Identification of a novel mitochondria-localized LKB1 variant required for the regulation of the oxidative stress response
- PMID: 37302555
- PMCID: PMC10404683
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104906
Identification of a novel mitochondria-localized LKB1 variant required for the regulation of the oxidative stress response
Abstract
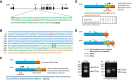
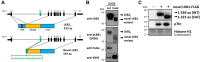
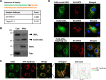
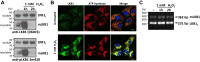
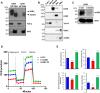
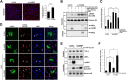
The tumor suppressor Liver Kinase B1 (LKB1) is a multifunctional serine/threonine protein kinase that regulates cell metabolism, polarity, and growth and is associated with Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome and cancer predisposition. The LKB1 gene comprises 10 exons and 9 introns. Three spliced LKB1 variants have been documented, and they reside mainly in the cytoplasm, although two possess a nuclear-localization sequence (NLS) and are able to shuttle into the nucleus. Here, we report the identification of a fourth and novel LKB1 isoform that is, interestingly, targeted to the mitochondria. We show that this mitochondria-localized LKB1 (mLKB1) is generated from alternative splicing in the 5' region of the transcript and translated from an alternative initiation codon encoded by a previously unknown exon 1b (131 bp) hidden within the long intron 1 of LKB1 gene. We found by replacing the N-terminal NLS of the canonical LKB1 isoform, the N-terminus of the alternatively spliced mLKB1 variant encodes a mitochondrial transit peptide that allows it to localize to the mitochondria. We further demonstrate that mLKB1 colocalizes histologically with mitochondria-resident ATP Synthase and NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin-3, mitochondrial (SIRT3) and that its expression is rapidly and transiently upregulated by oxidative stress. We conclude that this novel LKB1 isoform, mLKB1, plays a critical role in regulating mitochondrial metabolic activity and oxidative stress response.
Keywords: DNA damage; cellular localization; exon; intron; isoforms; mitochondrial respiration.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Characterization of the murine SIRT3 mitochondrial localization sequence and comparison of mitochondrial enrichment and deacetylase activity of long and short SIRT3 isoforms.J Cell Biochem. 2010 May;110(1):238-47. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22531. J Cell Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20235147 Free PMC article.
-
LKB1, a novel serine/threonine protein kinase and potential tumour suppressor, is phosphorylated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) and prenylated in vivo.Biochem J. 2000 Feb 1;345 Pt 3(Pt 3):673-80. Biochem J. 2000. PMID: 10642527 Free PMC article.
-
Resveratrol-induced Sirt1 phosphorylation by LKB1 mediates mitochondrial metabolism.J Biol Chem. 2021 Aug;297(2):100929. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100929. Epub 2021 Jul 1. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34216621 Free PMC article.
-
LKB1 biology: assessing the therapeutic relevancy of LKB1 inhibitors.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jun 6;22(1):310. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01689-5. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38844908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AMPKα-like proteins as LKB1 downstream targets in cell physiology and cancer.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 May;99(5):651-662. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02040-y. Epub 2021 Mar 4. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33661342 Review.
Cited by
-
Alternative splicing analysis of lignocellulose-degrading enzyme genes and enzyme variants in Aspergillus niger.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Apr 19;108(1):302. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13137-y. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38639796 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hezel A.F., Bardeesy N. LKB1; linking cell structure and tumor suppression. Oncogene. 2008;27:6908–6919. - PubMed
-
- Jansen M., Ten Klooster J.P., Offerhaus G.J., Clevers H. LKB1 and AMPK family signaling: the intimate link between cell polarity and energy metabolism. Physiol. Rev. 2009;89:777–798. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


