Vitamin D/Vitamin D Receptor Signaling Is Required for Normal Development and Function of Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells in the Gut
- PMID: 31272068
- PMCID: PMC6610723
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.06.026
Vitamin D/Vitamin D Receptor Signaling Is Required for Normal Development and Function of Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells in the Gut
Abstract
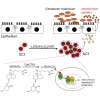
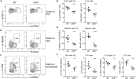
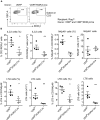
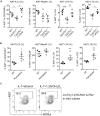
Group 3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC3) play key roles in protective immunity and mucosal barrier maintenance. Here we showed that vitamin D/vitamin D receptor (VDR) signaling regulates gut ILC3. VDR deletion or 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D deficiency in mice led to a marked reduction in colonic ILC3 populations at steady state and impaired ILC3 responses following Citrobacter rodentium infection, resulting in substantial increases in intestinal bacterial growth and mouse mortality. VDR regulation of ILC3 was independent of T and B lymphocytes or gut microflora. Correction of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D deficiency rescued the ILC3 defects. Mechanistically, VDR deletion or 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D deficiency markedly reduced colonic Ki67+ ILC3 populations, and in vivo and in vitro studies confirmed that vitamin D hormone directly stimulated ILC3 proliferation. Therefore, vitamin D/VDR signaling is required for ILC3-mediated innate immunity through regulation of ILC3 proliferation.
Keywords: Biomolecules; Components of the Immune System; Immune Response; Immunology.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Vitamin D Is Required for ILC3 Derived IL-22 and Protection From Citrobacter rodentium Infection.Front Immunol. 2019 Jan 22;10:1. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00001. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30723466 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolite-Sensing Receptor Ffar2 Regulates Colonic Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells and Gut Immunity.Immunity. 2019 Nov 19;51(5):871-884.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.09.014. Epub 2019 Oct 15. Immunity. 2019. PMID: 31628054 Free PMC article.
-
Complementarity and redundancy of IL-22-producing innate lymphoid cells.Nat Immunol. 2016 Feb;17(2):179-86. doi: 10.1038/ni.3332. Epub 2015 Nov 30. Nat Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26595889 Free PMC article.
-
Critical roles of intestinal epithelial vitamin D receptor signaling in controlling gut mucosal inflammation.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015 Apr;148:179-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2015.01.011. Epub 2015 Jan 17. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25603468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Group 3 innate lymphoid cells mediate host defense against attaching and effacing pathogens.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2021 Oct;63:83-91. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2021.06.005. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34274597 Review.
Cited by
-
The formidable guardian: Type 3 immunity in the intestine of pigs.Virulence. 2024 Dec;15(1):2424325. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2424325. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Virulence. 2024. PMID: 39497434 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vitamin D: An Essential Nutrient in the Dual Relationship between Autoimmune Thyroid Diseases and Celiac Disease-A Comprehensive Review.Nutrients. 2024 Jun 4;16(11):1762. doi: 10.3390/nu16111762. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38892695 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disease pathogenesis and barrier functions regulated by group 3 innate lymphoid cells.Semin Immunopathol. 2024 Jan;45(4-6):509-519. doi: 10.1007/s00281-024-01000-1. Epub 2024 Feb 2. Semin Immunopathol. 2024. PMID: 38305897 Review.
-
Gut microbiota-derived 12-ketolithocholic acid suppresses the IL-17A secretion from colonic group 3 innate lymphoid cells to prevent the acute exacerbation of ulcerative colitis.Gut Microbes. 2023 Dec;15(2):2290315. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2023.2290315. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Gut Microbes. 2023. PMID: 38062857 Free PMC article.
-
ILC3: a case of conflicted identity.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 17;14:1271699. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1271699. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37915588 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


