Protective effects of ginseng on neurological disorders
- PMID: 26236231
- PMCID: PMC4503934
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2015.00129
Protective effects of ginseng on neurological disorders
Abstract
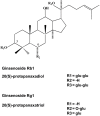
Ginseng (Order: Apiales, Family: Araliaceae, Genus: Panax) has been used as a traditional herbal medicine for over 2000 years, and is recorded to have antianxiety, antidepressant and cognition enhancing properties. The protective effects of ginseng on neurological disorders are discussed in this review. Ginseng species and ginsenosides, and their intestinal metabolism and bioavailability are briefly introduced. This is followed by molecular mechanisms of effects of ginseng on the brain, including glutamatergic transmission, monoamine transmission, estrogen signaling, nitric oxide (NO) production, the Keap1/Nrf2 adaptive cellular stress pathway, neuronal survival, apoptosis, neural stem cells and neuroregeneration, microglia, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and cerebral microvessels. The molecular mechanisms of the neuroprotective effects of ginseng in Alzheimer's disease (AD) including β-amyloid (Aβ) formation, tau hyperphosphorylation and oxidative stress, major depression, stroke, Parkinson's disease and multiple sclerosis are presented. It is hoped that this discussion will stimulate more studies on the use of ginseng in neurological disorders.
Keywords: brain; ginseng; ginsenoside; glial cells; neurodegeneration; neurons; neuroprotection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Role of Ginseng and Its Constituents in the Treatment of Central Nervous System Disorders.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:2614742. doi: 10.1155/2016/2614742. Epub 2016 Aug 18. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016. PMID: 27630732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Panax ginseng in Neurodegenerative Diseases.J Ginseng Res. 2012 Oct;36(4):342-53. doi: 10.5142/jgr.2012.36.4.342. J Ginseng Res. 2012. PMID: 23717136 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of Panax ginseng and its constituents, ginsenosides and gintonin, in neurological and neurodegenerative disorders: a patent review.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2019 Jan;29(1):55-72. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2019.1556258. Epub 2018 Dec 11. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2019. PMID: 30513224 Review.
-
Active Compounds of Panax ginseng in the Improvement of Alzheimer's Disease and Application of Spatial Metabolomics.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Dec 26;17(1):38. doi: 10.3390/ph17010038. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38256872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginseng: a promising neuroprotective strategy in stroke.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jan 20;8:457. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00457. eCollection 2014. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25653588 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for quantification of majonoside R2 as an authentication marker for Nngoc Linh and Lai Chau ginsengs.J Ginseng Res. 2024 Sep;48(5):474-480. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2024.05.004. Epub 2024 May 23. J Ginseng Res. 2024. PMID: 39263304 Free PMC article.
-
Ninjin'yoeito reduces fatigue-like conditions by alleviating inflammation of the brain and skeletal muscles in aging mice.PLoS One. 2024 May 20;19(5):e0303833. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303833. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38768175 Free PMC article.
-
Current View on How Human Gut Microbiota Mediate Metabolic and Pharmacological Activity of Panax ginseng. A Scoping Review.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(15):1756-1773. doi: 10.2174/0118715303270923240307120117. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38504564 Review.
-
Cadmium as a male reproductive toxicant and natural and non-natural ways to tackle it: a review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Mar;31(12):18340-18361. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-32210-7. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38349491 Review.
-
Comparative Assessment of In Vitro Xanthine Oxidase and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activities of Cultured Cambial Meristematic Cells, Adventitious Roots, and Field-Cultivated Ginseng.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 2;16(3):443. doi: 10.3390/nu16030443. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38337727 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


