Cardiac safety analysis of anti-HER2-targeted therapy in early breast cancer
- PMID: 35995984
- PMCID: PMC9395410
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-18342-1
Cardiac safety analysis of anti-HER2-targeted therapy in early breast cancer
Abstract
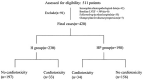
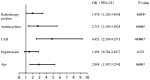
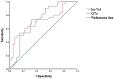
To evaluate the cardiac safety of anti-HER2-targeted therapy for early breast cancer; to investigate whether trastuzumab combined with pertuzumab increases cardiac toxicity compared with trastuzumab; to evaluate the predictive value of high-sensitivity Troponin (hs-TnI) and QTc for the cardiotoxicity associated with anti-HER2 targeted therapy in early breast cancer. A total of 420 patients with early-stage HER2-positive breast cancer who received trastuzumab or trastuzumab combined with pertuzumab for more than half a year in Tianjin Medical University Cancer Hospital from January 2018 to February 2021 were included. Left ventricle ejection fraction (LVEF), hs-TnI values, and QTc were measured at baseline and 3, 6, 9, 12 months. Cardiotoxicity was defined as a decrease in LVEF of at least 10 percentage points from baseline on follow-up echocardiography. Cardiotoxicity developed in 67 of the 420 patients (15.9%) and all patients had LVEF above 50% before and after treatment. The incidence of cardiotoxicity in trastuzumab and trastuzumab combined with pertuzumab was 14.3% and 17.9%, respectively (P > 0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that age, coronary heart disease, left chest wall radiotherapy, and anthracyclines sequential therapy were independent risk factors for cardiotoxicity (P < 0.05). The value of hs-TnI and QTc at the end of treatment (12th month) were selected for ROC curve prediction analysis and the area under the ROC curve was 0.724 and 0.713, respectively, which was significantly different from the area of 0.5 (P < 0.05). The decrease of LVEF in the study was mostly asymptomatic, from the heart safety point of view, the anti-HER2 targeted therapy for early breast cancer was well tolerated. Trastuzumab combined with pertuzumab did not significantly increase cardiotoxicity. However, subgroup analysis suggests that in the presence of coronary artery disease (CAD) and sequential treatment with anthracene, trastuzumab and pertuzumab may increase the cardiac burden compared with trastuzumab. Hs-TnI and QTc may be useful in monitoring and predicting cardiotoxicity associated with anti-HER2 targeted therapy for early breast cancer.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiac Safety of Paclitaxel Plus Trastuzumab and Pertuzumab in Patients With HER2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer.Oncologist. 2016 Apr;21(4):418-24. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2015-0321. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Oncologist. 2016. PMID: 26984450 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cardiac Safety of Dual Anti-HER2 Therapy in the Neoadjuvant Setting for Treatment of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer.Oncologist. 2017 Jun;22(6):642-647. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0406. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28341761 Free PMC article.
-
Deceleration capacity of heart rate predicts trastuzumab-related cardiotoxicity in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer: A prospective observational study.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2021 Feb;46(1):93-98. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13258. Epub 2020 Sep 25. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2021. PMID: 32975332
-
Cardiotoxicity of novel HER2-targeted therapies.Curr Med Res Opin. 2013 Aug;29(8):1015-24. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2013.807232. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013. PMID: 23692263 Review.
-
Trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity: a review of clinical risk factors, pharmacologic prevention, and cardiotoxicity of other HER2-directed therapies.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jul;188(1):21-36. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06280-x. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34115243 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting the Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone System (RAAS) for Cardiovascular Protection and Enhanced Oncological Outcomes: Review.Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2024 Nov;25(11):1406-1427. doi: 10.1007/s11864-024-01270-9. Epub 2024 Oct 18. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39422794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Troponin Elevation in Asymptomatic Cancer Patients: Unveiling Connections and Clinical Implications.Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2024 Dec;21(6):505-514. doi: 10.1007/s11897-024-00681-x. Epub 2024 Sep 10. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2024. PMID: 39254897 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Depicting Biomarkers for HER2-Inhibitor Resistance: Implication for Therapy in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 24;16(15):2635. doi: 10.3390/cancers16152635. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39123362 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Updates on the mechanisms of toxicities associated with monoclonal antibodies targeting growth factor signaling and immune cells in cancer.Toxicol Res. 2024 Apr 22;40(3):335-348. doi: 10.1007/s43188-024-00233-4. eCollection 2024 Jul. Toxicol Res. 2024. PMID: 38911540 Review.
-
New Insights in the Era of Clinical Biomarkers as Potential Predictors of Systemic Therapy-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Women with Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 22;15(13):3290. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133290. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444400 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021;71:209–249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous