Abstract
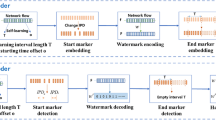
As the main active traffic analysis method, network flow watermarking (NFW) has been proven effective for flow correlation in anonymous communication system or stepping stone detection. In various types of network flow watermarking schemes, the interval-based ones can achieve significant better capability of resisting network interference. However, there still exists no work to give a comprehensive analysis of them, specifically on practicability as the implementation of NFW in Internet still remains a great challenge. In this paper, the existing interval-based NFW schemes are comparatively analyzed by benchmarking their performance on robustness, invisibility and practicability. Different from some prior work, we pay special attention to the practicability evaluation, which is related to time and storage overhead, communication and computation overhead, and the statistical model demand. Experimental results on CAIDA dataset give an overview of the existing interval-based NFW schemes.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dingledine, R., Mathewson, N., Syverson, P.F.: Tor: the second-generation onion router. Proc. Usenix Secur. Symp. 40(3), 191–212(2004)
Egger, C., Schlumberger, J., Kruegel, C., Vigna, G.: Practical attacks against the I2P network. In: Stolfo, S.J., Stavrou, A., Wright, C.V. (eds.) RAID 2013. LNCS, vol. 8145, pp. 432–451. Springer, Heidelberg (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-41284-4_22
Boyan, J,F.: The anonymizer: protecting user privacy on the web. Comput. Mediat. Commun. Mag. 4(9), 7–13 (1997)
Wang, X., Reeves, D.F.: The traceback problem. In: Traceback and Anonymity, pp. 5–13 (2015)
Lu, T., Guo, R., Zhao, L., et al.: A systematic review of network flow watermarking in anonymity systems. Int. J. Secur. Appl. 10(3), 129–138(2016)
Birth, O.C.: Correlated network flows detection. In: Network Architectures and Services, pp. 93–99 (2011)
Ramsbrock, D., Wang, X., Jiang, X.: A first step towards live botmaster traceback. In: Lippmann, R., Kirda, E., Trachtenberg, A. (eds.) RAID 2008. LNCS, vol. 5230, pp. 59–77. Springer, Heidelberg (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-87403-4_4
Wang, X., Reeves, D.S., Wu, S.F., Yuill, J.: Sleepy watermark tracing: an active network-based intrusion response framework. In: Dupuy, M., Paradinas, P. (eds.) SEC 2001. IIFIP, vol. 65, pp. 369–384. Springer, Boston, MA (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/0-306-46998-7_26
Lv, J., Zhang, T., Li, Z., et al.: Pacom: parasitic anonymous communication in the bittorrent network. Comput. Netw. 74, 13–33 (2014)
Yu, W., Fu, X., Graham, S., et al.: DSSS-based flow marking technique for invisible traceback. In: Security and Privacy, pp. 18–32(2007)
Houmansadr, A., Kiyavash, N., Borisov, N.F.: Non-blind watermarking of network flows. IEEE Trans. Netw. 22(4), 1232–1244 (2014)
Wang, X., Reeves, D.F.: Robust correlation of encrypted attack traffic through stepping stones by flow watermarking. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secure Comput. 8(3), 434–449 (2011)
Pyun, Y.J., Park, Y.H., Wang, X., et al.: Tracing traffic through intermediate hosts that repacketize flows. In: INFOCOM, pp. 634–642 (2007)
Houmansadr, A., Borisov, N.: F.: BotMosaic: collaborative network watermark for the detection of IRC-based botnets. J. Syst. Softw. 86(3), 707–715 (2013)
Wang, X., Chen, S., Jajodia, S.C.: Network flow watermarking attack on low latency anonymous communication systems, pp. 116–130. IEEE Computer Society (2007)
Wang, X., Luo, J., Yang, M.C.: A double interval centroid based watermark for network flow traceback. In: Computer Supported Cooperative Work, pp. 146–151 (2010)
Luo, J., Wang, X., Yang, M.F.: An interval centroid based spread spectrum watermarking scheme for multi-flow traceback. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 35(1), 60–71 (2010)
Houmansadr, A., Borisov, N.C.: SWIRL: a scalable watermark to detect correlated network flows. In: Network and Distributed System Security Symposium (2011)
Kiyavash, N., Houmansadr, A., Borisov, N.C.: Multi-flow attacks against network flow watermarking schemes. In: Usenix Security Symposium, pp. 307–320 (2008)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants nos. 61602247, 61702235, 61472188, and U1636117), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grants no. BK20160840 and BK20150472), CCF-VENUSTECH Foundation (Grant no. 2016011), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (30920140121006 and 30915012208).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2018 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper
Shi, J. et al. (2018). A Comprehensive Analysis of Interval Based Network Flow Watermarking. In: Sun, X., Pan, Z., Bertino, E. (eds) Cloud Computing and Security. ICCCS 2018. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 11066. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00015-8_7
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00015-8_7
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-030-00014-1
Online ISBN: 978-3-030-00015-8
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)