A Deep Learning approach for Diagnosis of Mild Cognitive Impairment Based on MRI Images
- PMID: 31466398
- PMCID: PMC6770590
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci9090217
A Deep Learning approach for Diagnosis of Mild Cognitive Impairment Based on MRI Images
Abstract
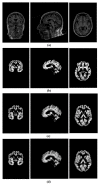
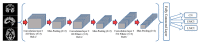
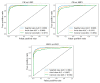
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI) is an intermediary stage condition between healthy people and Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients and other dementias. AD is a progressive and irreversible neurodegenerative disorder, which is a significant threat to people, age 65 and older. Although MCI does not always lead to AD, an early diagnosis at the stage of MCI can be very helpful in identifying people who are at risk of AD. Moreover, the early diagnosis of MCI can lead to more effective treatment, or at least, significantly delay the disease's progress, and can lead to social and financial benefits. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), which has become a significant tool for the diagnosis of MCI and AD, can provide neuropsychological data for analyzing the variance in brain structure and function. MCI is divided into early and late MCI (EMCI and LMCI) and sadly, there is no clear differentiation between the brain structure of healthy people and MCI patients, especially in the EMCI stage. This paper aims to use a deep learning approach, which is one of the most powerful branches of machine learning, to discriminate between healthy people and the two types of MCI groups based on MRI results. The convolutional neural network (CNN) with an efficient architecture was used to extract high-quality features from MRIs to classify people into healthy, EMCI, or LMCI groups. The MRIs of 600 individuals used in this study included 200 control normal (CN) people, 200 EMCI patients, and 200 LMCI patients. This study randomly selected 70 percent of the data to train our model and 30 percent for the test set. The results showed the best overall classification between CN and LMCI groups in the sagittal view with an accuracy of 94.54 percent. In addition, 93.96 percent and 93.00 percent accuracy were reached for the pairs of EMCI/LMCI and CN/EMCI, respectively.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; convolutional neural network; deep learning; mild cognitive impairment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Data-Limited Deep Learning Methods for Mild Cognitive Impairment Classification in Alzheimer's Disease Patients.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2021 Nov;2021:2641-2646. doi: 10.1109/EMBC46164.2021.9630598. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2021. PMID: 34891795
-
Comparing different algorithms for the course of Alzheimer's disease using machine learning.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Sep;10(9):9715-9724. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2013. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34628897
-
Cortical graph neural network for AD and MCI diagnosis and transfer learning across populations.Neuroimage Clin. 2019;23:101929. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101929. Epub 2019 Jul 4. Neuroimage Clin. 2019. PMID: 31491832 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning with multimodal neuroimaging data to classify stages of Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Cogn Neurodyn. 2024 Jun;18(3):775-794. doi: 10.1007/s11571-023-09993-5. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Cogn Neurodyn. 2024. PMID: 38826669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review on Alzheimer's disease classification from normal controls and mild cognitive impairment using structural MR images.J Neurosci Methods. 2023 Jan 15;384:109745. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2022.109745. Epub 2022 Nov 14. J Neurosci Methods. 2023. PMID: 36395961 Review.
Cited by
-
Machine learning-based prediction of mild cognitive impairment among individuals with normal cognitive function.Front Neurol. 2024 Feb 2;15:1352423. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1352423. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38370526 Free PMC article.
-
A Deep Learning-Based Ensemble Method for Early Diagnosis of Alzheimer's Disease using MRI Images.Neuroinformatics. 2024 Jan;22(1):89-105. doi: 10.1007/s12021-023-09646-2. Epub 2023 Dec 2. Neuroinformatics. 2024. PMID: 38042764 Free PMC article.
-
Application of machine learning in dementia diagnosis: A systematic literature review.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 4;9(11):e21626. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21626. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38027622 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive modelling of brain disorders with magnetic resonance imaging: A systematic review of modelling practices, transparency, and interpretability in the use of convolutional neural networks.Hum Brain Mapp. 2023 Dec 15;44(18):6561-6574. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26521. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Hum Brain Mapp. 2023. PMID: 37909364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimized Convolutional Fusion for Multimodal Neuroimaging in Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosis: Enhancing Data Integration and Feature Extraction.J Pers Med. 2023 Oct 14;13(10):1496. doi: 10.3390/jpm13101496. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37888107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kantarci K., Weigand S., Przybelski S., Shiung M., Whitwell J.L., Negash S., Knopman D.S., Boeve B.F., O’Brien P., Petersen R.C. Risk of dementia in MCI: Combined effect of cerebrovascular disease, volumetric MRI, and 1H MRS. Neurology. 2009;72:1519–1525. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181a2e864. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


