Abstract
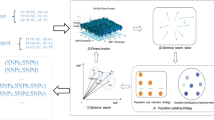
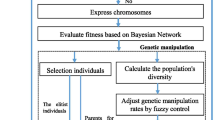
Detecting epistatic interaction between multiple single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) is crucial to identify susceptibility genes associated with complex human diseases. Stepwise search approaches have been extensively studied to greatly reduce the search space for follow-up SNP interactions detection. However, most of these stepwise methods are prone to filter out significant polymorphism combinations and thus have a low detection power. In this paper, we propose a two-stage approach called EpIntMC, which uses multiple clusterings to significantly shrink the search space and reduce the risk of filtering out significant combinations for the follow-up detection. EpIntMC firstly introduces a matrix factorization based approach to generate multiple diverse clusterings to group SNPs into different clusters from different aspects, which helps to more comprehensively explore the genotype data and reduce the chance of filtering out potential candidates overlooked by a single clustering. In the search stage, EpIntMC applies Entropy score to screen SNPs in each cluster, and uses Jaccard similarity to merge the most similar clusters into candidate sets. After that, EpIntMC uses exhaustive search on these candidate sets to precisely detect epsitatic interactions. Extensive simulation experiments show that EpIntMC has a higher (comparable) power than related competitive solutions, and results on Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium (WTCCC) dataset also expresses its effectiveness.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulrashid, K., AlHussaini, N., Ahmed, W., Thalib, L.: Prevalence of BRCA mutations among hereditary breast and/or ovarian cancer patients in Arab countries: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 19(1), 256 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5463-1
Albatineh, A.N., Niewiadomska-Bugaj, M.: Correcting Jaccard and other similarity indices for chance agreement in cluster analysis. Adv. Data Anal. Classif. 5(3), 179–200 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11634-011-0090-y
Bailey, J.: Alternative clustering analysis: a review. In: Data Clustering, pp. 535–550. Chapman and Hall/CRC (2018)
Balding, D.J.: A tutorial on statistical methods for population association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 7(10), 781 (2006)
Bermejo, J.L., et al.: Exploring the association between genetic variation in the SUMO isopeptidase gene USPL1 and breast cancer through integration of data from the population-based genica study and external genetic databases. Int. J. Cancer 133(2), 362–372 (2013)
Burton, P.R., et al.: Association scan of 14,500 nonsynonymous SNPs in four diseases identifies autoimmunity variants. Nat. Genet. 39(11), 1329 (2007)
Cao, X., Yu, G., Liu, J., Jia, L., Wang, J.: ClusterMI: detecting high-order SNP interactions based on clustering and mutual information. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19(8), 2267 (2018)
Cao, X., Yu, G., Ren, W., Guo, M., Wang, J.: DualWMDR: detecting epistatic interaction with dual screening and multifactor dimensionality reduction. Hum. Mutat. 40, 719–734 (2020)
Chattopadhyay, A.S., Hsiao, C.L., Chang, C.C., Lian, I.B., Fann, C.S.: Summarizing techniques that combine three non-parametric scores to detect disease-associated 2-way SNP-SNP interactions. Gene 533(1), 304–312 (2014)
Culverhouse, R., Suarez, B.K., Lin, J., Reich, T.: A perspective on epistasis: limits of models displaying no main effect. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 70(2), 461–471 (2002)
Ding, C.H., Li, T., Jordan, M.I.: Convex and semi-nonnegative matrix factorizations. TPAMI 32(1), 45–55 (2010)
Guo, X., Meng, Y., Yu, N., Pan, Y.: Cloud computing for detecting high-order genome-wide epistatic interaction via dynamic clustering. BMC Bioinform. 15(1), 102 (2014)
Jain, A.K., Murty, M.N., Flynn, P.J.: Data clustering: a review. ACM Comput. Surv. 31(3), 264–323 (1999)
Lee, H., Goodarzi, H., Tavazoie, S.F., Alarcón, C.R.: TMEM2 is a SOX4-regulated gene that mediates metastatic migration and invasion in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 76(17), 4994–5005 (2016)
Li, W., Reich, J.: A complete enumeration and classification of two-locus disease models. Hum. Hered. 50(6), 334–349 (2000)
Liu, J., Yu, G., Jiang, Y., Wang, J.: HiSeeker: detecting high-order SNP interactions based on pairwise SNP combinations. Genes 8(6), 153 (2017)
Ma, L., Runesha, H.B., Dvorkin, D., Garbe, J.R., Da, Y.: Parallel and serial computing tools for testing single-locus and epistatic SNP effects of quantitative traits in genome-wide association studies. BMC Bioinform. 9(1), 315 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-315
Mackay, T.F., Moore, J.H.: Why epistasis is important for tackling complex human disease genetics. Genome Med. 6(6), 42 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1186/gm561
Marchini, J., Donnelly, P., Cardon, L.R.: Genome-wide strategies for detecting multiple loci that influence complex diseases. Nat. Genet. 37(4), 413 (2005)
Moore, J.H., Asselbergs, F.W., Williams, S.M.: Bioinformatics challenges for genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics 26(4), 445–455 (2010)
Niel, C., Sinoquet, C., Dina, C., Rocheleau, G.: A survey about methods dedicated to epistasis detection. Front. Genet. 6, 285 (2015)
Ritchie, M.D., et al.: Multifactor-dimensionality reduction reveals high-order interactions among estrogen-metabolism genes in sporadic breast cancer. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 69(1), 138–147 (2001)
Sun, K., et al.: Oxidized ATM-mediated glycolysis enhancement in breast cancer-associated fibroblasts contributes to tumor invasion through lactate as metabolic coupling. EBioMedicine 41, 370–383 (2019)
Vivekanandhan, S., Mukhopadhyay, D.: Divergent roles of Plexin D1 in cancer. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 1872(1), 103–110 (2019)
Wan, X., et al.: BOOST: a fast approach to detecting gene-gene interactions in genome-wide case-control studies. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 87(3), 325–340 (2010)
Wang, J., Wang, X., Yu, G., Domeniconi, C., Yu, Z., Zhang, Z.: Discovering multiple co-clusterings with matrix factorization. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 99(1), 1–14 (2020)
Wang, X., Wang, J., Domeniconi, C., Yu, G., Xiao, G., Guo, M.: Multiple independent subspace clusterings. In: AAAI, pp. 5353–5360 (2019)
Wang, Y., Liu, X., Robbins, K., Rekaya, R.: AntEpiSeeker: detecting epistatic interactions for case-control studies using a two-stage ant colony optimization algorithm. BMC Res. Notes 3(1), 117 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-3-117
Wei, S., Wang, J., Yu, G., Zhang, X., et al.: Multi-view multiple clusterings using deep matrix factorization. In: AAAI, pp. 1–8 (2020)
Welter, D., et al.: The NHGRI GWAS catalog, a curated resource of SNP-trait associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 42(D1), D1001–D1006 (2013)
Xie, M., Li, J., Jiang, T.: Detecting genome-wide epistases based on the clustering of relatively frequent items. Bioinformatics 28(1), 5–12 (2011)
Yang, C.H., Chuang, L.Y., Lin, Y.D.: CMDR based differential evolution identifies the epistatic interaction in genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics 33(15), 2354–2362 (2017)
Yang, C.H., Chuang, L.Y., Lin, Y.D.: Multiobjective multifactor dimensionality reduction to detect SNP-SNP interactions. Bioinformatics 34(13), 2228–2236 (2018)
Yao, S., Yu, G., Wang, J., Domeniconi, C., Zhang, X.: Multi-view multiple clustering. In: IJCAI, pp. 4121–4127 (2019)
Yao, S., Yu, G., Wang, X., Wang, J., Domeniconi, C., Guo, M.: Discovering multiple co-clusterings in subspaces. In: SDM, pp. 423–431 (2019)
Zhang, Y., Liu, J.S.: Bayesian inference of epistatic interactions in case-control studies. Nat. Genet. 39(9), 1167 (2007)
Zou, H., Hastie, T.: Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net. J. Roy. Stat. Soc. B 67(2), 301–320 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by NSFC (61872300), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (XDJK2020B028 and XDJK2019B024), Natural Science Foundation of CQ CSTC (cstc2018jcyjAX0228).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Zhang, H., Yu, G., Ren, W., Guo, M., Wang, J. (2020). EpIntMC: Detecting Epistatic Interactions Using Multiple Clusterings. In: Cai, Z., Mandoiu, I., Narasimhan, G., Skums, P., Guo, X. (eds) Bioinformatics Research and Applications. ISBRA 2020. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 12304. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57821-3_6
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-57821-3_6
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-57820-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-57821-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)