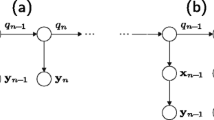
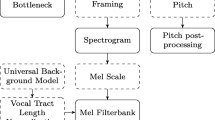
Abstract
More than ten years ago the first successful application of a nonlinear oscillator model to high-quality speech signal processing was reported (Kubin and Kleijn, 1994). Since then, numerous developments have been initiated to turn nonlinear oscillators into a standard tool for speech technology. The present contribution will review and compare several of these attempts with a special emphasis on adaptive model identification from data and the approaches to the associated machine learning problems. This includes Bayesian methods for the regularization of the parameter estimation problem (including the pruning of irrelevant parameters) and Ansatz library (Lainscsek et al., 2001) based methods (structure selection of the model). We conclude with the observation that these advanced identification methods need to be combined with a thorough background from speech science to succeed in practical modeling tasks.
This chapter corresponds to talks given at the Cost 277 summerschool at IIASS in Vietri sul Mare (IT), in Sept. 2004. We would sincerely like to thank Anna Esposito for organizing the summerschool, and for her patience editing this publication.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kubin, G.: Nonlinear processing of speech. In: Kleijn, W.B., Paliwal, K.K. (eds.) Speech Coding and Synthesis, pp. 557–610. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1995)
Kubin, G.: Synthesis and coding of continuous speech with the nonlinear oscillator model. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Atlanta, GA, pp. 267–270 (1996)
Kubin, G., Kleijn, W.B.: Time-scale modification of speech based on a nonlinear oscillator model. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Adelaide, South Australia, vol. 1, pp. 453–456 (1994)
Sauer, T.: A noise reduction method for signals from nonlinear systems. Physica D 52, 193–201 (1992)
Hegger, R., Kantz, H., Matassini, L.: Noise reduction for human speech signals by local projection in embedding spaces. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems 48, 1454–1461 (2001)
Terez, D.E.: Robust pitch determination using nonlinear state-space embedding. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Orlando, FL, USA, vol. 1, pp. 345–348 (2002)
Mann, I., McLaughlin, S.: A nonlinear algorithm for epoch marking in speech signals using Poincaré maps. In: Proceedings of the European Signal Processing Conference, vol. 2, pp. 701–704 (1998)
Lindgren, A.C., Johnson, M.T., Povinelli, R.J.: Joint frequency domain and reconstructed phase space features for speech recognition. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Montreal, Quebec, Canada. 1, pp. 533–536 (2004)
Birgmeier, M.: A fully Kalman-trained radial basis function network for nonlinear speech modeling. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks, Perth, Australia, pp. 259–264 (1995)
Kubin, G.: Synthesis and coding of continuous speech with the nonlinear oscillator model. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Atlanta (GA), vol. 1, pp. 267–270 (1996)
Haas, H., Kubin, G.: A multi-band nonlinear oscillator model for speech. In: Proceedings of the 32nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA (1998)
Mann, I., McLaughlin, S.: Stable speech synthesis using recurrent radial basis functions. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Speech Communication and Technology, Budapest, Hungary, vol. 5, pp. 2315–2318 (1999)
Narasimhan, K., Pr´ıncipe, J.C., Childers, D.G.: Nonlinear dynamic modeling of the voiced excitation for improved speech synthesis. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Phoenix, Arizona, pp. 389–392 (1999)
Rank, E., Kubin, G.: Nonlinear synthesis of vowels in the LP residual domain with a regularized RBF network. In: Mira, J., Prieto, A.G. (eds.) IWANN 2001. LNCS, vol. 2085, pp. 746–753. Springer, Heidelberg (2001) part II
Mann, I., McLaughlin, S.: Synthesising natural-sounding vowels using a nonlinear dynamical model. Signal Processing 81, 1743–1756 (2001)
Rank, E.: Application of Bayesian trained RBF networks to nonlinear time-series modeling. Signal Processing 83, 1393–1410 (2003)
Takens, F.: Detecting strange attractors in turbulence. In: Steffens, P. (ed.) EAMT-WS 1993. LNCS, vol. 898, p. 366. Springer, Heidelberg (1995)
Sauer, T., Yorke, J.A., Casdagli, M.: Embedology. Journal of Statistical Physics 65, 579–616 (1991)
Haykin, S., Príncipe, J.: Making sense of a complex world. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 15, 66–81 (1998)
Judd, K., Mees, A.: Embedding as a modeling problem. Physica D 120, 273–286 (1998)
Bernhard, H.P.: The Mutual Information Function and its Application to Signal Processing. PhD thesis, Vienna University of Technology (1997)
Hegger, R., Kantz, H., Schreiber, T.: Practical implementation of nonlinear time series methods: The TISEAN package. CHAOS 9, 413–435 (1999)
Bernhard, H.P., Kubin, G.: Detection of chaotic behaviour in speech signals using Fraser’s mutual information algorithm. In: Proc. 13th GRETSI Symp. Signal and Image Process, Juan-les-Pins, France, pp. 1301–1311 (1991)
Mann, I.: An Investigation of Nonlinear Speech Synthesis and Pitch Modification Techniques. PhD thesis, University of Edinburgh (1999)
Rank, E., Kubin, G.: Nonlinear synthesis of vowels in the LP residual domain with a regularized RBF network. In: Mira, J., Prieto, A.G. (eds.) IWANN 2001. LNCS, vol. 2085, pp. 746–753. Springer, Heidelberg (2001) part II
Li, J., Zhang, B., Lin, F.: Nonlinear speech model based on support vector machine and wavelet transform. In: Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI 2003), Sacramento, CA, pp. 259–264 (2003)
Haas, H., Kubin, G.: A multi-band nonlinear oscillator model for speech. In: Proc. 32nd Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems, and Computers, Pacific Grove, CA (1998)
Townshend, B.: Nonlinear prediction of speech. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, pp. 425–428 (1991)
Tikhonov, A.N., Arsenin, V.Y.: Solutions of Ill-posed Problems. W.H. Winston (1977)
Poggio, T., Girosi, F.: A theory of networks for approximation and learning. A.I. Memo 1140, Massachusetts Institute of Technology (1989)
Stone, M.: Cross-validation choice and assessment of statistical predictions. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B 36, 111–147 (1974)
MacKay, D.J.: Bayesian interpolation. Neural Computation 4, 415–447 (1992)
MacKay, D.J.: A practical Bayesian framework for backprop networks. Neural Computation 4, 448–472 (1992)
MacKay, D.J.: The evidence framework applied to classification networks. Neural Computation 4, 698–714 (1992)
Dempster, A.P., Laird, N.M., Rubin, D.B.: Maximum likelyhood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B 39, 1–38 (1977)
Tipping, M.E.: Sparse Bayesian learning and the relevance vector machine. Journal of Machine Learning Research 1, 211–244 (2001)
Fant, G., Liljencrants, J., Lin, Q.G.: A four parameter model of glottal flow. Quarterly Progress Status Report 4, Speech Transmission Laboratory/Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, Sweden (1985)
Köppl, H., Kubin, G., Paoli, G.: Bayesian methods for sparse RLS adaptive filters. Thirty-Seventh IEEE Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers 2, 1273–1277 (2003)
Kubin, G., Atal, B.S., Kleijn, W.B.: Performance of noise excitation for unvoiced speech. In: Proc. IEEE Workshop on Speech Coding for Telecommunication, St.Jovite, Québec, Canada, pp. 1–2 (1993)
Holm, S.: Automatic generation of mixed excitation in a linear predictive speech synthesizer. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Atlanta (GA), vol. 6, pp. 118–120 (1981)
Hermes, D.J.: Synthesis of breathy vowels: Some research methods. Speech Communication 10, 497–502 (1991)
Skoglund, J., Kleijn, W.B.: On the significance of temporal masking in speech coding. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Spoken Language Processing, Sydney, vol. 5, pp. 1791–1794 (1998)
Jackson, P.J., Shadle, C.H.: Aero-acoustic modelling of voiced and unvoiced fricatives based on MRI data. In: Proceedings of 5th Speech Production Seminar, Kloster Seeon, Germany, pp. 185–188 (2000)
Jackson, P.J., Shadle, C.H.: Frication noise modulated by voicing, as revealed by pitch-scaled decomposition. Journal of the Acoustic Society of America 108, 1421–1434 (2000)
Stylianou, Y., Laroche, J., Moulines, E.: High-quality speech modification based on a harmonic + noise model. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Speech Communication and Technology, Madrid, Spain, pp. 451–454 (1995)
Bailly, G.: A parametric harmonic+noise model. In: Keller, E., Bailly, G., Monaghan, A., Terken, J., Huckvale, M. (eds.) Improvements in Speech Synthesis, pp. 22–38. Wiley, Chichester (2002)
Rank, E., Kubin, G.: An oscillator-plus-noise model for speech synthesis. Speech Communication, Accepted for publication (2005)
Lu, H.L., Smith, I.J.O.: Glottal source modeling for singing voice. In: Proc. International Computer Music Conference, Berlin, Germany, pp. 90–97 (2000)
Lainscsek, C., Letellier, C., Schürrer, F.: Ansatz library for global modeling with a structure selection. Physical Review E 64, 016206:1–15 (2001)
Lainscsek, C., Letellier, C., Gorodnitsky, I.: Global modeling of the Rössler system from the z-variable. Physics Letters A 314(5-6), 127–409 (2003)
Judd, K., Mees, A.: On selecting models for nonlinear time series. Physica D 82, 426–444 (1995)
Gouesbet, G., Letellier, C.: Global vector-field reconstruction by using a multivariate polynomial l2 approximation on nets. Phys. Rev. E 49, 4955 (1994)
Press, W., Flannery, B., Teukolsky, S., Vetterling, W.: Numerical Recipes in C. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1990)
Lainscsek, C., Gorodnitsky, I.: Ansatz libraries for systems with quadratic and cubic non-linearities (2002), http://cloe.ucsd.edu/claudia/posterDD2002.pdf
Eichhorn, R., Linz, S., Hänggi, P.: Transformations of nonlinear dynamical systems to jerky motion and its application to minimal chaotic flows. Physical Review E 58 (6), 7151–7164 (1998)
Goldberg, D.: Genetic Algorithms in Search, Optimization and Machine Learning. Addison-Wesley, Reading (1998)
Holland, J.H.: Adaptation in natural and artificial systems. MIT Press, Cambridge (1992)
Ishizaka, K., Flanagan, J.L.: Synthesis of voiced sounds from a two-mass model of the vocal cords. Bell Systems Technical Journal 51, 1233–1267 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2005 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Kubin, G., Lainscsek, C., Rank, E. (2005). Identification of Nonlinear Oscillator Models for Speech Analysis and Synthesis. In: Chollet, G., Esposito, A., Faundez-Zanuy, M., Marinaro, M. (eds) Nonlinear Speech Modeling and Applications. NN 2004. Lecture Notes in Computer Science(), vol 3445. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/11520153_5
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/11520153_5
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-540-27441-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-540-31886-6
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)