Biomarkers of Trastuzumab-Induced Cardiac Toxicity in HER2- Positive Breast Cancer Patient Population
- PMID: 35884413
- PMCID: PMC9313458
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14143353
Biomarkers of Trastuzumab-Induced Cardiac Toxicity in HER2- Positive Breast Cancer Patient Population
Abstract
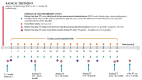
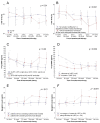
Trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity (TIC) can lead to early treatment discontinuation. The aim of this study was to evaluate: N-terminal brain natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP), creatine kinase-MB (CK-MB), myoglobin, and selected biochemical and clinical factors as predictors of TIC. One hundred and thirty patients with HER2-positive BC receiving adjuvant trastuzumab therapy (TT) were enrolled. Measurement of cardiac markers and biochemical tests as well as echocardiography were performed prior to TT initiation and every three months thereafter. Cardiotoxicity leading to treatment interruption occurred in 24 patients (18.5%). While cardiotoxicity caused early treatment discontinuation in 14 patients (10.8%), the TIC resolved in 10 (7.7%) and TT was resumed. The most common complication was a decrease in left ventricular ejection fraction of more than 10% from baseline or below 50% (7.7%). In patients with TIC, there was no increase in the levels of NT-proBNP, myoglobin, and CK-MB. BMI, hypertension, ischemic heart disease, diabetes, age, cancer stage, type of surgery, use of radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and hormone therapy were shown to not have an effect on TIC occurrence. NT-proBNP, myoglobin, and CK-MB are not predictors of TIC. There is an ongoing need to identify biomarkers for TIC.
Keywords: HER-2 positive breast cancer; cardiac markers; cardio-oncology; cardiotoxicity; trastuzumab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Delta NT-proBNP predicts cardiotoxicity in HER2-positive breast cancer patients treated with trastuzumab.Acta Oncol. 2021 Apr;60(4):475-481. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2020.1842904. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Acta Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33191817
-
NT-proBNP correlates with LVEF decline in HER2-positive breast cancer patients treated with trastuzumab.Cardiooncology. 2019 May 28;5:4. doi: 10.1186/s40959-019-0039-4. eCollection 2019. Cardiooncology. 2019. PMID: 32154011 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the long term cardiac effects associated with 9 and 52 weeks of trastuzumab in HER2-positive early breast cancer.Curr Med Res Opin. 2015 Mar;31(3):547-56. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2015.1005834. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Curr Med Res Opin. 2015. PMID: 25586297
-
Trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity: a review of clinical risk factors, pharmacologic prevention, and cardiotoxicity of other HER2-directed therapies.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jul;188(1):21-36. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06280-x. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 34115243 Review.
-
Cardiotoxicity of novel HER2-targeted therapies.Curr Med Res Opin. 2013 Aug;29(8):1015-24. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2013.807232. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Curr Med Res Opin. 2013. PMID: 23692263 Review.
Cited by
-
Proposed framework regarding management of patients with breast cancer and anti-cancer treatment-related elevation in cardiac troponin.Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024 Oct 17;55:101522. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2024.101522. eCollection 2024 Dec. Int J Cardiol Heart Vasc. 2024. PMID: 39498346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictors of trastuzumab-induced cardiotoxicity among racially and ethnically diverse patients with HER2-positive breast cancer.Cardiooncology. 2024 Oct 12;10(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s40959-024-00272-8. Cardiooncology. 2024. PMID: 39396009 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Prediction, Diagnosis and Management of a Breast Cancer Patient with Treatment-Related Cardiovascular Toxicity: An Essential Overview.Cancers (Basel). 2024 May 11;16(10):1845. doi: 10.3390/cancers16101845. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38791923 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mutation of PTEN: Loss and Likelihood of Being a Non-responder to Trastuzumab in a Sample of Iraqi Her2+ Breast Cancer Patients.Cureus. 2024 Feb 23;16(2):e54765. doi: 10.7759/cureus.54765. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38524002 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal Imaging of Cancer Therapy-Related Cardiac Dysfunction in Breast Cancer-A State-of-the-Art Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Sep 29;12(19):6295. doi: 10.3390/jcm12196295. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37834939 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous


