Abstract
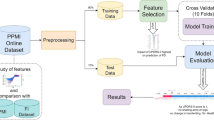
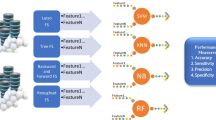
Detecting divergence between Neuro-degenerative diseases is essential for right treatment. This intelligent system is implemented through computational methods to predict the class of Neuro-degenerative disease (Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s or common) from the structural and physicochemical properties (1437 attributes respectively) of protein sequences extracted from genes. The Gene Set Enrichment Analysis database (GSEA db) was utilized to obtain the gene sets that contributed to the development of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. Optimal features for classification were obtained by applying Gain Ratio followed by Correlation-based Feature Selection (CFS) and Decremental Feature Selection (DFS) on extracted properties from Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) dataset for the GSEA database. The selected features are evaluated using Random Forest model. The Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS) was build which extract rules from the least sized Decision tree automatically and predict the type of Neuro-degenerative disorder as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease or common to both diseases. The CDSS predicts the disease with classification accuracy as 79.7% and Mathew’s Correlation Coefficient as 0.689.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brain Disorders by Numbers (for brain research at MIT) (2018). https://mcgovern.mit.edu/brain-disorders/by-the-numbers. Accessed 03 June 2018
Jacob, S.G., Athilakshmi, R.: Extraction of protein sequence features for prediction of neuro-degenerative brain disorders: Pioneering the CGAP database. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Informatics and Analytics, p. 30. ACM, August 2016
Shree, S.B., Sheshadri, H.S.: Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using rule based approach. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 9(13) (2016)
Shree, S.B., Sheshadri, H.S.: An initial investigation in the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease using various classification techniques. In: 2014 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research (ICCIC), pp. 1–5. IEEE, December 2014
Bind, S., Tiwari, A.K., Sahani, A.K., Koulibaly, P.M., Nobili, F., Pagani, M., Sabri, O., Borght, T.V., Laere, K.V., Tatsch, K.: A survey of machine learning based approaches for Parkinson disease prediction. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Inform. Technol. 6(2), 1648–1655 (2015)
Ramani, R.G., Sivagami, G.: Parkinson disease classification using data mining algorithms. Int. J. Comput. Appl. 32(9), 17–22 (2011)
Ramani, R.G., Jacob, S.G.: Improved classification of lung cancer tumors based on structural and physicochemical properties of proteins using data mining models. PLoS ONE 8(3), e58772 (2013)
Kaladhar, D.S.V.G.K., Pottumuthu, B.K., Rao, P.V.N., Vadlamudi, V., Chaitanya, A.K., Reddy, R.H.: The elements of statistical learning in colon cancer datasets: data mining, inference and prediction. Algorithms Res. 2(1), 8–17 (1926)
Hoogendoorn, M., Moons, L.M., Numans, M.E., Sips, R.J.: Utilizing data mining for predictive modeling of colorectal cancer using electronic medical records. In: International Conference on Brain Informatics and Health, pp. 132–141. Springer, Cham (2014)
KEGG dataset for neuro-degenerative diseases (2018). http://www.genome.jp/kegg-bin/gethtext?br08402.keg. Accessed 6 June 2018
Uniprot database Server, 22 June 2017. http://www.uniprot.org. Accessed 6 June 2018
PROFEAT web server (2018). http://bidd2.nus.edu.sg/cgi-bin/prof2015/prof_home.cgi. Accessed 05 June 2018
Han, J., Pei, J., Kamber, M.: Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques. Elsevier, New York (2011)
Karegowda, A.G., Manjunath, A.S., Jayaram, M.A.: Comparative study of attribute selection using gain ratio and correlation based feature selection. Int. J. Inf. Technol. Knowl. Manag. 2(2), 271–277 (2010)
Jacob, S.G., Ramani, R.G., Nancy, P.: Feature selection and classification in breast cancer datasets through data mining algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research (ICCIC 2011), Kanyakumari, India, IEEE Catalog Number: CFP1120 J-PRT, December 2011, ISBN 978-1
Hall, M.A.: Correlation-based feature selection for machine learning (1999)
Doshi, M.: Correlation based feature selection (Cfs) technique to predict student perfromance. Int. J. Comput. Networks Commun. 6(3), 197 (2014)
Richards, J.W., Eads, D., Bloom, J.S., Brink, H., Starr, D.: WiseRFTM: a fast and scalable Random Forest (2013)
Tejeswinee, K., Jacob, S.G.: Binary classification of cognitive disorders: investigation on the effects of protein sequence properties in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. In: IAENG-IMECS 2017, 166–170 (2017)
Implementing WEKA in java, 03 June 2018. https://weka.wikispaces.com/Use+WEKA+in+your+Java+code
Acknowledgements
This research work is part of project work funded by Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), Department of Science and Technology (DST) funded project under Young Scientist Scheme – Early Start-up Research Grant- titled “Investigation on the effect of Gene and Protein Mutants in the onset of Neuro-Degenerative Brain Disorders (Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease): A Computational Study” with Reference No- SERB – YSS/2015/000737.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2020 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Venkataramana, L., Jacob, S.G., Saraswathi, S., Athilakshmi, R. (2020). Clinical Decision Support System for Neuro-Degenerative Disorders: An Optimal Feature Selective Classifier and Identification of Predictor Markers. In: Abraham, A., Cherukuri, A.K., Melin, P., Gandhi, N. (eds) Intelligent Systems Design and Applications. ISDA 2018 2018. Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing, vol 940. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16657-1_2
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-16657-1_2
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-16656-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-16657-1
eBook Packages: Intelligent Technologies and RoboticsIntelligent Technologies and Robotics (R0)