Aβ and tau toxicities in Alzheimer's are linked via oxidative stress-induced p38 activation: protective role of vitamin E
- PMID: 25061569
- PMCID: PMC4099506
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2014.03.002
Aβ and tau toxicities in Alzheimer's are linked via oxidative stress-induced p38 activation: protective role of vitamin E
Abstract
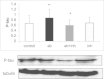
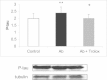
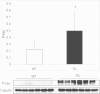
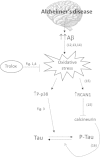
Oxidative stress is a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease (AD). We propose that rather than causing damage because of the action of free radicals, oxidative stress deranges signaling pathways leading to tau hyperphosphorylation, a hallmark of the disease. Indeed, incubation of neurons in culture with 5 µM beta-amyloid peptide (Aβ) causes an activation of p38 MAPK (p38) that leads to tau hyperphosphorylation. Inhibition of p38 prevents Aβ-induced tau phosphorylation. Aβ-induced effects are prevented when neurons are co-incubated with trolox (the water-soluble analog of vitamin E). We have confirmed these results in vivo, in APP/PS1 double transgenic mice of AD. We have found that APP/PS1 transgenic mice exhibit a high level of P-p38 in the hippocampus but not in cortex and this is prevented by feeding animals with a diet supplemented with vitamin E. Our results underpin the role of oxidative stress in the altered cell signaling in AD pathology and suggest that antioxidant prevention may be useful in AD therapeutics.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Beta-amyloid; P-p38; Vitamin E.
Figures


Similar articles
-
APP/PS1 mice overexpressing SREBP-2 exhibit combined Aβ accumulation and tau pathology underlying Alzheimer's disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2013 Sep 1;22(17):3460-76. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddt201. Epub 2013 May 6. Hum Mol Genet. 2013. PMID: 23648430 Free PMC article.
-
Ebselen ameliorates β-amyloid pathology, tau pathology, and cognitive impairment in triple-transgenic Alzheimer's disease mice.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2017 Aug;22(6):851-865. doi: 10.1007/s00775-017-1463-2. Epub 2017 May 13. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2017. PMID: 28502066
-
Amyloid-β toxicity and tau hyperphosphorylation are linked via RCAN1 in Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2011;27(4):701-9. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-110890. J Alzheimers Dis. 2011. PMID: 21876249 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin E as an antioxidant/free radical scavenger against amyloid beta-peptide-induced oxidative stress in neocortical synaptosomal membranes and hippocampal neurons in culture: insights into Alzheimer's disease.Rev Neurosci. 1999;10(2):141-9. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.1999.10.2.141. Rev Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10658956 Review.
-
Current advances on different kinases involved in tau phosphorylation, and implications in Alzheimer's disease and tauopathies.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2005 Jan;2(1):3-18. doi: 10.2174/1567205052772713. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2005. PMID: 15977985 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Inhibits Oxidative Stress Through the Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway to Improve Alzheimer Disease.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Sep 20. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04498-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39299981 Review.
-
Age-associated temporal decline in butyrate-producing bacteria plays a key pathogenic role in the onset and progression of neuropathology and memory deficits in 3×Tg-AD mice.Gut Microbes. 2024 Jan-Dec;16(1):2389319. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2389319. Epub 2024 Aug 25. Gut Microbes. 2024. PMID: 39182227 Free PMC article.
-
The duality of amyloid-β: its role in normal and Alzheimer's disease states.Mol Brain. 2024 Jul 17;17(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13041-024-01118-1. Mol Brain. 2024. PMID: 39020435 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-nucleus analysis reveals microenvironment-specific neuron and glial cell enrichment in Alzheimer's disease.BMC Genomics. 2024 May 28;25(1):526. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10447-3. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38807051 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Oxidative Stress, Methionine Oxidation and Methionine Sulfoxide Reductases (MSR) in Alzheimer's Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Dec 21;13(1):21. doi: 10.3390/antiox13010021. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38275641 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sheng J.G., Jones R.A., Zhou X.Q., McGinness J.M., Van Eldik L.J., Mrak R.E., Griffin W.S. Interleukin-1 promotion of MAPK-p38 overexpression in experimental animals and in Alzheimer’s disease: potential significance for Tau protein phosphorylation. Neurochemistry International. 2001;39:341–348. 11578769 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical


