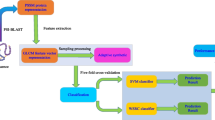
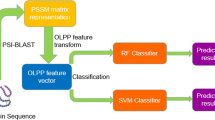
Abstract
Protein-protein interactions (PPIs) in plants plays a significant role in plant biology and functional organization of cells. Although, a large amount of plant PPIs data have been generated by high-throughput techniques, but due to the complexity of plants cells, the PPIs pairs currently obtained by experimental methods cover only a small fraction of the complete plants PPIs network. In addition, the experimental approaches for identifying PPIs in plants are laborious, time-consuming, and costly. Hence, it is highly desirable to develop more efficient approaches to detect PPIs in plants. In this study, we present a novel computational method combining weighted sparse representation-based classifier (WSRC) with inverse fast Fourier transform (IFFT) representation scheme which was adopted in position specific scoring matrix (PSSM) to extract features from plant protein sequences. When performing the proposed method on the plant PPIs data set of Maize, we achieved excellent results with high accuracies of 89.12%. To further assess the prediction performance of the proposed approach, we compared it with the state-of-art support vector machine (SVM) classifier. Experimental results demonstrated that the proposed method has a great potential to become a powerful tool for exploring the plants cells function.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, Y., Weckwerth, W.: Mass spectrometry untangles plant membrane protein signaling networks. Trends Plant Sci. 25(9), 930–944 (2020)
Matiolli, C.C., Melotto, M.: A comprehensive Arabidopsis yeast two-hybrid library for protein-protein interaction studies: a resource to the plant research community. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 31, 899–902 (2018)
Di Silvestre, D., Bergamaschi, A., Bellini, E., Mauri, P.: Large scale proteomic data and network-based systems biology approaches to explore the plant world. Proteomes 6, 27 (2018)
Waese, J., et al.: ePlant: visualizing and exploring multiple levels of data for hypothesis generation in plant biology. Plant Cell 29, 1806–1821 (2017)
Hartmann, J., et al.: The effective design of sampling campaigns for emerging chemical and microbial contaminants in drinking water and its resources based on literature mining. Sci. Total Environ. 742, 140546 (2020)
An, D., Cao, H.X., Li, C., Humbeck, K., Wang, W.: Isoform sequencing and state-of-art applications for unravelling complexity of plant transcriptomes. Genes 9, 43 (2018)
Chou, K.-C., Shen, H.-B.: Plant-mPLoc: a top-down strategy to augment the power for predicting plant protein subcellular localization. PLoS One 5, e11335 (2010)
Lamesch, P., et al.: The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): improved gene annotation and new tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, D1202–D1210 (2012)
Gu, H., Zhu, P., Jiao, Y., Meng, Y., Chen, M.: PRIN: a predicted rice interactome network. BMC Bioinform. 12, 1–13 (2011)
Licata, L., et al.: MINT, the molecular interaction database: 2012 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, D857–D861 (2012)
Li, J.-Q., You, Z.-H., Li, X., Ming, Z., Chen, X.: PSPEL: in silico prediction of self-interacting proteins from amino acids sequences using ensemble learning. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 14, 1165–1172 (2017)
You, Z.-H., Lei, Y.-K., Zhu, L., Xia, J., Wang, B.: Prediction of protein-protein interactions from amino acid sequences with ensemble extreme learning machines and principal component analysis. In: BMC Bioinformatics, pp. 1–11. Springer (2013)
You, Z.-H., Lei, Y.-K., Gui, J., Huang, D.-S., Zhou, X.: Using manifold embedding for assessing and predicting protein interactions from high-throughput experimental data. Bioinformatics 26, 2744–2751 (2010)
Wang, Y.-B., et al.: Predicting protein–protein interactions from protein sequences by a stacked sparse autoencoder deep neural network. Mol. BioSyst. 13, 1336–1344 (2017)
You, Z.-H., Yu, J.-Z., Zhu, L., Li, S., Wen, Z.-K.: A MapReduce based parallel SVM for large-scale predicting protein–protein interactions. Neurocomputing 145, 37–43 (2014)
Hu, L., Wang, X., Huang, Y.-A., Hu, P., You, Z.-H.: A survey on computational models for predicting protein–protein interactions. Brief. Bioinform. (2021)
Lei, Y.-K., You, Z.-H., Dong, T., Jiang, Y.-X., Yang, J.-A.: Increasing reliability of protein interactome by fast manifold embedding. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 34, 372–379 (2013)
Li, Z.-W., You, Z.-H., Chen, X., Gui, J., Nie, R.: Highly accurate prediction of protein-protein interactions via incorporating evolutionary information and physicochemical characteristics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 17, 1396 (2016)
Zhu, L., You, Z.-H., Huang, D.-S., Wang, B.: t-LSE: a novel robust geometric approach for modeling protein-protein interaction networks. PLoS One 8, e58368 (2013)
Wang, Y., You, Z.-H., Yang, S., Li, X., Jiang, T.-H., Zhou, X.: A high efficient biological language model for predicting protein–protein interactions. Cells 8, 122 (2019)
Huang, Y.-A., You, Z.-H., Chen, X., Chan, K., Luo, X.: Sequence-based prediction of protein-protein interactions using weighted sparse representation model combined with global encoding. BMC Bioinform. 17, 1–11 (2016)
Wang, L., et al.: An ensemble approach for large-scale identification of protein-protein interactions using the alignments of multiple sequences. Oncotarget 8, 5149 (2017)
Chen, Z.-H., You, Z.-H., Zhang, W.-B., Wang, Y.-B., Cheng, L., Alghazzawi, D.: Global vectors representation of protein sequences and its application for predicting self-interacting proteins with multi-grained cascade forest model. Genes 10, 924 (2019)
Sun, T., Zhou, B., Lai, L., Pei, J.: Sequence-based prediction of protein protein interaction using a deep-learning algorithm. BMC Bioinform. 18, 1–8 (2017)
Skoblov, M., et al.: Protein partners of KCTD proteins provide insights about their functional roles in cell differentiation and vertebrate development. BioEssays 35, 586–596 (2013)
Xia, J.-F., Zhao, X.-M., Huang, D.-S.: Predicting protein–protein interactions from protein sequences using meta predictor. Amino Acids 39, 1595–1599 (2010)
Song, X.-Y., Chen, Z.-H., Sun, X.-Y., You, Z.-H., Li, L.-P., Zhao, Y.: An ensemble classifier with random projection for predicting protein–protein interactions using sequence and evolutionary information. Appl. Sci. 8, 89 (2018)
Wang, Y.-B., You, Z.-H., Li, X., Jiang, T.-H., Cheng, L., Chen, Z.-H.: Prediction of protein self-interactions using stacked long short-term memory from protein sequences information. BMC Syst. Biol. 12, 107–115 (2018)
You, Z.-H., Li, S., Gao, X., Luo, X., Ji, Z.: Large-scale protein-protein interactions detection by integrating big biosensing data with computational model. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014 (2014)
Yi, H.-C., You, Z.-H., Guo, Z.-H., Huang, D.-S., Chan, K.C.: Learning representation of molecules in association network for predicting intermolecular associations. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. (2020)
Tian, T., et al.: AgriGO v2. 0: a GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community, 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, W122–W129 (2017)
Zhu, G., et al.: PPIM: a protein-protein interaction database for maize. Plant Physiol. 170, 618–626 (2016)
Gribskov, M., McLachlan, A.D., Eisenberg, D.: Profile analysis: detection of distantly related proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 84, 4355–4358 (1987)
Li, Z.-W., et al.: Accurate prediction of protein-protein interactions by integrating potential evolutionary information embedded in PSSM profile and discriminative vector machine classifier. Oncotarget 8, 23638 (2017)
Zhu, H.-J., You, Z.-H., Shi, W.-L., Xu, S.-K., Jiang, T.-H., Zhuang, L.-H.: Improved prediction of protein-protein interactions using descriptors derived from PSSM via gray level co-occurrence matrix. IEEE Access 7, 49456–49465 (2019)
Wang, L., et al.: Using two-dimensional principal component analysis and rotation forest for prediction of protein-protein interactions. Sci. Rep. 8, 1–10 (2018)
Li, L.-P., Wang, Y.-B., You, Z.-H., Li, Y., An, J.-Y.: PCLPred: a bioinformatics method for predicting protein–protein interactions by combining relevance vector machine model with low-rank matrix approximation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 1029 (2018)
Altschul, S.F., Koonin, E.V.: Iterated profile searches with PSI-BLAST—a tool for discovery in protein databases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 23, 444–447 (1998)
Nussbaumer, H.J.: The fast Fourier transform. In: Fast Fourier Transform and Convolution Algorithms, pp. 80–111. Springer (1981)
Anitha, T., Ramachandran, S.: Novel algorithms for 2-D FFT and its inverse for image compression. In: 2013 International Conference on Signal Processing, Image Processing & Pattern Recognition, pp. 62–65. IEEE (2013)
Liao, B., Jiang, Y., Yuan, G., Zhu, W., Cai, L., Cao, Z.: Learning a weighted meta-sample based parameter free sparse representation classification for microarray data. PLoS One 9, e104314 (2014)
Wright, J., Yang, A.Y., Ganesh, A., Sastry, S.S., Ma, Y.: Robust face recognition via sparse representation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 31, 210–227 (2008)
Wang, J., Yang, J., Yu, K., Lv, F., Huang, T., Gong, Y.: Locality-constrained linear coding for image classification. In: 2010 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp. 3360–3367. IEEE (2010)
Sharma, A., Paliwal, K.K.: A deterministic approach to regularized linear discriminant analysis. Neurocomputing 151, 207–214 (2015)
Roweis, S.T., Saul, L.K.: Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science 290, 2323–2326 (2000)
Lu, C.-Y., Min, H., Gui, J., Zhu, L., Lei, Y.-K.: Face recognition via weighted sparse representation. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 24, 111–116 (2013)
Wong, L., You, Z.-H., Li, S., Huang, Y.-A., Liu, G.: Detection of protein-protein interactions from amino acid sequences using a rotation forest model with a novel PR-LPQ descriptor. In: International Conference on Intelligent Computing, pp. 713–720. Springer (2015)
Lei, Y.-K., You, Z.-H., Ji, Z., Zhu, L., Huang, D.-S.: Assessing and predicting protein interactions by combining manifold embedding with multiple information integration. In: BMC Bioinformatics, pp. 1–18. Springer (2012)
Zhu, L., You, Z.-H., Huang, D.-S.: Increasing the reliability of protein–protein interaction networks via non-convex semantic embedding. Neurocomputing 121, 99–107 (2013)
An, J.-Y., et al.: Identification of self-interacting proteins by exploring evolutionary information embedded in PSI-BLAST-constructed position specific scoring matrix. Oncotarget 7, 82440 (2016)
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant NO. 61722212 and Grant NO. 62002297.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Pan, J. et al. (2021). Computational Prediction of Protein-Protein Interactions in Plants Using Only Sequence Information. In: Huang, DS., Jo, KH., Li, J., Gribova, V., Bevilacqua, V. (eds) Intelligent Computing Theories and Application. ICIC 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12836. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84522-3_9
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-84522-3_9
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-84521-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-84522-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)