calibration for augmented reality surgical navigation. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 40, 147–159 (2015)
Ma, L., Fan, Z., Ning, G., Zhang, X., Liao, H.: 3D visualization and augmented reality for orthopedics. In: Zheng, G., Tian, W., Zhuang, X. (eds.) Intelligent Orthopaedics. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol. 1093, pp. 193–205. Springer, Singapore (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1396-7_16
Wang, J., Suenaga, H.: Video see-through augmented reality for oral and maxillofacial surgery. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. (2017)
Zhu, M., Liu, F., Chai, G.: A novel augmented reality system for displaying inferior alveolar nerve bundles in maxillofacial surgery. Sci. Rep. 7, 42365 (2017)
Lüthi, M.: Statismo-a framework for PCA based statistical models. Insight 1,1–18 (2012)
Besl, P.J., Mckay, H.D.: A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 14(2), 239–256 (1992)
Cui, X.: Augmented Reality Assistance System Framework Research Based on Boeing 737 Aircraft Pre-flight Maintenance, pp. 21–27. Civil Aviation University of China, Tianjin (2019)
Rublee, E., Rabaud, V., Konolige, K.: ORB: an efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In: International Conference on Computer Vision. IEEE (2012)
Calonder, M., Lepetit, V., Strecha, C., Fua, P.: BRIEF: binary robust independent elementary features. In: Daniilidis, K., Maragos, P., Paragios, N. (eds.) ECCV 2010. LNCS, vol. 6314, pp. 778–792. Springer, Heidelberg (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-15561-1_56
Fischler, M.A., Bolles, R.C.: Random sample consensus: a paradigm for model fitting with applications to image analysis and automated cartography. Commun. ACM 24(6), 381–395 (1981)
Jiang, T., Zhu, M., Chai, G., Li, Q.: Precision of a novel craniofacial surgical navigation system based on augmented reality using an occlusal splint as a registration strategy. Sci. Rep. 9(1), 501 (2019)
Murugesan, Y.P., Alsadoon, A., Manoranjan, P.: A novel rotational matrix and translation vector algorithm: geometric accuracy for augmented reality in oral and maxillofacial surgeries. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. (2018)
Chen, L., Li, H., Shao, L.: An augmented reality surgical guidance method based on 3D model design. In: The 20th National Conference on Image and Graphics (NGIG), vol. 144, pp. 28–30 (2020)
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2019YFC0119300), the National Science Foundation Program of China (62025104, 61901031), and Beijing Nova Program (Z201100006820004) from Beijing Municipal Science & Technology Commission.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest related to this article.
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ding, L. et al. (2021). Novel Augmented Reality System for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. In: Peng, Y., Hu, SM., Gabbouj, M., Zhou, K., Elad, M., Xu, K. (eds) Image and Graphics. ICIG 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12889. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87358-5_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87358-5_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-87357-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-87358-5
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)