miRTarBase update 2018: a resource for experimentally validated microRNA-target interactions
- PMID: 29126174
- PMCID: PMC5753222
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx1067
miRTarBase update 2018: a resource for experimentally validated microRNA-target interactions
Abstract
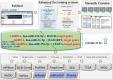
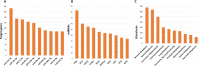
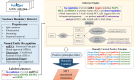
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs of ∼ 22 nucleotides that are involved in negative regulation of mRNA at the post-transcriptional level. Previously, we developed miRTarBase which provides information about experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions (MTIs). Here, we describe an updated database containing 422 517 curated MTIs from 4076 miRNAs and 23 054 target genes collected from over 8500 articles. The number of MTIs curated by strong evidence has increased ∼1.4-fold since the last update in 2016. In this updated version, target sites validated by reporter assay that are available in the literature can be downloaded. The target site sequence can extract new features for analysis via a machine learning approach which can help to evaluate the performance of miRNA-target prediction tools. Furthermore, different ways of browsing enhance user browsing specific MTIs. With these improvements, miRTarBase serves as more comprehensively annotated, experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions databases in the field of miRNA related research. miRTarBase is available at http://miRTarBase.mbc.nctu.edu.tw/.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
miRTarBase 2016: updates to the experimentally validated miRNA-target interactions database.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jan 4;44(D1):D239-47. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1258. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26590260 Free PMC article.
-
miRTarBase 2020: updates to the experimentally validated microRNA-target interaction database.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jan 8;48(D1):D148-D154. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz896. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31647101 Free PMC article.
-
miRTarBase: a database curates experimentally validated microRNA-target interactions.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Jan;39(Database issue):D163-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq1107. Epub 2010 Nov 10. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011. PMID: 21071411 Free PMC article.
-
Review of databases for experimentally validated human microRNA-mRNA interactions.Database (Oxford). 2023 Apr 25;2023:baad014. doi: 10.1093/database/baad014. Database (Oxford). 2023. PMID: 37098414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational Resources for Prediction and Analysis of Functional miRNA and Their Targetome.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1912:215-250. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8982-9_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30635896 Review.
Cited by
-
An integrative network-based approach to identify driving gene communities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2024 Oct 26;10(1):125. doi: 10.1038/s41540-024-00425-6. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2024. PMID: 39461973 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Circulating microRNAs in Liver Disease and HCC: Focus on miR-122.Genes (Basel). 2024 Oct 12;15(10):1313. doi: 10.3390/genes15101313. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA Inhibiting Atheroprotective Proteins in Patients with Unstable Angina Comparing to Chronic Coronary Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 2;25(19):10621. doi: 10.3390/ijms251910621. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39408950 Free PMC article.
-
Next-Cell Hypothesis: Mechanism of Obesity-Associated Carcinogenesis.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1460:727-766. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-63657-8_25. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39287871 Review.
-
MicroRNAs Regulate the Expression of Genes Related to the Innate Immune and Inflammatory Response in Rabbits Infected with Lagovirus europaeus GI.1 and GI.2 Genotypes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 2;25(17):9531. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179531. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel D.P. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004; 116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Chen D., Farwell M.A., Zhang B.. MicroRNA as a new player in the cell cycle. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010; 225:296–301. - PubMed
-
- Lima R.T., Busacca S., Almeida G.M., Gaudino G., Fennell D.A., Vasconcelos M.H.. MicroRNA regulation of core apoptosis pathways in cancer. Eur. J. Cancer. 2011; 47:163–174. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


