Comparison of methods that use whole genome data to estimate the heritability and genetic architecture of complex traits
- PMID: 29700474
- PMCID: PMC5934350
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-018-0108-x
Comparison of methods that use whole genome data to estimate the heritability and genetic architecture of complex traits
Abstract
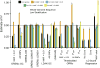
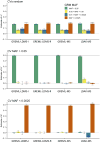
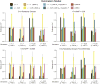
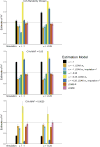
Multiple methods have been developed to estimate narrow-sense heritability, h2, using single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in unrelated individuals. However, a comprehensive evaluation of these methods has not yet been performed, leading to confusion and discrepancy in the literature. We present the most thorough and realistic comparison of these methods to date. We used thousands of real whole-genome sequences to simulate phenotypes under varying genetic architectures and confounding variables, and we used array, imputed, or whole genome sequence SNPs to obtain 'SNP-heritability' estimates. We show that SNP-heritability can be highly sensitive to assumptions about the frequencies, effect sizes, and levels of linkage disequilibrium of underlying causal variants, but that methods that bin SNPs according to minor allele frequency and linkage disequilibrium are less sensitive to these assumptions across a wide range of genetic architectures and possible confounding factors. These findings provide guidance for best practices and proper interpretation of published estimates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
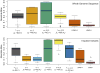
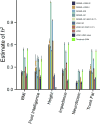
Similar articles
-
Reevaluation of SNP heritability in complex human traits.Nat Genet. 2017 Jul;49(7):986-992. doi: 10.1038/ng.3865. Epub 2017 May 22. Nat Genet. 2017. PMID: 28530675 Free PMC article.
-
Accurate estimation of SNP-heritability from biobank-scale data irrespective of genetic architecture.Nat Genet. 2019 Aug;51(8):1244-1251. doi: 10.1038/s41588-019-0465-0. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Nat Genet. 2019. PMID: 31358995 Free PMC article.
-
Signatures of negative selection in the genetic architecture of human complex traits.Nat Genet. 2018 May;50(5):746-753. doi: 10.1038/s41588-018-0101-4. Epub 2018 Apr 16. Nat Genet. 2018. PMID: 29662166
-
SNP-based heritability and selection analyses: Improved models and new results.Bioessays. 2022 May;44(5):e2100170. doi: 10.1002/bies.202100170. Epub 2022 Mar 13. Bioessays. 2022. PMID: 35279859 Review.
-
Estimation and partition of heritability in human populations using whole-genome analysis methods.Annu Rev Genet. 2013;47:75-95. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-111212-133258. Epub 2013 Aug 22. Annu Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 23988118 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide meta-analysis of myasthenia gravis uncovers new loci and provides insights into polygenic prediction.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 13;15(1):9839. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53595-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39537604 Free PMC article.
-
[Single nucleotide polymorphism heritability of non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in Chinese population].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Oct 18;56(5):775-780. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2024.05.004. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39397453 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Rare variant contribution to the heritability of coronary artery disease.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 9;15(1):8741. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52939-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39384761 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of machine learning methods for genomic prediction of selected Arabidopsis thaliana traits.PLoS One. 2024 Aug 28;19(8):e0308962. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0308962. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39196916 Free PMC article.
-
Polygenic scores and Mendelian randomization identify plasma proteins causally implicated in Alzheimer's disease.Front Neurosci. 2024 Jul 23;18:1404377. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2024.1404377. eCollection 2024. Front Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39108314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tenesa A, Haley CS. The heritability of human disease: estimation, uses and abuses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013;14:139–149. - PubMed
-
- Visscher PM, Hill WG, Wray NR. Heritability in the genomics era--concepts and misconceptions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008;9:255–66. - PubMed
-
- Keller MC, Coventry WL. Quantifying and addressing parameter indeterminacy in the classical twin design. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2005;8:201–213. - PubMed
-
- Eaves LJ, Last KA, Young PA, Martin NG. Model-fitting approaches to the analysis of human behaviour. Heredity (Edinb) 1978;41:249–320. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


