Highly efficient bi-allelic mutation rates using TALENs in Xenopus tropicalis
- PMID: 23408158
- PMCID: PMC3558749
- DOI: 10.1242/bio.20123228
Highly efficient bi-allelic mutation rates using TALENs in Xenopus tropicalis
Abstract
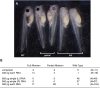
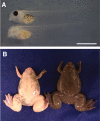
In the past decade, Xenopus tropicalis has emerged as a powerful new amphibian genetic model system, which offers all of the experimental advantages of its larger cousin, Xenopus laevis. Here we investigated the efficiency of transcription activator-like effector nucleases (TALENs) for generating targeted mutations in endogenous genes in X. tropicalis. For our analysis we targeted the tyrosinase (oculocutaneous albinism IA) (tyr) gene, which is required for the production of skin pigments, such as melanin. We injected mRNA encoding TALENs targeting the first exon of the tyr gene into two-cell-stage embryos. Surprisingly, we found that over 90% of the founder animals developed either partial or full albinism, suggesting that the TALENs induced bi-allelic mutations in the tyr gene at very high frequency in the F0 animals. Furthermore, mutations tyr gene were efficiently transmitted into the F1 progeny, as evidenced by the generation of albino offspring. These findings have far reaching implications in our quest to develop efficient reverse genetic approaches in this emerging amphibian model.
Keywords: Nuclease; Reverse genetics; TAL effector; Targeted mutagenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeted mutagenesis of multiple and paralogous genes in Xenopus laevis using two pairs of transcription activator-like effector nucleases.Dev Growth Differ. 2014 Jan;56(1):108-14. doi: 10.1111/dgd.12105. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Dev Growth Differ. 2014. PMID: 24329851
-
High efficiency TALENs enable F0 functional analysis by targeted gene disruption in Xenopus laevis embryos.Biol Open. 2013 Mar 4;2(5):448-52. doi: 10.1242/bio.20133855. Print 2013 May 15. Biol Open. 2013. PMID: 23789092 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a new approach for targeted gene editing in primordial germ cells using TALENs in Xenopus.Biol Open. 2015 Feb 6;4(3):259-66. doi: 10.1242/bio.201410926. Biol Open. 2015. PMID: 25661867 Free PMC article.
-
TALENs and CRISPR/Cas9 fuel genetically engineered clinically relevant Xenopus tropicalis tumor models.Genesis. 2017 Jan;55(1-2). doi: 10.1002/dvg.23005. Genesis. 2017. PMID: 28095622 Review.
-
Xenopus, the next generation: X. tropicalis genetics and genomics.Dev Dyn. 2002 Dec;225(4):422-33. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.10178. Dev Dyn. 2002. PMID: 12454920 Review.
Cited by
-
CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Disruption Studies in F0 Xenopus Tadpoles: Understanding Development and Disease in the Frog.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2633:111-130. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3004-4_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 36853461
-
Phosphoproteomics Reveals the AMPK Substrate Network in Response to DNA Damage and Histone Acetylation.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2022 Aug;20(4):597-613. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2020.09.003. Epub 2021 Feb 17. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 33607295 Free PMC article.
-
Dual function model revised by thyroid hormone receptor alpha knockout frogs.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2018 Sep 1;265:214-218. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2018.04.020. Epub 2018 Apr 22. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 29689262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cellular and molecular mechanisms of tissue repair and regeneration as revealed by studies in Xenopus.Regeneration (Oxf). 2016 Oct 28;3(4):198-208. doi: 10.1002/reg2.69. eCollection 2016 Aug. Regeneration (Oxf). 2016. PMID: 27800170 Free PMC article.
-
Functional joint regeneration is achieved using reintegration mechanism in Xenopus laevis.Regeneration (Oxf). 2016 Jan 6;3(1):26-38. doi: 10.1002/reg2.49. eCollection 2016 Feb. Regeneration (Oxf). 2016. PMID: 27499877 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous


