Lating-gí
Guā-māu
(Tùi Latin-gí choán--lâi)
| Lating-gú | |
|---|---|
| lingua Latīna | |
 | |
| Hoat-im | [laˈtiːna] |
| Goân-chū kok-ka | |
| Sú-iōng tē-khu | Originally in the Italian Peninsula, and the zone of influence of the Roman Empire. Today, it is official in Vatican City, although Italian is the working language there. |
| Bîn-cho̍k | Latins, Romans |
| Era | 7th century BC Pang-bô͘:Endash 18th century AD |
| Gí-hē |
Indo-European
|
| Bûn-jī hē-thóng | Latin alphabet |
| Koaⁿ-hong tē-ūi | |
| Koaⁿ-hong gí-giân |
|
| Koán-lí ki-kò͘ |
|
| Gí-giân tāi-bé | |
| ISO 639-1 |
la |
| ISO 639-2 |
lat |
| ISO 639-3 |
lat |
| Glottolog |
impe1234lati1261 |
| Linguasphere |
51-AAB-aa to 51-AAB-ac |
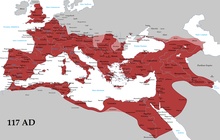 Map indicating the greatest extent of the Roman Empire under Emperor Trajan (c. 117 AD) and the area governed by Latin speakers (dark red). Many languages other than Latin were spoken within the empire. | |
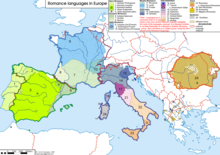 Range of the Romance languages, the modern descendants of Latin, in Europe. | |
Lating-gí (Lingua Latina), he̍k-chiá La-teng-gí, Lat-teng-gí[2], Lia̍p-teng-gí[3], sī chi̍t-chióng kó͘-chá Roma-lâng kóng ê gí-giân. Roma Thian-chú-kàu Kàu-hoē chit-má tī chèng-sek to͘-ha̍p iû-goân ēng Lating-gí, só͘-í i sī Vaticano ê koaⁿ-hong gí-giân.
Kho-ha̍k kap i-ha̍k ū chiâⁿ chē jī-sû sī Latin-gí. Hiān-tāi ê gí-giân mā ū chiâⁿ chē sī ùi Latin-gí lâi--ê, chhin-chhiūⁿ Se-pan-gâ-gí, Portugal-gí, Hoat-gí, Italia-gí kap Romania-gí.
Chham-khó
[siu-kái | kái goân-sí-bé]- ↑ "Schools". Encyclopædia Britannica. 24 (11 pán.). 1911. pp. 363–376.
- ↑ John Macgowan (1883). "Latin". English and Chinese dictionary of the Amoy dialect.
拉丁 Lat teng
- ↑ Thomas Barclay (1923). "拉". Supplement to Dictionary of the Vernacular or Spoken Language of Amoy.
lia̍p-teng, Latin.
Gōa-pō͘ liân-kiat
[siu-kái | kái goân-sí-bé]
| Pún bûn-chiuⁿ sī chi̍t phiⁿ phí-á-kiáⁿ. Lí thang tàu khok-chhiong lâi pang-chō͘ Wikipedia. |



