A Novel Deep Learning Method for Recognition and Classification of Brain Tumors from MRI Images
- PMID: 33919358
- PMCID: PMC8143310
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics11050744
A Novel Deep Learning Method for Recognition and Classification of Brain Tumors from MRI Images
Abstract
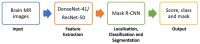
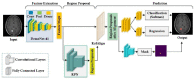
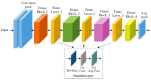
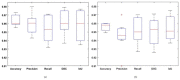
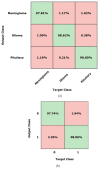
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth in brain cells that causes damage to various blood vessels and nerves in the human body. An earlier and accurate diagnosis of the brain tumor is of foremost important to avoid future complications. Precise segmentation of brain tumors provides a basis for surgical planning and treatment to doctors. Manual detection using MRI images is computationally complex in cases where the survival of the patient is dependent on timely treatment, and the performance relies on domain expertise. Therefore, computerized detection of tumors is still a challenging task due to significant variations in their location and structure, i.e., irregular shapes and ambiguous boundaries. In this study, we propose a custom Mask Region-based Convolution neural network (Mask RCNN) with a densenet-41 backbone architecture that is trained via transfer learning for precise classification and segmentation of brain tumors. Our method is evaluated on two different benchmark datasets using various quantitative measures. Comparative results show that the custom Mask-RCNN can more precisely detect tumor locations using bounding boxes and return segmentation masks to provide exact tumor regions. Our proposed model achieved an accuracy of 96.3% and 98.34% for segmentation and classification respectively, demonstrating enhanced robustness compared to state-of-the-art approaches.
Keywords: MRI; Mask-RCNN; brain tumor; deep learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Analysis of Brain MRI Images Using Improved CornerNet Approach.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Oct 8;11(10):1856. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11101856. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34679554 Free PMC article.
-
Mass Detection and Segmentation in Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Using 3D-Mask Region-Based Convolutional Neural Network: A Comparative Analysis.Front Mol Biosci. 2020 Nov 11;7:599333. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.599333. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Biosci. 2020. PMID: 33263004 Free PMC article.
-
Melanoma lesion detection and segmentation using deep region based convolutional neural network and fuzzy C-means clustering.Int J Med Inform. 2019 Apr;124:37-48. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.01.005. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Int J Med Inform. 2019. PMID: 30784425
-
Fully Automated Skull Stripping from Brain Magnetic Resonance Images Using Mask RCNN-Based Deep Learning Neural Networks.Brain Sci. 2023 Aug 28;13(9):1255. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13091255. Brain Sci. 2023. PMID: 37759856 Free PMC article.
-
VoxResNet: Deep voxelwise residual networks for brain segmentation from 3D MR images.Neuroimage. 2018 Apr 15;170:446-455. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.04.041. Epub 2017 Apr 23. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 28445774 Review.
Cited by
-
Trade-off between training and testing ratio in machine learning for medical image processing.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024 Sep 6;10:e2245. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.2245. eCollection 2024. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2024. PMID: 39314694 Free PMC article.
-
ContourTL-Net: Contour-Based Transfer Learning Algorithm for Early-Stage Brain Tumor Detection.Int J Biomed Imaging. 2024 Apr 29;2024:6347920. doi: 10.1155/2024/6347920. eCollection 2024. Int J Biomed Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38716037 Free PMC article.
-
Brain tumour detection from magnetic resonance imaging using convolutional neural networks.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2023;27(4):230-241. doi: 10.5114/wo.2023.135320. Epub 2024 Feb 10. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2023. PMID: 38405206 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Use of Deep Learning for the Analysis of Magnetic Resonance Image in Neuro-Oncology.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jan 10;16(2):300. doi: 10.3390/cancers16020300. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38254790 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Circular Box-Based Deep Learning Model for the Identification of Signet Ring Cells from Histopathological Images.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Sep 29;10(10):1147. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10101147. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37892876 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sultan H.H., Salem N.M., Al-Atabany W. Multi-classification of Brain Tumor Images using Deep Neural Network. IEEE Access. 2019;7:69215–69225. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2919122. - DOI
-
- Akil M., Saouli R., Kachouri R. Fully automatic brain tumor segmentation with deep learning-based selective attention using overlapping patches and multi-class weighted cross-entropy. Med. Image Anal. 2020;63:101692. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


