A Healthy Dietary Pattern Reduces Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 26959051
- PMCID: PMC4808863
- DOI: 10.3390/nu8030134
A Healthy Dietary Pattern Reduces Lung Cancer Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Diet and nutrients play an important role in cancer development and progress; a healthy dietary pattern has been found to be associated with several types of cancer. However, the association between a healthy eating pattern and lung cancer risk is still unclear.
Objective: Therefore, we conducted a systematic review with meta-analysis to evaluate whether a healthy eating pattern might reduce lung cancer risk.
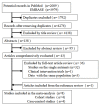
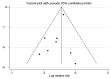
Methods: We identified relevant studies from the PubMed and Embase databases up to October 2015, and the relative risks were extracted and combined by the fixed-effects model when no substantial heterogeneity was observed; otherwise, the random-effects model was employed. Subgroup and publication bias analyses were also performed.
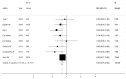
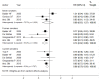
Results: Finally, eight observational studies were included in the meta-analysis. The pooled relative risk of lung cancer for the highest vs. lowest category of healthy dietary pattern was 0.81 (95% confidence interval, CI: 0.75-0.86), and no significant heterogeneity was detected. The relative risks (RRs) for non-smokers, former smokers and current smokers were 0.89 (95% CI: 0.63-1.27), 0.74 (95% CI: 0.62-0.89) and 0.86 (95% CI: 0.79-0.93), respectively. The results remained stable in subgroup analyses by other confounders and sensitivity analysis.
Conclusions: The results of our meta-analysis suggest that a healthy dietary pattern is associated with a lower lung cancer risk, and they provide more beneficial evidence for changing the diet pattern in the general population.
Keywords: dietary pattern; lung cancer; meta-analysis; nutrition; risk factors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Associations of Fruit and Vegetable Intake with Lung Cancer Risk in Participants with Different Smoking Status: A Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies.Nutrients. 2019 Aug 2;11(8):1791. doi: 10.3390/nu11081791. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31382476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dietary fibre intake and mortality from cardiovascular disease and all cancers: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2016 Jan;109(1):39-54. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2015.09.005. Epub 2015 Dec 18. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2016. PMID: 26711548 Review.
-
Associations of Mediterranean Diet and a Posteriori Derived Dietary Patterns with Breast and Lung Cancer Risk: A Case-Control Study.Nutrients. 2018 Apr 11;10(4):470. doi: 10.3390/nu10040470. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29641468 Free PMC article.
-
Fish intake and the risk of brain tumor: a meta-analysis with systematic review.Nutr J. 2017 Jan 11;16(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12937-016-0223-4. Nutr J. 2017. PMID: 28077138 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations between dietary patterns and the risk of breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Jan 29;21(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1096-1. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30696460 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies on coffee consumption and risk of lung cancer.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 1;14(1):14991. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62619-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38951141 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Incidence Rates in the US in 2016-2020 with Respect to Solar UVB Doses, Diabetes and Obesity Prevalence, Lung Cancer Incidence Rates, and Alcohol Consumption: An Ecological Study.Nutrients. 2024 May 11;16(10):1450. doi: 10.3390/nu16101450. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38794688 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of dietary factors with gastric cancer risk: insights from NHANES 2003-2016 and mendelian randomization analyses.Front Genet. 2024 May 2;15:1377434. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1377434. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 38756450 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Urinary N7-(1-hydroxyl-3-buten-1-yl) Guanine (EB-GII) Adducts and Butadiene-Mercapturic Acids with Lung Cancer Development in Cigarette Smokers.Chem Res Toxicol. 2024 Feb 19;37(2):374-384. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.3c00336. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Chem Res Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38315500
-
Associations of dietary patterns with kidney cancer risk, kidney cancer-specific mortality and all-cause mortality among postmenopausal women.Br J Cancer. 2023 Dec;129(12):1978-1987. doi: 10.1038/s41416-023-02469-7. Epub 2023 Oct 28. Br J Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37898720 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical