Abstract
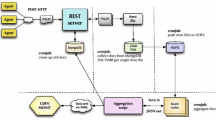
We have developed a Web-based architecture and user interface for archiving and manipulating results of numerical simulations being generated by the UK Turbulence Consortium on the United Kingdom’s new national scientific supercomputing resource. These simulations produce large datasets, requiring Web-based mechanisms for storage, searching and retrieval of simulation results in the hundreds of gigabytes range. We demonstrate that the new DATALINK type, defined in the draft SQL Management of External Data Standard, which facilitates database management of distributed external data, can help to overcome problems associated with limited bandwidth. We show that a database can meet the apparently divergent requirements of storing both the relatively small simulation result metadata, and the large result files, in a unified way, whilst maintaining database security, recovery and integrity. By managing data in this distributed way, the system allows post-processing of archived simulation results to be performed directly without the cost of having to rematerialise to files. This distribution also reduces access bottlenecks and processor loading. We also show that separating the user interface specification from the user interface processing can provide a number of advantages. We provide a tool to generate automatically a default user interface specification, in the form of an XML document, for a given database. The XML document can be customised to change the appearance of the interface. Our architecture can archive not only data in a distributed fashion, but also applications. These applications are loosely coupled to the datasets (in a many-to-many relationship) via XML defined interfaces. They provide reusable server-side post-processing operations such as data reduction and visualisation.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sandham, N.D. and Howard, R.J.A. Direct Simulation of Turbulence Using Massively Parallel Computers. In: A. Ecer et al., eds. Parallel Computational Fluid Dynamics’ 97, Elsevier, 1997.
Williams, R., Bunn, J., Reagan, M., and Pool, C., T. Workshop on Interfaces to Scientific Data Achives, California, USA, 25–27 March, 1998, Technical Report CACR-160, CALTECH, 42pp.
Eisenberg, A. and Melton, J., SQL:1999, formerly known as SQL3. SIGMOD Record, 28(1), March, 1999.
Mattos, N., Melton, J. and Richey, J. Database Language SQL-Part 9:Management of External Data (SQL/MED), ISO/IEC Committee Draft, CD 9075-9, December, 1988. ftp://jerry.ece.umassd.edu/isowg3/dbl/YGJdocs/ygj023.pdf
Jim Bray, J., Paoli, J. and Sperberg-McQueen, C., M. eds. Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0, W3C Recommendation, 10 February, 1998. http://www.w3.org/TR/REC-xml
Zloof M.M. Query By Example. American Federation of Information Processing (AFIPS) Conf. Proc., Vol. 44, National Computer Conference, 1975, 431–8.
Manber, U. Future Directions and Research Problems in the World Wide Web. Proc ACM SIGMOD Conf., Montreal, Canada, June 3–5, 1996, 213–15.
Warren, M., S., et al. Avalon: An Alpha/Linux Cluster Achieves 10 Gflops for $150k. Gordon Bell Price/Performance Prize, Supercomputing 1998. http://cnls.lanl.gov/avalon/
Davidson, J., D., and Ahmed, S. Java Servlet API Specification, Version 2.1a, November, 1988. http://java.sun.com/products/Servlet/index.html
White, S., Hapner, M. JDBC 2.0 API, Sun Microsystems Inc., Version 1.0, May, 1998.
Haw D., Goble, C., A., and Rector, A., L. GUIDANCE: Making it easy for the user to be an expert. Proc. 2nd Int. workshop on User Interfaces to Databases, Ambleside, UK, 13–15th July, 1994, 19–44.
McGrath, R., E. A Scientific Data Server: The Conceptual Design. White Paper, NCSA, University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign, January, 1997.
Catarci, T., Costabile, M., F., Levialdi, S., and Batini, C. Visual Query Systems for Databases: A Survey. Journal of Visual Languages and Computing, 8, 1997, 215–60.
Carey, M., J., Haas, L., M., Maganty, V., and Williams, J., H. PESTO: An Integrated Query/Browser for Object Databases. Proc. VLDB Int. Conf., India, 3–6 September, 1996, 203–14.
Yaeger, N. A Web Based Scientific Data Access Service: The Central Component of a Lightweight Data Archive, National Center for Supercomputing Applications, University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign. http://hopi.ncsa.uiuc.edu/sdb/sdb.html
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2000 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Papiani, M., Wason, J.L., Nicole, D.A. (2000). An Architecture for Archiving and Post-Processing Large, Distributed, Scientific Data Using SQL/MED and XML. In: Zaniolo, C., Lockemann, P.C., Scholl, M.H., Grust, T. (eds) Advances in Database Technology — EDBT 2000. EDBT 2000. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 1777. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-46439-5_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-46439-5_31
Published:
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-67227-2
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-46439-6
eBook Packages: Springer Book Archive